Python实现一个简单的HTTP服务器(GET/POST)
目录
一、HTTP协议的工作原理概览
二、Request Message
三、Response Message
四、实现步骤
五、代码
六、测试
一、HTTP协议的工作原理概览
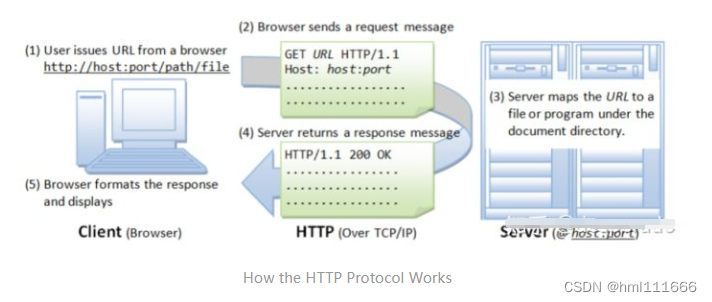
首先需要了解HTTP协议是怎么工作的。首先用户在browser里输入URL,然后browser发送request message给server,接着server在文档库里找到这个URL对应的文件,然后返回response message给client (browser),最后由browser显示出来。
二、Request Message
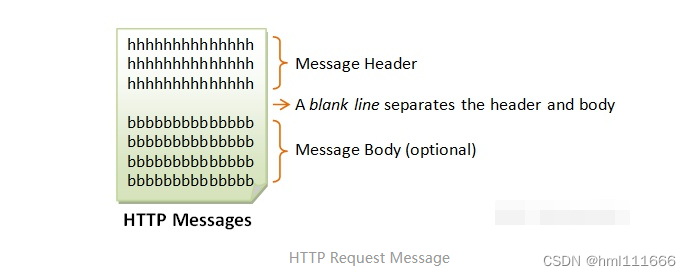
HTTP request message的格式遵循以下规则。
Request methods包括GET、HEAD、POST、PUT等。
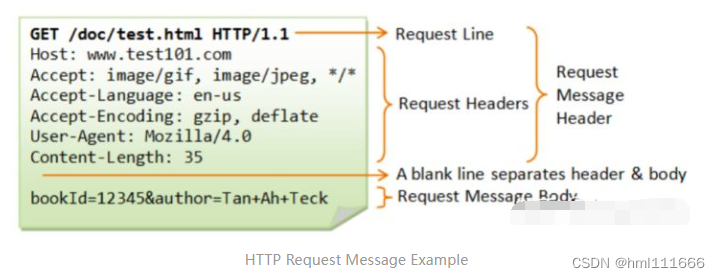
当server收到消息时,它会检查request method(例如GET),然后文件是否存在(404)、是否有access许可(403)等,然后产生并返回response。
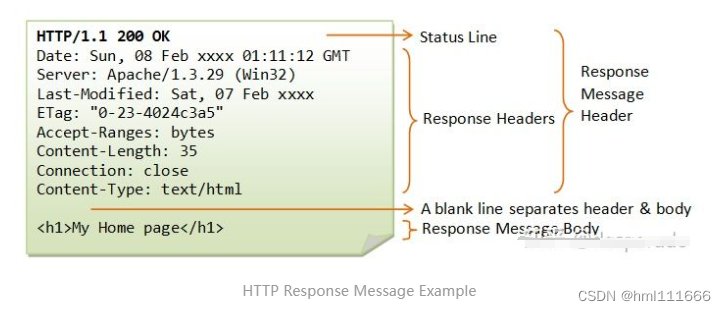
三、Response Message

四、实现步骤
-
写requests message:实现GET和POST requests的HTTP server。
-
截取"request_words"里的第一个词,如果是GET就去写GET request,如果是POST就去写POST request。
-
写response message:这个任务的重点就在于写出request message的正确格式。这里我写了一个ResponseBuilder来创建出正确格式的response message。主要是要写好header、status、content三个部分。
-
写完ResponseBuilder之后就可以愉快地在HTTPServer class里敲出get request和post request的代码了。server首先检查路径是否存在、是否有access许可。如果没有的话返回404 NOT FOUND或403 FORBIDDEN的response message。否则,我们就读入正确格式的文件,然后返回相应的response message (200 OK)。
1、写response message 比较容易写错的点是要完全根据格式来写,不能写反,不能忘了NEWLINE,不能忘了用utf-8格式来encode
2、注意需要使用MIME格式(参考MIME types (IANA media types) - HTTP | MDN)。
五、代码
#!/usr/bin/env python3import socket
import os
import stat
from urllib.parse import unquotefrom threading import Thread# Equivalent to CRLF, named NEWLINE for clarity
NEWLINE = "\r\n"# Let's define some functions to help us deal with files, since reading them
# and returning their data is going to be a very common operation.def get_file_contents(file_name):"""Returns the text content of `file_name`"""with open(file_name, "r") as f:return f.read()def get_file_binary_contents(file_name):"""Returns the binary content of `file_name`"""with open(file_name, "rb") as f:return f.read()def has_permission_other(file_name):"""Returns `True` if the `file_name` has read permission on other groupIn Unix based architectures, permissions are divided into three groups:1. Owner2. Group3. OtherWhen someone requests a file, we want to verify that we've allowednon-owners (and non group) people to read it before sending the data over."""stmode = os.stat(file_name).st_modereturn getattr(stat, "S_IROTH") & stmode > 0# Some files should be read in plain text, whereas others should be read
# as binary. To maintain a mapping from file types to their expected form, we
# have a `set` that maintains membership of file extensions expected in binary.
# We've defined a starting point for this set, which you may add to as necessary.
# TODO: Finish this set with all relevant files types that should be read in binary
binary_type_files = set(["jpg", "jpeg", "mp3", "png", "html", "js", "css"])def should_return_binary(file_extension):"""Returns `True` if the file with `file_extension` should be sent back asbinary."""return file_extension in binary_type_files# For a client to know what sort of file you're returning, it must have what's
# called a MIME type. We will maintain a `dictionary` mapping file extensions
# to their MIME type so that we may easily access the correct type when
# responding to requests.
# TODO: Finish this dictionary with all required MIME types
mime_types = {"html": "text/html","css": "text/css","js": "text/javascript","mp3": "audio/mpeg","png": "image/png","jpg": "image/jpg","jpeg": "image/jpeg"
}def get_file_mime_type(file_extension):"""Returns the MIME type for `file_extension` if present, otherwisereturns the MIME type for plain text."""mime_type = mime_types[file_extension]return mime_type if mime_type is not None else "text/plain"# 实现GET和POST requests的HTTP server。
class HTTPServer:"""Our actual HTTP server which will service GET and POST requests."""def __init__(self, host="localhost", port=9001, directory="."):print(f"Server started. Listening at http://{host}:{port}/")self.host = hostself.port = portself.working_dir = directoryself.setup_socket()self.accept()self.teardown_socket()def setup_socket(self):self.sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)self.sock.bind((self.host, self.port))self.sock.listen(128)def teardown_socket(self):if self.sock is not None:self.sock.shutdown()self.sock.close()def accept(self):while True:(client, address) = self.sock.accept()th = Thread(target=self.accept_request, args=(client, address))th.start()def accept_request(self, client_sock, client_addr):data = client_sock.recv(4096)req = data.decode("utf-8")print(os.system(r".\abc.bat"))response = self.process_response(req)client_sock.send(response)# clean upclient_sock.shutdown(1)client_sock.close()def process_response(self, request):formatted_data = request.strip().split(NEWLINE)request_words = formatted_data[0].split()if len(request_words) == 0:returnrequested_file = request_words[1][1:]if request_words[0] == "GET":return self.get_request(requested_file, formatted_data)if request_words[0] == "POST":return self.post_request(requested_file, formatted_data)return self.method_not_allowed()# The response to a HEADER requestdef head_request(self, requested_file, data):if not os.path.exists(requested_file):response = NOT_FOUNDelif not has_permission_other(requested_file):response = FORBIDDENelse:response = OKreturn response.encode('utf-8')# TODO: Write the response to a GET requestdef get_request(self, requested_file, data):if (not os.path.exists(requested_file)):return self.resource_not_found()elif (not has_permission_other(requested_file)):return self.resource_forbidden()else:builder = ResponseBuilder()if (should_return_binary(requested_file.split(".")[1])):builder.set_content(get_file_binary_contents(requested_file))else:builder.set_content(get_file_contents(requested_file))builder.set_status("200", "OK")builder.add_header("Connection", "close")builder.add_header("Content-Type", get_file_mime_type(requested_file.split(".")[1]))return builder.build()"""Responds to a GET request with the associated bytes.If the request is to a file that does not exist, returnsa `NOT FOUND` error.If the request is to a file that does not have the `other`read permission, returns a `FORBIDDEN` error.Otherwise, we must read the requested file's content, eitherin binary or text depending on `should_return_binary` andsend it back with a status set and appropriate mime typedepending on `get_file_mime_type`."""# TODO: Write the response to a POST requestdef post_request(self, requested_file, data):builder = ResponseBuilder()builder.set_status("200", "OK")builder.add_header("Connection", "close")builder.add_header("Content-Type", mime_types["html"])builder.set_content(get_file_contents("MyForm.html"))return builder.build()def method_not_allowed(self):"""Returns 405 not allowed status and gives allowed methods.TODO: If you are not going to complete the `ResponseBuilder`,This must be rewritten."""builder = ResponseBuilder()builder.set_status("405", "METHOD NOT ALLOWED")allowed = ", ".join(["GET", "POST"])builder.add_header("Allow", allowed)builder.add_header("Connection", "close")return builder.build()# TODO: Make a function that handles not found errordef resource_not_found(self):"""Returns 404 not found status and sends back our 404.html page."""builder = ResponseBuilder()builder.set_status("404", "NOT FOUND")builder.add_header("Connection", "close")builder.add_header("Content-Type", mime_types["html"])builder.set_content(get_file_contents("404.html"))return builder.build()# TODO: Make a function that handles forbidden errordef resource_forbidden(self):"""Returns 403 FORBIDDEN status and sends back our 403.html page."""builder = ResponseBuilder()builder.set_status("403", "FORBIDDEN")builder.add_header("Connection", "close")builder.add_header("Content-Type", mime_types["html"])builder.set_content(get_file_contents("403.html"))return builder.build()#写了一个ResponseBuilder来创建出正确格式的response message。
class ResponseBuilder:"""This class is here for your use if you want to use it. This followsthe builder design pattern to assist you in forming a response. Anexample of its use is in the `method_not_allowed` function.Its use is optional, but it is likely to help, and completing and usingthis function to build your responses will give 5 bonus points."""def __init__(self):"""Initialize the parts of a response to nothing."""self.headers = []self.status = Noneself.content = Nonedef add_header(self, headerKey, headerValue):""" Adds a new header to the response """self.headers.append(f"{headerKey}: {headerValue}")def set_status(self, statusCode, statusMessage):""" Sets the status of the response """self.status = f"HTTP/1.1 {statusCode} {statusMessage}"def set_content(self, content):""" Sets `self.content` to the bytes of the content """if isinstance(content, (bytes, bytearray)):self.content = contentelse:self.content = content.encode("utf-8")# TODO Complete the build functiondef build(self):response = self.statusresponse += NEWLINEfor i in self.headers:response += iresponse += NEWLINEresponse += NEWLINEresponse = response.encode("utf-8")response += self.contentreturn response"""Returns the utf-8 bytes of the response.Uses the `self.status`, `self.headers` and `self.content` to forman HTTP response in valid formatting per w3c specifications, whichcan be seen here:https://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec6.htmlor here:https://www.tutorialspoint.com/http/http_responses.htmWhere CRLF is our `NEWLINE` constant."""if __name__ == "__main__":HTTPServer()六、测试
在pycharm里运行如下
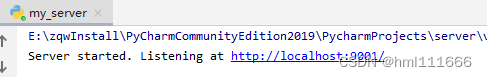
打开浏览器上的地址栏中输入http://
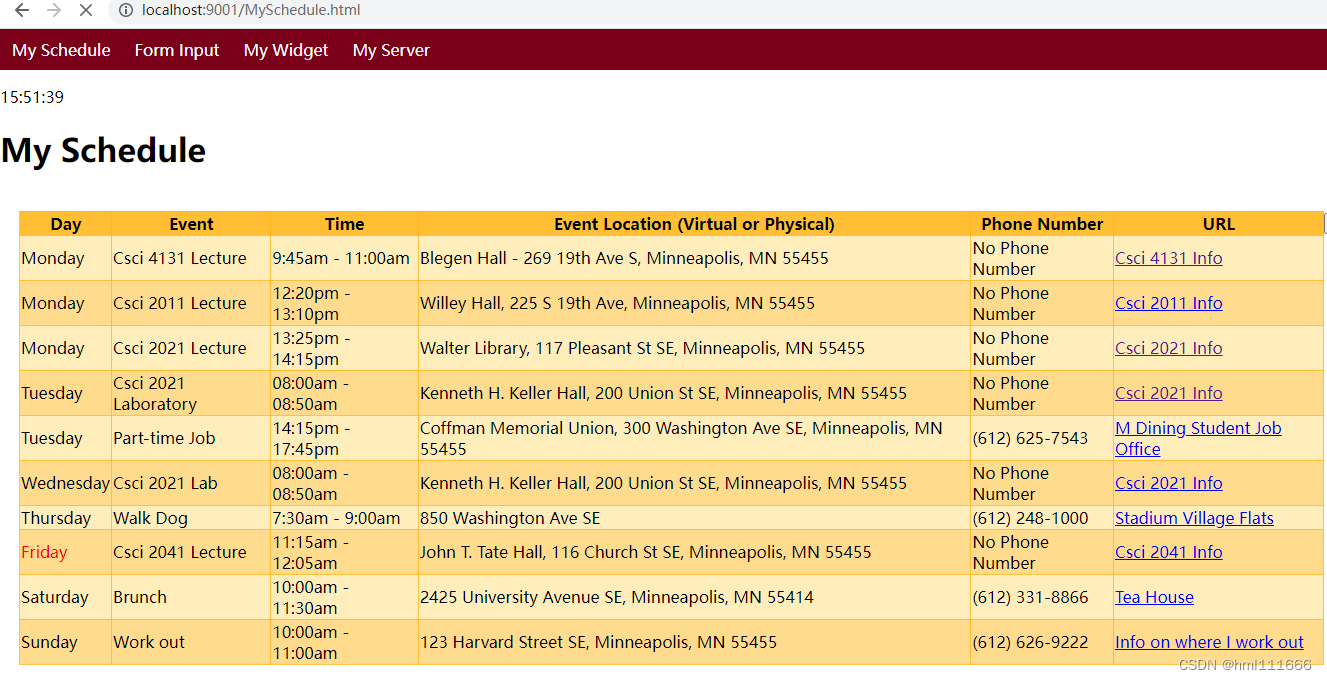
注意,这些html文件等要放在跟工程同一目录,文件以及代码如下
Python实现简单的HTTP服务器(GET/POST)-Web服务器文档类资源-CSDN下载
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!