集合入门说明
java集合
集合的理解和好处
数组的不足之处
- 长度开始时必须指定,而且一旦指定,不能更改。
- 保存的必须为同一类型的元素。
- 使用数组进行增加元素的示意代码比较麻烦。
数组扩容,不灵活,比较麻烦,实例如下:
package com.grey.test_01;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;/*** @Description: 数组扩容:灵活性差,比较麻烦* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/16*/
public class ArrayExample {@Testpublic void expandArray() {Person[] people = new Person[3];//添加几个元素进去people[0] = new Person("小明", 10);people[1] = new Person("小刚", 20);people[2] = new Person("小红", 30);for (Person person : people) {System.out.println(person);}System.out.println("-----------扩容后----------");Person[] peopleAdd = new Person[5];for (int i = 0; i < people.length; i++) {peopleAdd[i] = people[i];}peopleAdd[3] = new Person("梅梅", 40);peopleAdd[4] = new Person("兰兰", 50);for (Person person : peopleAdd) {System.out.println(person);}}
}class Person {private String name;private Integer age;public Person(String name, Integer age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
集合的好处
- 可以动态保存任意多个对象,使用比较方便
- 提供了一系列方便的操作对象的方法:add、remove、set、get等
- 使用集合添加,删除新元素更加简洁
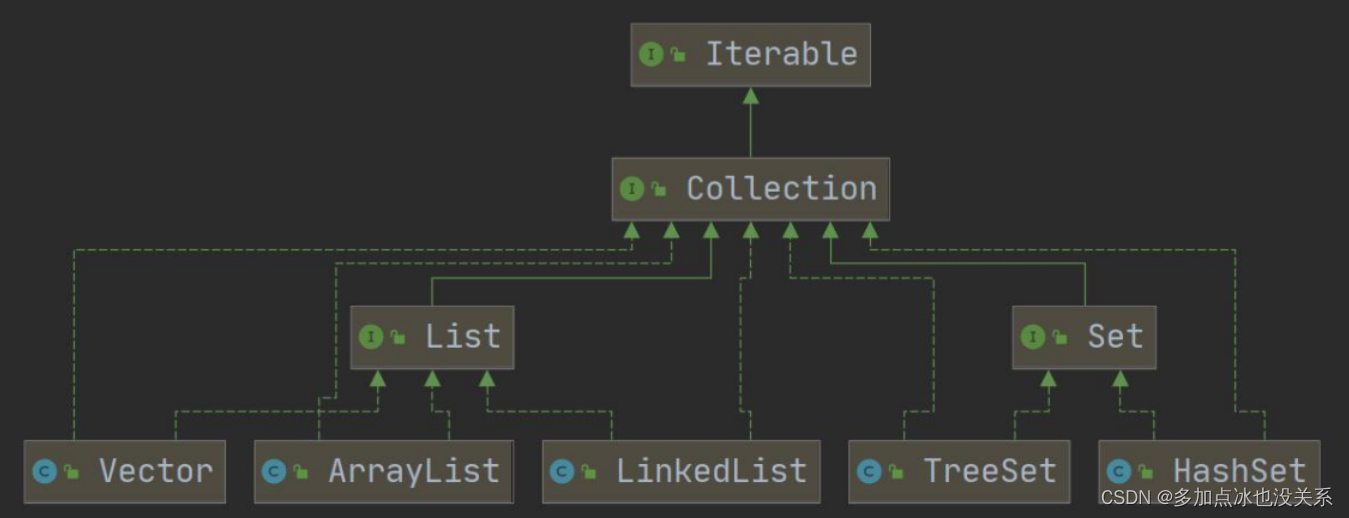
集合类图
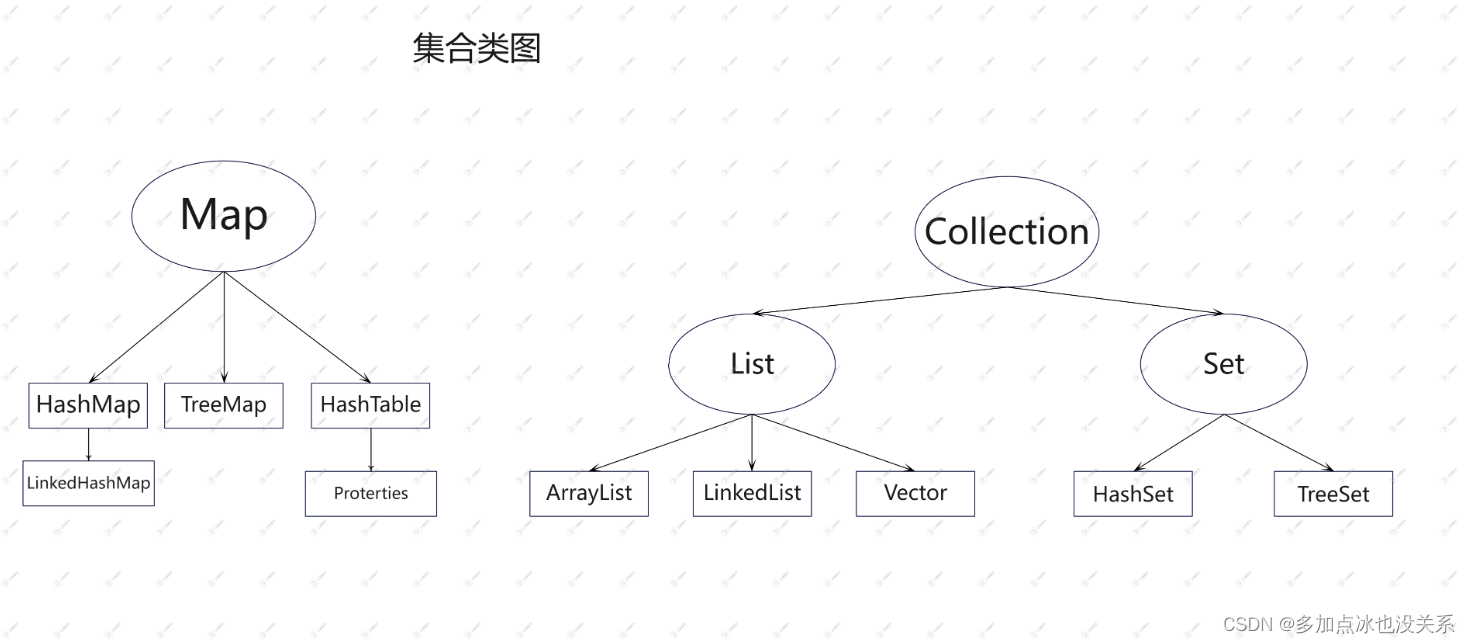
Collection 接口图
Map接口图
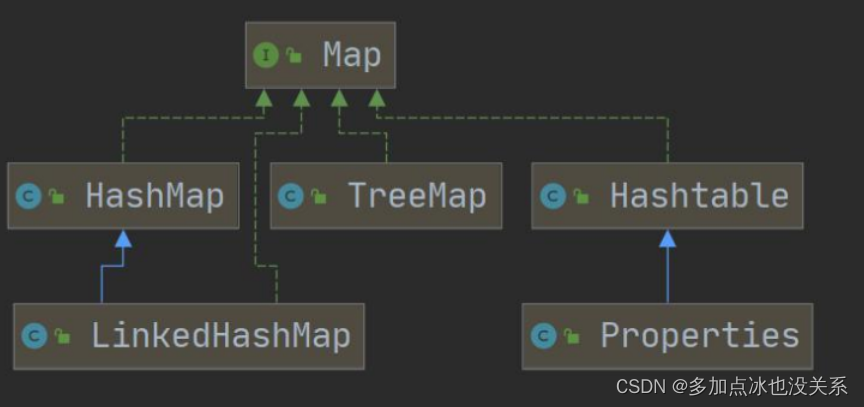
1.集合主要是两组(单列集合、双列集合)
2.Collection接口有两个重要的子接口List Set 它们的实现子类都是单列集合
3.Map接口的实现子类 是双列集合,存放的 Key-Value
Collection接口实现类的特点
public interface Collection extends Iterable
- Collection实现子类可以存放多个元素,每个元素可以是Object
- 有些Collection的实现类,可以存放重复的元素,有些不可以
- 有些Collection的实现类是有序的(List),有些是无序的(Set)–这里说的有序和无序是指取出的顺序是否和放入顺序一致
- Collection接口没有直接的实现子类,是通过它的子接口Set和List来实现的
示例:
package com.grey.test_01;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class CollectionExp {@Test@SuppressWarnings("all")public void konwCollection() {//Collection//Map//LinkedHashMap//ArrayList//创建一个ArrayList(单列集合)List list = new ArrayList();//add添加单个元素list.add("hello");list.add(10);list.add(new Integer(100));list.add(true);list.add(new Integer(30));list.add(new String("word"));System.out.println(list);//remove删除元素list.remove(0);//删除第一个元素hellolist.remove("word");//指定删除对象System.out.println(list);//contains查找某个元素是否存在System.out.println(list.contains(true));System.out.println(list.contains("hello"));//size获取元素个数System.out.println("size:" + list.size());//isEmpty是否为空System.out.println(list.isEmpty());//clear清空list.clear();System.out.println(list);//addAll可以添加集合,多个元素List list2 = new ArrayList();list2.add(35.5d);list2.add(45.5f);list.addAll(list2);System.out.println(list);//containsAll查找多个元素是否存在System.out.println(list.containsAll(list2));//removeAll 删除多个元素List list3 = new ArrayList();list3.add("特别的爱特别的你");list.addAll(list3);System.out.println("removeAll前:" + list);list.removeAll(list3);System.out.println("removeAll后:" + list);}}
Collection接口的遍历形式
使用迭代器Iterator(迭代器)
- Itrator对象称为迭代器,只要用于遍历Collection集合中的元素。
- 所有实现了Collection接口的集合类都有一个Iterator()方法,用以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象,即可以返回一个迭代器
- Iterator仅用于遍历集合,Iterator本身并不存放对象
迭代器的执行原理

Itrator接口的方法

示例:
package com.grey.test_01;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;public class ItratorExercise {@Test@SuppressWarnings("all")public void getItrator() {Collection arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add(new Book("三国演义", "罗贯中", 42.99));arrayList.add(new Book("西游记", "吴承恩", 38.5));arrayList.add(new Book("水浒传", "施耐庵", 66.66));System.out.println("直接输出:" + arrayList);System.out.println("----------------");//先得到对应的迭代器Iterator iterator = arrayList.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) { //判断是否还有数据//返回下一个元素,类型是ObjectObject next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}//当退出while循环后,这时迭代器指向最后一个元素//报错 iterator.next(); //java.util.NoSuchElementException//如果希望再次遍历,需要重置迭代器arrayList.add("今天天气不错");System.out.println("重置迭代器之后...........");iterator = arrayList.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}}}class Book {private String name;private String author;private Double price;public Book(String name, String author, Double price) {this.name = name;this.author = author;this.price = price;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getAuthor() {return author;}public void setAuthor(String author) {this.author = author;}public Double getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(Double price) {this.price = price;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Book{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", author='" + author + '\'' +", price=" + price +'}';}
}
for循环增强遍历
增强for循环,可以替代itrator迭代器,特点:增强for就是简化版的iterator,本质一样。只能用于遍历集合或者数组
基本语法:
for(元素类型 元素名:集合名或数组名){访问元素
}
示例:
package com.grey.test_01;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;public class StrongFor {@Testpublic void strongFor() {ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add(new Teacher("王老师", 45, 1.68));arrayList.add(new Teacher("李老师", 25, 1.58));arrayList.add(new Teacher("刘老师", 27, 1.78));//使用增强for循环,在Collection集合//底层仍然是迭代器//增强for循环,可以理解成简化版的迭代器for (Object o : arrayList) {System.out.println(o);}//增强for循环也可以在数组中使用int[] nums = {1, 8, 9, 10};for (int num : nums) {System.out.println(num);}}
}class Teacher {private String name;private Integer age;private Double height;public Teacher(String name, Integer age, Double height) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.height = height;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public Double getHeight() {return height;}public void setHeight(Double height) {this.height = height;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Teacher{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", height=" + height +'}';}
}
课堂练习:
编写程序CollectionExercise
- 创建3个Dog{name,age}对象,放入到ArrayList中,赋给List使用
- 用迭代器和增强for循环两种方式来遍历
- 重写Dog的toString方法,输出name和age
package com.grey.test_01;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;/*** @Description:* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/16*/
public class CollectionExerciseAndIterator {@Testpublic void collectionExerciseAndIterator() {List list = new ArrayList();list.add(new Dog("大黄", 1));list.add(new Dog("小贝", 2));list.add(new Dog("来福", 3));//迭代器System.out.println("迭代器");Iterator iterator = list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}System.out.println("增强for循环");//增强for循环for (Object o : list) {System.out.println(o);}}}class Dog {private String name;private Integer age;public Dog(String name, Integer age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Dog{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
List接口和常用方法
List接口是Collection接口的子接口
- List集合类中元素有序(即添加顺序和取出顺序一致)、并且可以重复
- List集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引,即支持索引
- List容器中的元素都对应一个整数型的序号记载其在容器中的位置,可以根据序号存取容器中的元素。
- List接口的常用实现类有:ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector
List接口和常用方法
- add 在index位置插入元素
- addAll 从index位置开始将所有元素添加进来
- get 获取指定index位置的元素
- indexOf 返回在集合中首次出现的位置
- lastIndexOf 返回在当前集合中末次出现的位置
- remove 移除index位置的元素,并返回此元素
- set 设置指定index位置的元素(替换)
- subList 返回一个范围位置中的子集合
示例:
package com.grey.test_01;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;/*** @Description: ListMethod* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/17*/
public class ListMethod {@Testpublic void ListMethodExercise() {List list = new ArrayList();list.add("张三丰");list.add("贾宝玉");//插入一个元素list.add(1, "林黛玉");System.out.println(list);//插入一个集合List list2 = new ArrayList();list2.add("Jack");list2.add("Tom");list.addAll(1, list2);System.out.println(list);//获取集合中的索引值System.out.println("get(2):" + list.get(2));//Tom//返回首个出现的位置System.out.println(list.indexOf("林黛玉"));//3//返回末次出现的位置list.add("林黛玉");System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("林黛玉"));//5//移除元素并且输出该元素list.remove(5);System.out.println(list);//替换list.set(1, "王宝强");System.out.println(list);//返回范围值内的子集合[0,3)所以只有0,1,2三个元素List listReturn = list.subList(0, 3);System.out.println(listReturn);}
}
练习:
package com.grey.test_01;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;/*** @Description: ListExercise02* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/17*/
public class ListExercise02 {@Test@SuppressWarnings("all")public void ListExer02() {List list = new ArrayList();list.add("1 你好");list.add("2 hello world");list.add("3 10");list.add("4 今天天气不错");list.add("5 开心");list.add("6 难过");list.add("7 悲伤");list.add("8 喜悦");list.add("9 幸福");list.add("10 自豪");System.out.println(list);list.add(1, "韩顺平教育");System.out.println("在2号位插入:" + list);System.out.println("获取弟5个元素:" + list.get(4));list.remove(5);System.out.println("删除第5个元素后:" + list);list.set(6, "很悲伤");System.out.println("修改第7个元素后:" + list);Iterator iterator = list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}}}
List的三种遍历方式
- 方式一:使用迭代器
- 方式二:增强for循环
- 方式三:使用普通for循环
package com.grey.test_01;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Vector;/*** @Description: Bianli* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/17*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Bianli {@Testpublic void getBianli() {List list = new ArrayList();list.add("Jack");list.add("Tom");list.add("鱼香肉丝");list.add("北京烤鸭");//迭代器遍历System.out.println("-----迭代器遍历-----");Iterator iterator = list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}//增强for循环遍历System.out.println("-----增强for循环遍历-----");for (Object o : list) {System.out.println(o);}//普通for循环遍历(类似数组)System.out.println("------普通for循环遍历(类似数组)------");for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.println(list.get(i));}}@Testpublic void getBianLi02() {List vector = new Vector();vector.add("Jack");vector.add("Tom");vector.add("鱼香肉丝");vector.add("北京烤鸭");//迭代器遍历System.out.println("-----迭代器遍历-----");Iterator iterator = vector.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}//增强for循环遍历System.out.println("-----增强for循环遍历-----");for (Object o : vector) {System.out.println(o);}//普通for循环遍历(类似数组)System.out.println("-----普通for循环遍历(类似数组)-----");for (int i = 0; i < vector.size(); i++) {System.out.println(vector.get(i));}}
}
课堂练习2

冒泡排序排列集合中对象的某个属性
package com.grey.test_01;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;/*** @Description: ListExercise03* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/17*/
public class ListExercise03 {@Testpublic void listExercise03() {List list = new ArrayList();list.add(new BookTwo("红楼梦", 100.0, "曹雪芹"));list.add(new BookTwo("西游记", 10.0, "吴承恩"));list.add(new BookTwo("水浒传", 9.0, "施耐庵"));list.add(new BookTwo("三国演义", 80.0, "罗贯中"));list.add(new BookTwo("西游记", 10.0, "吴承恩"));//正常顺序System.out.println("-----正常顺序-----");for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.println(list.get(i));}//冒泡排序之后的顺序,从小到大this.BubbleSort(list);//冒泡排序之后System.out.println("-----冒泡排序之后-----");for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.println(list.get(i));}}private void BubbleSort(List list) {int size = list.size();for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < size - i - 1; j++) {Object ob1 = list.get(j);Object ob2 = list.get(j + 1);//向下转型BookTwo bookTwo1 = (BookTwo) ob1;BookTwo bookTwo2 = (BookTwo) ob2;if (bookTwo1.getPrice() > bookTwo2.getPrice()) {list.set(j + 1, bookTwo1);list.set(j, bookTwo2);}}}}
}class BookTwo {private String name;private Double price;private String author;public BookTwo(String name, Double price, String author) {this.name = name;this.price = price;this.author = author;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Double getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(Double price) {this.price = price;}public String getAuthor() {return author;}public void setAuthor(String author) {this.author = author;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "BookTwo{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", price=" + price +", author='" + author + '\'' +'}';}
}
ArrayList底层结构和源码分析
- ArrayList可以放所有的元素甚至是空元素,可以放入多个空值。
- ArrayList是由数组来实现数据存储的。
- ArrayList基本等同于Vector,除了ArrayList是线程不安全(执行效率高),在多线程下,不建议用ArrayList。
- ArrayList中维护了一个Object类型的数组elementData --> transient Object[] elementData --> transient:短暂的,瞬间的,表示该属性不会被序列化
- 当创建ArrayList对象时,如果使用的是无参构造器,则初始elementData容量是0,第1次添加,则扩容elementData为10,如需再次扩容,则扩容elementData为1.5倍
- 如果使用的是指定大小的构造器,则初始elementData容量为指定大小,如果需要扩容,则直接扩容elementData为1.5倍
Vector底层机构和源码剖析
Vector的基本介绍
- Vector类的定义说明:
- public class Vector
- extends AbstractList
- implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable,Serializable
- Vector底层也是一个对象数组,protected Object[] elementData
- Vector 是线程同步的,即线程安全,Vector类的操作方法带有synchronized
- 在开发中,需要线程同步安全时,优先考虑用Vector
Vector和List比较
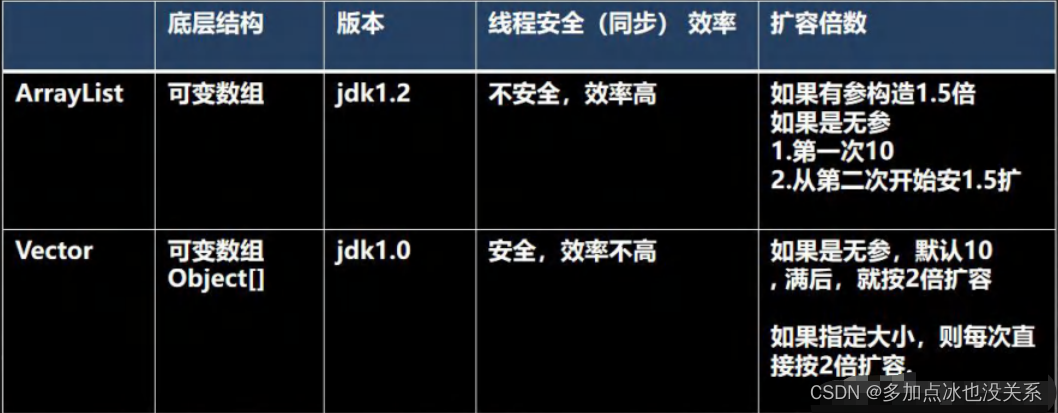
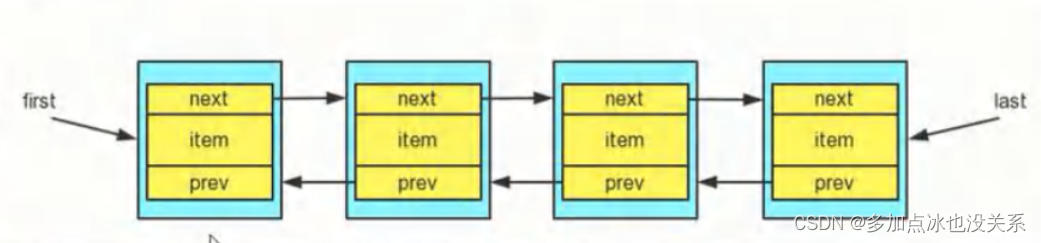
LinkedList底层结构
- LinkedList底层维护了一个双向链表
- LinkedList中维护了两个属性first和last分别指向首节点和尾节点
- 每个节点(Node对象),里面又维护了prev,next,item三个属性,其中通过prev指向前一个,通过next指向后一个节点 ,最终实现双向链表。
- 所以LinkedList的元素的添加和删除,不是通过数组完成的,相对来说效率较高
模拟一个双向链表简单示例:
package com.grey.test_02;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;/*** @Description: 模拟一个双向链表* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/17*/
public class LinkedListExercise02 {@Testpublic void getLinked() {Linked one = new Linked("One");Linked two = new Linked("Two");Linked four = new Linked("Four");one.setNext(two);two.setNext(four);four.setPre(two);two.setPre(one);Linked first = one; //定义头结点System.out.println("------从头到尾遍历------");while (true) {if (first == null) {break;}System.out.println(first);first = first.getNext();}Linked last = four; //定义尾结点System.out.println("------从尾到头遍历------");while (true) {if (last == null) {break;}System.out.println(last);last = last.getPre();}//插入一个元素Linked three = new Linked("Three");two.setNext(three);four.setPre(three);three.setNext(four);three.setPre(two);first = one; //定义头结点System.out.println("------插入元素3之后,从头到尾遍历------");while (true) {if (first == null) {break;}System.out.println(first);first = first.getNext();}last = four; //定义尾结点System.out.println("------插入元素3之后,从尾到头遍历------");while (true) {if (last == null) {break;}System.out.println(last);last = last.getPre();}}}class Linked {private Linked pre;private Linked next;private Object name;public Linked(Object name) {this.name = name;}public Linked getPre() {return pre;}public void setPre(Linked pre) {this.pre = pre;}public Linked getNext() {return next;}public void setNext(Linked next) {this.next = next;}public Object getName() {return name;}public void setName(Object name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Linked{" +"name=" + name +'}';}
}
关于LinkedList源码分析
package com.grey.test_02;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;/*** @Description: LinkedList源码分析* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/17*/
public class LinkedListCRUD {@Testpublic void linkedListCRUD() {LinkedList list = new LinkedList();list.add(100);list.add(200);list.add(300);System.out.println(list);//修改,把200改成400System.out.println(list.set(1, 400));//删除400System.out.println(list.remove(1));//查找第2个元素System.out.println(list.get(1));//迭代器遍历System.out.println("-----迭代器遍历-----");Iterator iterator = list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}System.out.println("增强for循环遍历");for (Object o : list) {System.out.println(o);}System.out.println("普通for循环遍历");for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.println(list.get(i));}}}
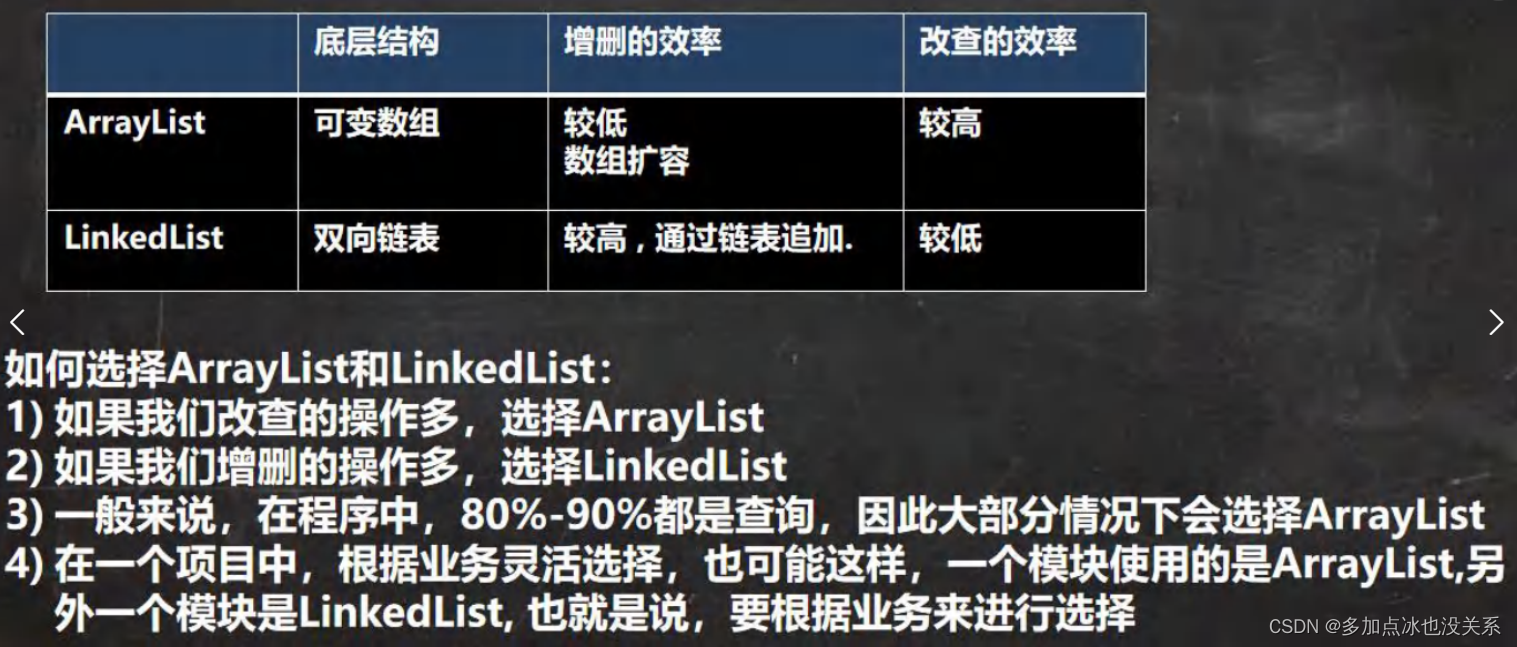
Set接口和常用方法
- 无序(添加和取出的顺序不一致),没有索引
- 不允许元素重复,所以最多包含一个null
- JDK API中Set接口的实现类
Set接口的遍历方式
同Collection的遍历方式一样,因为Set接口是Collection接口的子接口。
- 可以使用迭代器
- 增强for循环
- 不能使用索引的方式来获取
常用方法示例:
package com.grey.test_02;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;/*** @Description: SetMethod* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/17*/
public class SetMethod {@Testpublic void SetMethodEx() {//以Set接口的实现类,HashSet为例//Set接口的实现类的对象(Set接口对象)不能存放重复元素//可以添加一个null//Set接口对象存放数据,对象是无序的(添加顺序和取出顺序不一致)//取出顺序是固定的Set set = new HashSet();set.add("小明");set.add("小芳");set.add("小刚");set.add("小明");set.add(null);set.add(null);System.out.println(set);//遍历//方式1;迭代器System.out.println("-----迭代器-----");Iterator iterator = set.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}//增强for循环System.out.println("-----增强for循环遍历-----");for (Object o : set) {System.out.println(o);}System.out.println("size:" + set.size());System.out.println("是否为空:" + set.isEmpty());System.out.println("是否包含元素[小刚]:" + set.contains("小刚"));System.out.println("remove:" + set.remove("小刚"));System.out.println("remove:" + set.remove(null));System.out.println(set);}}
HashSet的全面说明
- HashSet实现了Set接口
- HashSet实际上是HashMap
- 可以存放null值,但是只能有一个null
- HashSet不保证元素是有序的,取决于hash后,再确定索引的结果(不保证元素存放和取出顺序一致)
- 不能有重复元素/对象。在前面Set接口使用已经讲过了
package com.grey.test_02;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;/*** @Description: HashSetStructure* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/17*/
public class HashSetStructure {@Testpublic void getHashSetStr() {//模拟一个HashSet的底层(其实就是HashMap)//创建一个Node数组,有些人称为tableNode[] table = new Node[16];System.out.println("table:" + table);//把john放在2的位置Node jhon = new Node("Jhon", null);table[2] = jhon;System.out.println("table:" + table);Node jack = new Node("Jack", null);jhon.next = jack; //将jack挂载到jhno后边System.out.println("table:" + table);//继续把Rose挂载到Jack后面Node rose = new Node("Rose", null);jack.next = rose;System.out.println("table:" + table);//把Lucy放到table表索引为3的位置Node lucy = new Node("Lucy", null);table[3] = lucy;System.out.println("table:" + table);}}//节点,存储数据,可以指向下一个节点
class Node {Object item;//存放数据Node next;//指向下一个节点public Node(Object item, Node next) {this.item = item;this.next = next;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Node{" +"item=" + item +", next=" + next +'}';}
}
HashSet的底层机制
分析:HashSet底层是HashMap,HashMap底层是(数组+链表+红黑树)
浓缩成6句话
- HashSet底层是HashMap
- 添加一个元素时,先得到hash值,会转成索引值
- 找到存储数据表table,看这个索引位置是否已经存放的有元素
- 如果没有,直接加入
- 如果有,调用equals比较,如果相同,就放弃添加,如果不相同,则添加到最后
- 在JAVA 8 中,如果一条链表的元素个数,到达TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且table的大小>= MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认64)就进行树化(红黑树)
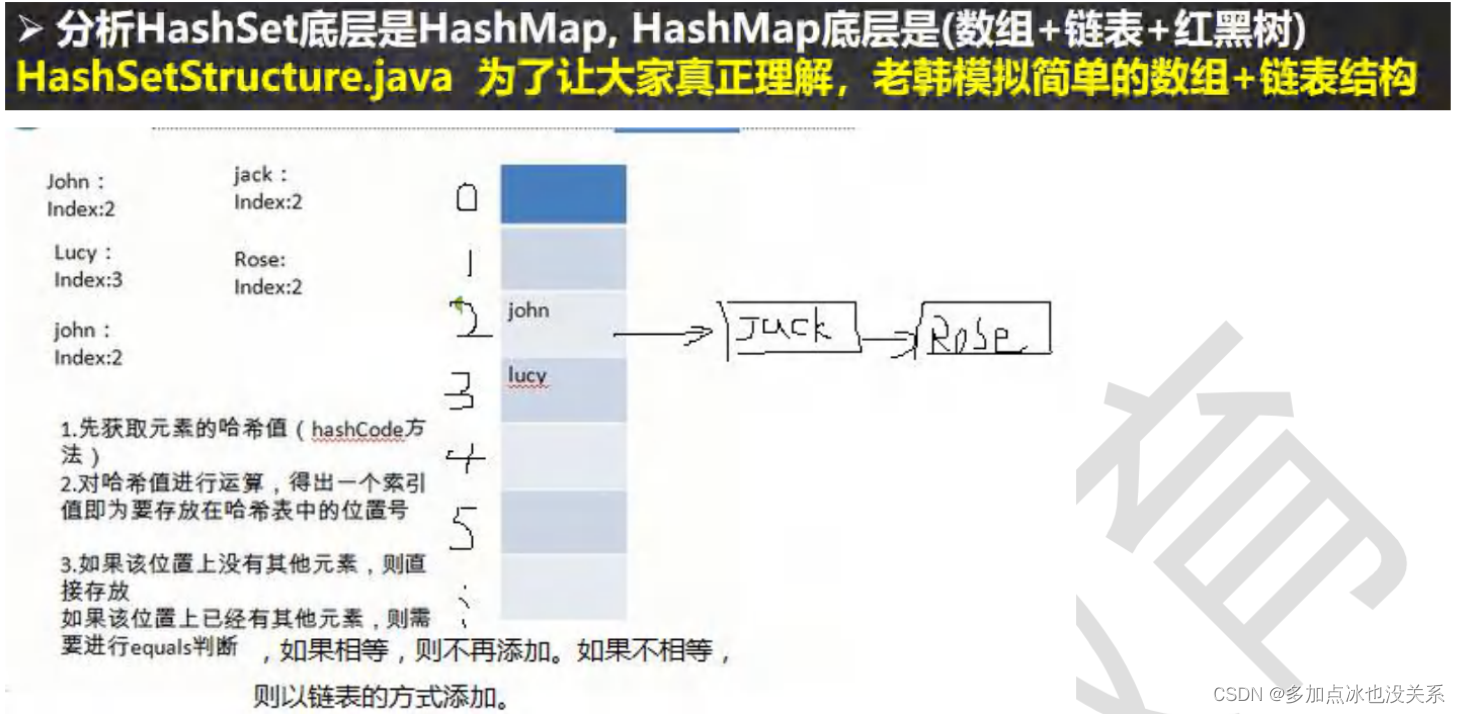

课堂练习
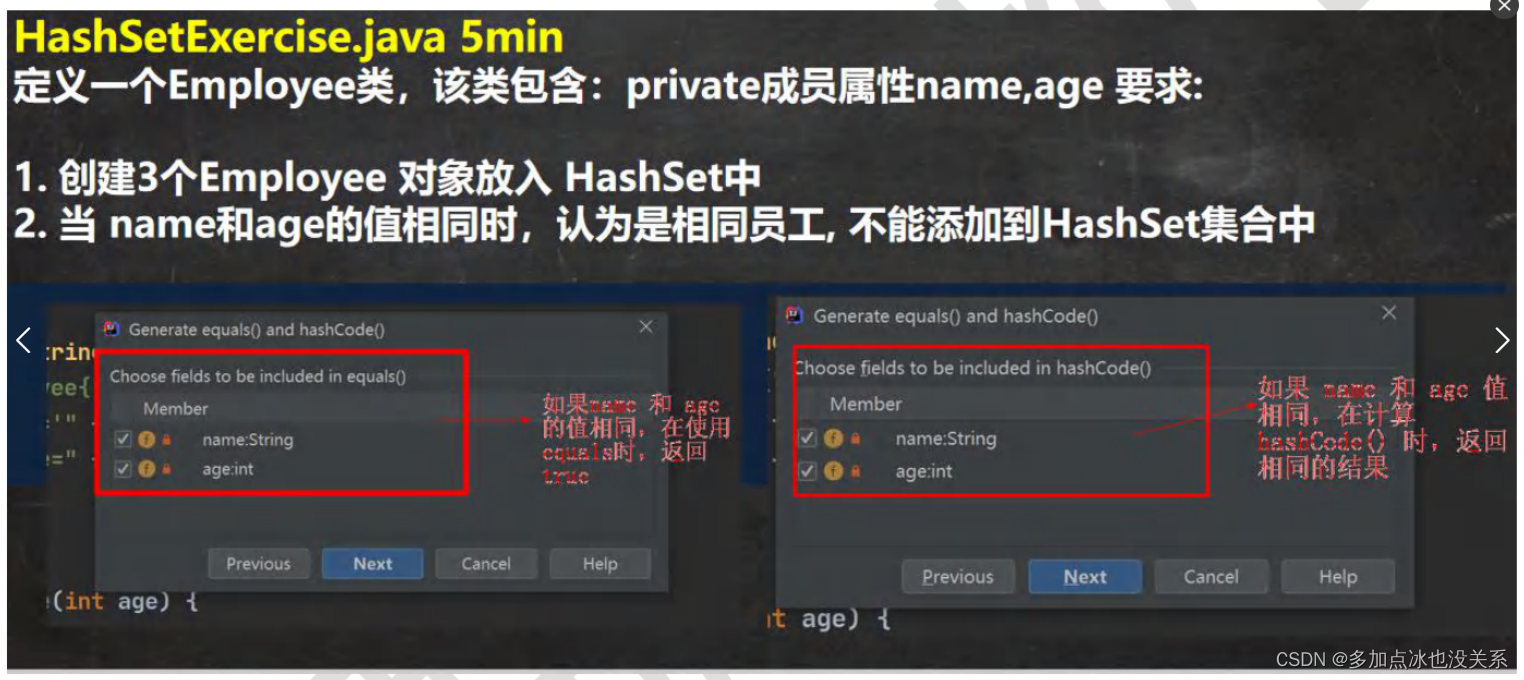
课后练习
equals和hashCode示例1:

package com.grey.test_02;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;/*** @Description: Employee* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/18*/
public class Employee {@Testpublic void employee() {HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();hashSet.add(new Workers("小明", 10));hashSet.add(new Workers("小红", 20));hashSet.add(new Workers("小明", 30));hashSet.add(new Workers("小刚", 40));hashSet.add(new Workers("小明", 10));System.out.println("size:" + hashSet.size());System.out.println(hashSet);}}class Workers {String name;Integer age;public Workers(String name, Integer age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Workers{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}//如果name和age相同,要返回相同的哈希值@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {
// return super.equals(obj);if (this == obj) return true;if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;Workers workers = (Workers) obj;return Objects.equals(name, workers.name) && this.age == workers.age;}//如果age和name相同,要返回相同的哈希值 (先比较age在比较name)/*@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {
// return super.equals(obj);if (this == obj) return true;if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;Workers workers = (Workers) obj;return this.age == workers.age && Objects.equals(name, workers.name);}*/@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, age);}
}
equals和hashCode示例2:重写2次
package com.grey.test_02;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;/*** @Description: Employee02* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/18*/
public class Employee02 {@Testpublic void getPerson() {HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();hashSet.add(new Employ("小明", 10000.88d, new MyDate("1996", "01", "01")));//姓名一样,出生年份不同hashSet.add(new Employ("小明", 10001.88d, new MyDate("1997", "01", "01")));//出生年份和工资不同hashSet.add(new Employ("小明", 10001.88d, new MyDate("1998", "01", "01")));//工资和第一个比不同(按照规则,这个应该不展示)hashSet.add(new Employ("小明", 10002.88d, new MyDate("1996", "01", "01")));//重写了toString()方法,这里可以遍历一下,看看值System.out.println("size:" + hashSet.size());for (Object o : hashSet) {System.out.println(o);}}}class Employ {private String name;private double sal;private MyDate birthday;public Employ(String name, double sal, MyDate birthday) {this.name = name;this.sal = sal;this.birthday = birthday;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {
// return super.equals(obj);if (this == obj) return true;if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;Employ employ = (Employ) obj;return Objects.equals(name, employ.name)&& Objects.equals(birthday, employ.birthday);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, birthday);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Employ{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", sal=" + sal +", birthday=" + birthday +'}';}
}class MyDate {String year;String month;String day;public MyDate(String year, String month, String day) {this.year = year;this.month = month;this.day = day;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {
// return super.equals(obj);if (this == obj) return true;if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;MyDate myDate = (MyDate) obj;return Objects.equals(year, myDate.year)&& Objects.equals(month, myDate.month) && Objects.equals(day, myDate.day);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(year, month, day);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "MyDate{" +"year='" + year + '\'' +", month='" + month + '\'' +", day='" + day + '\'' +'}';}
}
equals和hashCode示例2:重写1次
package com.grey.test_02;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;/*** @Description: Employee03* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/18*/
public class Employee03 {@Testpublic void getPerson() {HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();hashSet.add(new Employ02("小明", 10000.88d, new MyDate02("1996", "01", "01")));hashSet.add(new Employ02("小明", 10001.88d, new MyDate02("1997", "01", "01")));hashSet.add(new Employ02("小明", 10001.88d, new MyDate02("1998", "01", "01")));//按照重复数据去重hashSet.add(new Employ02("小明", 10002.88d, new MyDate02("1996", "01", "01")));System.out.println("size:" + hashSet.size());for (Object o : hashSet) {System.out.println(o);}}}class Employ02 {private String name;private double sal;private MyDate02 birthday;public Employ02(String name, double sal, MyDate02 birthday) {this.name = name;this.sal = sal;this.birthday = birthday;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {if (this == obj) return true;if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;Employ02 employ02 = (Employ02) obj;return Objects.equals(name, employ02.name)&& Objects.equals(birthday.getYear(), employ02.birthday.getYear())&& Objects.equals(birthday.getMonth(), employ02.birthday.getMonth())&& Objects.equals(birthday.getDay(), employ02.birthday.getDay());}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {//这里直接重写一次hashCode方法即可return Objects.hash(name, birthday.getYear(), birthday.getMonth(), birthday.getDay());}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Employ02{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", sal=" + sal +", birthday=" + birthday +'}';}
}class MyDate02 {private String year;private String month;private String day;public MyDate02(String year, String month, String day) {this.year = year;this.month = month;this.day = day;}public String getYear() {return year;}public void setYear(String year) {this.year = year;}public String getMonth() {return month;}public void setMonth(String month) {this.month = month;}public String getDay() {return day;}public void setDay(String day) {this.day = day;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "MyDate02{" +"year='" + year + '\'' +", month='" + month + '\'' +", day='" + day + '\'' +'}';}
}
LinkedHashSe
LinkedHashSet的全面说明
- LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类
- LinkedHashSet底层是一个LinkedHashMap,底层维护了一个数组+双向链表
- LinkedHashSet根据元素的hashCode值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使用链表维护元素的次序图(图),这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的。
- LinkedHashSet不允许添加重复元素
说明:
- 在LinkedHashSet中维护一个hash表和双向链表(LinkedHashSet 有head和tail)
- 每一个结点有before和after属性,这样可以形成双向链表
- 在添加一个元素时,先求hash值,再求索引,确定该元素在table的位置,然后将添加的元素加入到双向链表(如果已经存在,不添加[原则和hashset一样])
tail.next = newElement
newElement.pre = tail
tail = newElement; - 这样的话,我们遍历LinkedHashSet 也能确保插入顺序和遍历顺序一致
equals和hashCode重写
package com.grey.test_02;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Objects;/*** @Description: 如果name和price一样就认为是一样的元素* @author: 多加点冰也没关系* @since: 2023/8/18*/
public class LinkedHashSetExercise01 {@Testpublic void getHashSet() {LinkedHashSet set = new LinkedHashSet();set.add(new Car("奥迪", 1000d));set.add(new Car("奥迪", 30000d));set.add(new Car("法拉利", 100000d));set.add(new Car("保时捷", 7000000d));set.add(new Car("奥迪", 1000d));for(Object o : set){System.out.println(o);}}
}class Car {private String name;private Double price;public Car(String name, Double price) {this.name = name;this.price = price;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Car{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", price=" + price +'}';}//重写equals和hash方法@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {
// return super.equals(obj);if (this == obj) return true;if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false;Car car = (Car) obj;return Double.compare(car.price, price) == 0 && Objects.equals(name, car.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, price);}
}
Map集合
Map接口实现类的特点
- Map与Collection并列存在,用于保存具有映射关系的数据Key-Value(双列元素)
- Map中的key和value可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到HashMap$Node对象中
- Map中的key不允许重复,原因和HashSet一样,前面分析过源码。
- Map中的value可以重复
- Map的key可以为null,value也可以为null,注意key为null,只能有一个,value为null可以多个
- 常用String类作为Map的key
- key和value之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的key总能找到对应的value
- Map存放数据的key-value示意图,一对key-value 是放在一个Node中的,又因为Node实现了Entry接口,有些书上也说一对key-value就是一个Entry(如图)
package com.grey.test_03;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;/*** @Description: MapExercise* @author: 多加点冰也没关系* @since: 2023/8/18*/
public class MapExercise {@Testpublic void getExercise() {//Map接口具有的特点//常用String类作为Map的keyMap hashMap = new HashMap();hashMap.put("1", "Jack");hashMap.put("2", 10);hashMap.put("3", "贾斯汀比伯");hashMap.put("4", "迈克尔杰克逊");hashMap.put("5", "贾斯汀比伯");hashMap.put("6", "Alice");hashMap.put("7", "VERTGA");hashMap.put("8", "LAM");hashMap.put("9", "GIN");hashMap.put("10", "TIO");hashMap.put("11", "AIO");hashMap.put("12", "Tony");hashMap.put("13", "Joy");//替换机制:当有相同key值时,就替换hashMap.put("1", "Rose");hashMap.put(null, null);//Map的key可以为null,value也可以为null,//注意:key为null,只能有一个,value为null可以有多个hashMap.put(null, null);hashMap.put("17", null);//替换hashMap.put(null, 181);//key可以用别的类型hashMap.put(1, "Jack");System.out.println(hashMap);System.out.println("get(1):" + hashMap.get(1));}
}
entrySet()获取entrySet
entrySet是一个Set
Map的常用方法
- put:添加
- remove:根据键删除映射关系
- get:根据键获取值
- size:获取元素个数
- isEmpty:判断个数是否为0
- clear:清除
- containsKey:查找键是否存在
package com.grey.test_03;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;/*** @Description: MapUse* @author: 多加点冰也没关系* @since: 2023/8/18*/
public class MapUse {@Testpublic void mapUse() {/*** (1)put:添加* (2)remove:根据键删除映射关系* (3)get:根据键获取值* (4)size:获取元素个数* (5)isEmpty:判断个数是否为0* (6)clear:清除* (7)containsKey:查找键是否存在*/Map map = new HashMap();map.put("1", "Book");map.put("邓超", "孙俪");map.put("马蓉", "王宝强");map.put("马蓉", "宋喆");System.out.println(map);map.remove("1");System.out.println(map);System.out.println(map.get("邓超"));System.out.println("size:" + map.size());System.out.println("是否为空:" + map.isEmpty());System.out.println("有没有马蓉:" + map.containsKey("马蓉"));map.clear();System.out.println("clear之后:" + map);}
}
Map接口遍历方法
Map遍历的示意图(比List,和Set复杂一点,但是基本原理一样)
- containsKey:查找键是否存在
- keySet:获取所有的键
- entrySet:获取所有关系
- values:获取所有的值
package com.grey.test_03;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.*;/*** @Description: MapBl* @author: lz* @since: 2023/8/18*/
public class MapBl {@Testpublic void MapBl() {Map map = new HashMap();map.put("1", "Jack");map.put("上单", "老夫子");map.put("中单", "诸葛亮");map.put("射手", "后裔");System.out.println(map);//遍历(自己想的)System.out.println("----增强for循环----");Set set = map.entrySet();for (Object o : set) {System.out.println(o);}//遍历(自己想的)System.out.println("----迭代器----");Iterator iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}//韩老师讲的//1.先取出所有的key,通过key找到对应的valueSystem.out.println("-----map.keySet()-----");Set keySet = map.keySet();for (Object o : keySet) {//向下转型System.out.println("key = " + o + " value = " + map.get(0));}//2.通过迭代器System.out.println("----map.keySet()的迭代器----");Iterator iterator1 = keySet.iterator();while (iterator1.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator1.next();System.out.println("key = " + next + " value = " + map.get(next));}//3.只是把所有的values取出System.out.println("----map.values()----");Collection values = map.values();for (Object value : values) {System.out.println("value = " + value);}System.out.println("----map.values()迭代器----");Iterator iterator2 = values.iterator();while (iterator2.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator2.next();System.out.println("value = " + next);}//3.通过EntrySet//增强for循环System.out.println("----map.entrySet()增强for循环----");Set entrySet = map.entrySet();for (Object o : entrySet) {Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) o;System.out.println("key = " + entry.getKey() + "value = " + entry.getValue());}//通过迭代器System.out.println("----entrySet迭代器----");Set entrySet2 = map.entrySet();Iterator iterator3 = entrySet2.iterator();while (iterator3.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator3.next();
// System.out.println(next.getClass());//HashMap$NodeMap.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) next;System.out.println("key = " + entry.getKey() + " value = " + entry.getValue());}}
}
课后练习

package com.grey.test_03;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;/*** @Description: AfterClassExercise* @author: 多加点冰也没关系* @since: 2023/8/18*/
public class AfterClassExercise {@Testpublic void showWorkers() {/*HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();hashSet.add(new Workers("王晓亮", 15000.5, "no.1"));hashSet.add(new Workers("钟飞扬", 16060.5, "no.2"));hashSet.add(new Workers("潘长江", 18060.5, "no.3"));hashSet.add(new Workers("小悦悦", 27060.5, "no.4"));System.out.println(hashSet);for (Object o : hashSet) {Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) o;entry.getKey();}*/HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();hashMap.put("no.1", new Workers("王晓亮", 15000.5, "no.1"));hashMap.put("no.2", new Workers("钟飞扬", 16060.5, "no.2"));hashMap.put("no.3", new Workers("潘长江", 18060.5, "no.3"));hashMap.put("no.4", new Workers("小悦悦", 27060.5, "no.4"));hashMap.put("no.5", "Jack");//显示工资大于18000的人System.out.println("--------keySet()--------");Set set = hashMap.keySet();for (Object o : set) { //String//System.out.println(o.getClass());//instanceof 作用是:测试它左边的对象是否是它右边的类的实例,返回 boolean 的数据类型。if (hashMap.get(o) instanceof Workers) {//hashMap.get(o)是对象WorkersWorkers workers = (Workers) hashMap.get(o);if (workers.getSal() > 18000) {System.out.println("key = " + o + " value = " + hashMap.get(o));}} else {System.out.println("key = " + o + " value = " + hashMap.get(o));}}//迭代器System.out.println("-----------------keySet()迭代器------------------");Iterator iterator = set.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();if (hashMap.get(next) instanceof Workers) {Workers workers = (Workers) hashMap.get(next);if (workers.getSal() > 18000) {System.out.println("key = " + next + " value = " + hashMap.get(next));}} else {System.out.println("key = " + next + " value = " + hashMap.get(next));}}//使用entrySet()方法System.out.println("-----------entrySet()增强for循环-----------");Set set1 = hashMap.entrySet();for (Object o : set1) {Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) o;if (entry.getValue() instanceof Workers) {Workers workers = (Workers) entry.getValue();if (workers.getSal() > 18000) {System.out.println("key = " + entry.getKey() + " value = " + entry.getValue());}} else {System.out.println("key = " + entry.getKey() + " value = " + entry.getValue());}}}}class Workers {private String id;private String name;private Double sal;public Workers(String name, Double sal, String id) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.sal = sal;}public String getId() {return id;}public void setId(String id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Double getSal() {return sal;}public void setSal(Double sal) {this.sal = sal;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Workers{" +"id='" + id + '\'' +", name='" + name + '\'' +", sal=" + sal +'}';}
}
HashMap小结
- Map接口的常用实现类:HashMap、Hashtable和Properties
- HashMap是Map接口使用频率最高的实现类
- HashMap是以key-value 对的方式来存储数据(HashMap$Node类型)
- key不能重复,但是值可以重复,允许使用null值和null键(null键只能有1个)
- 如果添加相同的key,则会覆盖原来的key-val,等同于修改(key不会替换,val会替换)
- 与HashSet一样,不保证映射的顺序,因为底层是以hash表的方式来存储的。
- HashMap没有实现同步,因此是线程不安全的,方法没有做同步互斥的操作,没有synchronized
HashMap底层机制以及源码剖析
- HashMap底层维护了Node类型的数组table,默认为null
- 当创建对象时,将加载因子(loadFactor)初始化为0.75
- 当添加key-value时,通过key的哈希值得到在table的索引。然后判断该索引处是否有元素,如果没有元素,则直接添加。如果该处索引有元素,则继续判断该元素的key是否和准备加入的key相等,如果相等,则直接替换成新的val,如果不相等,需要判断是树结构还是链表结构,做出相应的处理。如果添加时发现容量不够,则需要扩容。
- 第1次添加,则需要扩容table容量为16,临界值(threshold)为12
- 以后再扩容,则需要扩容table容量为原来的2倍,临界值为原来的2倍,即24,以此类推。
- 在Java8中,如果一条链表的元素个数超过了TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且table的大小>= MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认64),就会进行树化(红黑树)
模拟HashMap触发扩容、树化情况
package com.grey.test_03;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;/*** @Description: HashMapSource* @author: 多加点冰也没关系* @since: 2023/8/18*/
public class HashMapSource {@Testpublic void getSource() {HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
// HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
// LinkedHashSet linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet();hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 1), "no1.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 2), "no2.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 3), "no3.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 4), "no4.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 5), "no5.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 6), "no6.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 7), "no7.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 8), "no8.Jack");/*** // 从第二次put之后才会进这里,并且第二次循环时 var12 0 第二次循环结束 var12 1 -- 即第三次循环开始 var12 1* 所以var12比put的次数少2,一直到put第9的时候,var12 >= 7才会满足* while(true) {* if ((var10 = ((HashMap.Node)var7).next) == null) {* ((HashMap.Node)var7).next = this.newNode(var1, var2, var3, (HashMap.Node)null);* if (var12 >= 7) {* this.treeifyBin(var6, var1);* }* break;* }** if (((HashMap.Node)var10).hash == var1 && ((var11 = ((HashMap.Node)var10).key) == var2 || var2 != null && var2.equals(var11))) {* break;* }** var7 = var10;* ++var12;* }*/hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 9), "no9.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 10), "no10.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 11), "no11.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 12), "no12.Jack");/*** if (++this.size > this.threshold) { 所以是第13次put的时候扩容 16 → 32* this.resize();* }*/hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 13), "no13.Jack"); //hashMap.put(new Cat("小红", 14), "no14.Jack");hashMap.put(new Cat("小蓝", 9), "no9.Jack"); // 扩容table 32hashMap.put(new Cat("小蓝", 10), "no10.Jack"); // 扩容table 64hashMap.put(new Cat("小蓝", 11), "no11.Jack"); // 将链表转换成红黑树//hashMap.put("11", "no111.Jack");//hashMap.put("12", "no12.Jack");//hashMap.put("13", "no13.Jack"); // 超过12才扩容
/* hashMap.remove(new Cat("小蓝", 11));hashMap.remove(new Cat("小蓝", 10));hashMap.remove(new Cat("小蓝", 9));hashMap.remove(new Cat("小红", 8));hashMap.remove(new Cat("小红", 7));hashMap.remove(new Cat("小红", 6));hashMap.remove(new Cat("小红", 5));hashMap.remove(new Cat("小红", 4)); // 执行完之后剪枝hashMap.remove(new Cat("小红", 3));hashMap.remove(new Cat("小红", 3));*/Set set = hashMap.keySet();for (Object o : set) {System.out.println("key = " + o + " value = " + hashMap.get(o));}System.out.println(hashMap);}}class Cat {private String name;private Integer age;public Cat(String name, Integer age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Cat{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(100);}
}
Map接口实现类-Hashtable
- 存放的元素是键值对:即K-V
- hashtable的键和值都不能为null,否则会抛出NullPointerException
- hashTable使用方法基本上和HashMap一样
- hashTable是线程安全的(synchronized),hashMap是线程不安全的
- 实现Map接口
注意:
- 底层有数组 Hashtable$Entry[] 初始化大小为11
- 临界值 threshold = 11 * 0.75 ≈ 8
- 扩容:按照自己的扩容机制来进行
- 执行方法 addEntry(hash, key, value, index); 添加键值对,封装到Entry
Hashtable和HashMap对比
| 名称 | 版本 | 线程安全(同步) | 效率 | 允许null键null值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hashtable | 1.2 | 不安全 | 高 | 可以 |
| HashMap | 1.0 | 安全 | 较低 | 不可以 |
Properties
基本介绍
- Properties类继承自Hashtable类并且实现了Map接口,也是一种键值对的形式来保存数据。
- 它的使用特点和Hashtable类似。
- Properties还可以用于从xxx.properties文件中,加载数据到Properties类对象,并进行读取和修改。
- 说明:工作后xxx.properties文件通常作为配置文件,这个知识点在IO流举例,有兴趣可先看文章。
配置文件不会显示乱码,统一调整为UTF-8
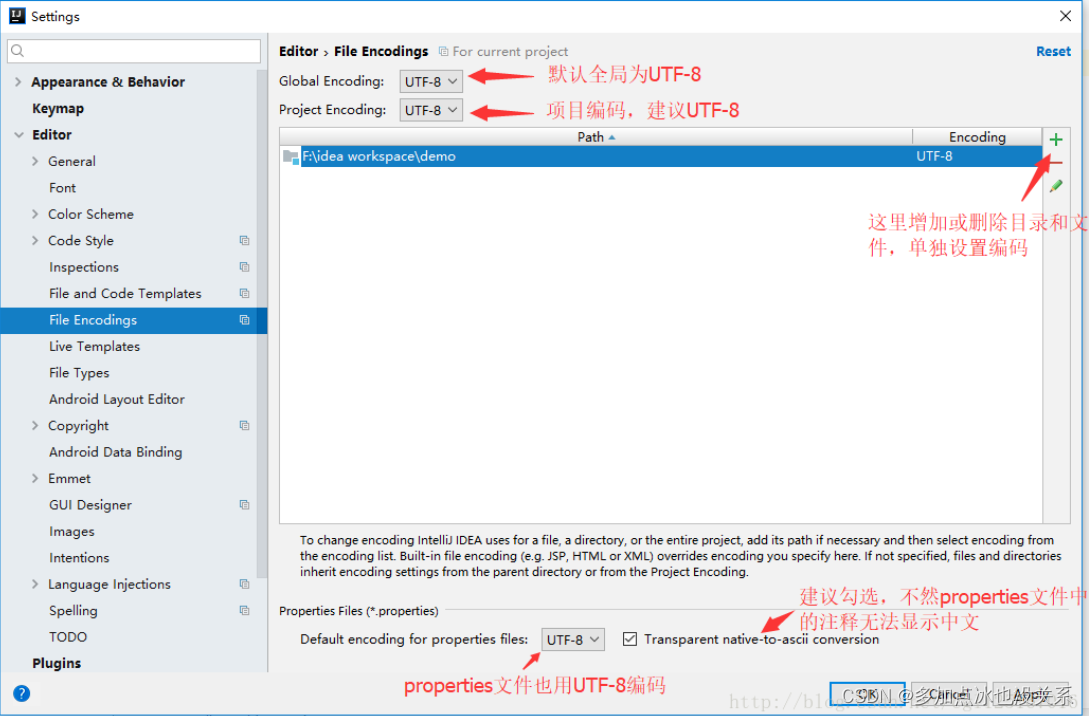
package com.Map.Properties;import org.junit.Test;import java.io.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;public class PropertiesEx {@Testpublic void propertiesEx() {Properties properties = new Properties();String path = "src/com/Map/File/res.properties";BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null;try {bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));properties.load(bufferedReader);Set<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> entries = properties.entrySet();Iterator<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> iterator = entries.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Map.Entry<Object, Object> next = iterator.next();System.out.println("key = " + next.getKey() + " value = " + next.getValue());}// 写入bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(path));properties.setProperty("signature", "rose");properties.setProperty("signature", "厉害");properties.store(bufferedWriter, "This is my destney哈哈");} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {bufferedReader.close();bufferedWriter.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
res.properties
name=root
key=value
pass=liu
基本用法
package com.Map.Properties;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Properties;public class PropertiesExercise {@Testpublic void getEx() {Properties properties = new Properties();properties.put("no.1", "Jack");properties.put("no.2", "Jone");// 有相同的key,value会被替换properties.put("no.2", "Joy");//properties.put(null,null); // java.lang.NullPointerException// 键不能为空//properties.put(null,"1"); // java.lang.NullPointerException// 值不能为空//properties.put("no.3",null); // java.lang.NullPointerExceptionproperties.put("no.3", "Rose");System.out.println(properties);// 通过key获取对应的值System.out.println("no.2: " + properties.get("no.2"));properties.remove("no.3");System.out.println("删除no.3之后");System.out.println(properties);// 修改:properties.setProperty("no.2", "Alice");System.out.println("setProperty修改no.2之后");System.out.println(properties);properties.put("no.2", "Rice");System.out.println("putno.2之后");System.out.println(properties);// 查找System.out.println("getProperty no.1之后");System.out.println(properties.getProperty("no.1"));}
}
集合选型
在开发中,选择什么集合实现类,主要取决于业务操作特点,然后根据集合实现类特性进行选择,分析如下:
(1)先判断存储类型(一组对象(单列)或者键值对(双列))
(2)一组对象: Collection接口 允许重复:List 增删多:LinkedList(底层是双向链表) 查改多:ArrayList(底层维护Object类型的可变数组) 不允许重复:Set无序:HashSet底层是HashMap,维护一个Hash表(数组+链表+红黑树) 排序:TreeSet 插入和取出顺序一样: LinkedHashSet(继承自LinkedHashMap),维护数组+双向链表
(3)键值对:Map键无序:HashMap(底层是:哈希表:数组+链表+红黑树) 键有序:TreeMap 键插入和取出顺序一致:LinkedHashMap(继承自HashMap) 读取文件: Properties
TreeSet
TreeSet含Comparator构造器
package com.SetExercise;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;public class TreeSetExercise {@Test@SuppressWarnings({"all"})public void getTreeSet() {// 当使用无参构造器创建TreeSet的时候是无序的TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();// 添加数据treeSet.add("Derrick");treeSet.add("Rose");treeSet.add("Jam");treeSet.add("Timmy");treeSet.add("Tom");System.out.println(treeSet);System.out.println("---字符串按照首字母顺序比较---");// 添加的元素按照字符串大小来排序// 可以传入一个比较器(匿名内部类),并指定规则TreeSet treeSet1 = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Object o, Object t1) {return ((String) o).compareTo((String) t1);}});treeSet1.add("Derrick");treeSet1.add("Rose");treeSet1.add("Jam");treeSet1.add("Timmy");treeSet1.add("Tom");System.out.println(treeSet1);// 源码解读/*** public TreeMap(Comparator var1) {* this.comparator = var1; 把new Comparator() 给到TreeMap的comparator属性* }*/System.out.println("---字符串长度大小比较---");TreeSet treeSet2 = new TreeSet(new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Object o, Object t1) {String str_a = (String) o;String str_t1 = (String) t1;int a = ((String) o).length();int b = ((String) t1).length();int result = a - b;return result = result == 0 ? str_a.compareTo(str_t1) : result;}});treeSet2.add("Derrick");treeSet2.add("Amy");treeSet2.add("Rose");treeSet2.add("Jam"); // 相同长度加不进去treeSet2.add("Timmy");treeSet2.add("Tom");// 相同长度加不进去System.out.println(treeSet2);}
}
TreeMap
package com.Map;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeMap;public class TreeMapExercise {@Testpublic void getTreeMap() {// 无参数,无序取出TreeMap treeMap = new TreeMap();treeMap.put("1", "Jack");treeMap.put("no2", "Tom");treeMap.put("李小璐", "PGONE");treeMap.put("smith", "史密斯");System.out.println(treeMap);// 按照key字符串首字母倒叙排序TreeMap treeMap2 = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {return ((String) o2).compareTo((String) o1);}});System.out.println("按照key字符串首字母倒叙排序");treeMap2.put("1", "Jack");treeMap2.put("no2", "Tom");treeMap2.put("李小璐", "PGONE");treeMap2.put("smith", "史密斯");treeMap2.put("alice", "漫游记");System.out.println(treeMap2);// 按照key字符串长度排序,相同长度按首字母倒叙排序TreeMap treeMap3 = new TreeMap(new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {String str_o1 = (String) o1;String str_o2 = (String) o2;int a = str_o1.length();int b = str_o2.length();int result = a == b ? str_o1.compareTo(str_o2) : a - b;return result;}});System.out.println("按照key字符串长度排序,相同长度按首字母顺叙排序");treeMap3.put("1", "Jack");treeMap3.put("no2", "Tom");treeMap3.put("李小璐", "PGONE");treeMap3.put("smith", "史密斯");treeMap3.put("alice", "漫游记");treeMap3.put("tonny", "理发师");System.out.println(treeMap3);}
}
Collections工具类
Collections工具类介绍
- Collections是一个操作Set、List和Map等集合的工具类
- Collections中提供了一系列静态的方法对集合元素进行排序、查询和修改操作
排序操作(均为static方法)
- reverse(List):反转List中元素的顺序
- shuffle(List):对List集合元素进行随机排序
- sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定List集合元素按升序排序
- sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的Comparator产生的顺序对List集合进行排序
- swap(List,int,int):将指定list集合中的i处元素和j处元素进行交换
package com.CollectionsUse;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;public class CollectionsUse {@Testpublic void getUse() {HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();hashMap.put("Jack", "Rose");hashMap.put("no.1", "Tony");hashMap.put("no.2", "Jancy");hashMap.put("This", "is my destney");/*** (1)reverse(List):反转List中元素的顺序* (2)shuffle(List):对List集合元素进行随机排序* (3)sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定List集合元素按升序排序* (4)sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的Comparator产生的顺序对List集合进行排序* (5)swap(List,int,int):将指定list集合中的i处元素和j处元素进行交换*/System.out.println(hashMap);ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add("Derrick");arrayList.add("Rose");arrayList.add("no.1");arrayList.add("2");arrayList.add("周润发");arrayList.add("周杰伦");arrayList.add("洪辰");System.out.println("----正常-----");System.out.println(arrayList);Collections.reverse(arrayList); // (1)reverse(List):反转List中元素的顺序System.out.println("----倒叙----");System.out.println(arrayList);System.out.println("----随机顺序----");Collections.shuffle(arrayList); // (2)shuffle(List):对List集合元素进行随机排序System.out.println(arrayList);System.out.println("----再次随机顺序----");Collections.shuffle(arrayList);System.out.println(arrayList);System.out.println("----自然排序----"); // 根据元素的自然顺序对指定List集合元素按升序排序Collections.sort(arrayList);System.out.println(arrayList);// sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的Comparator产生的顺序对List集合进行排序System.out.println("----自然排序Comparator:按照字符串长度大小排序----");Collections.sort(arrayList, new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {if (o1 instanceof String && o2 instanceof String) {String str_o1 = (String) o1;String str_o2 = (String) o2;int a = str_o1.length();int b = str_o2.length();int result = a == b ? str_o1.compareTo(str_o2) : a - b;return result;} else {return 0;}}});System.out.println(arrayList);// (5)swap(List,int,int):将指定list集合中的i处元素和j处元素进行交换System.out.println("----交换第一个和第三个元素----");Collections.swap(arrayList, 0, 2);System.out.println(arrayList);}
}
查找和替换
- Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object max(Collection, Comparator):根据Compartor指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素
- Object min(Collection)
- Object min(Collection, Object)
- int frequency(Collection, Object):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数
- void copy(List dest, List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中
- boolean replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal):使用新值替换List对象的所有旧值
@Test
public void getUseCollections() {/*** (1)reverse(List):反转List中元素的顺序* (2)shuffle(List):对List集合元素进行随机排序* (3)sort(List):根据元素的自然顺序对指定List集合元素按升序排序* (4)sort(List,Comparator):根据指定的Comparator产生的顺序对List集合进行排序* (5)swap(List,int,int):将指定list集合中的i处元素和j处元素进行交换*/ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add("Derrick");arrayList.add("Rose");arrayList.add("no.1");arrayList.add("2");arrayList.add("周润发");arrayList.add("周杰伦");arrayList.add("洪辰");arrayList.add("Rose");System.out.println("----正常-----");System.out.println(arrayList);/*** (1)Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素* (2)Object max(Collection, Comparator):根据Compartor指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素* (3)Object min(Collection)* (4)Object min(Collection, Object)* (5)int frequency(Collection, Object):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数* (6)void copy(List dest, List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中* (7)boolean replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal):使用新值替换List对象的所有旧值*/// (1)Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素System.out.println("Object max(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素");System.out.println(Collections.max(arrayList));// Object max(Collection, Comparator):根据Compartor指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素System.out.println("Object max(Collection, Comparator):根据Compartor指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素 ");System.out.println(Collections.max(arrayList, new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {if (o1 instanceof String && o2 instanceof String) {String str_o1 = (String) o1;String str_o2 = (String) o2;int a = str_o1.length();int b = str_o2.length();int result = a == b ? str_o1.compareTo(str_o2) : a - b;return result;} else {return 0;}}}));// (3)Object min(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素System.out.println("Object min(Collection):根据元素的自然顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素");System.out.println(Collections.min(arrayList));// Object max(Collection, Comparator):根据Compartor指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最大元素System.out.println("Object min(Collection, Comparator):根据Compartor指定的顺序,返回给定集合中的最小元素 ");System.out.println(Collections.min(arrayList, new Comparator() {@Overridepublic int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {if (o1 instanceof String && o2 instanceof String) {String str_o1 = (String) o1;String str_o2 = (String) o2;int a = str_o1.length();int b = str_o2.length();int result = a == b ? str_o1.compareTo(str_o2) : a - b;return result;} else {return 0;}}}));// int frequency(Collection, Object):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数System.out.println("int frequency(Collection, Object):返回指定集合中指定元素的出现次数 ");System.out.println(Collections.frequency(arrayList, "Rose"));// void copy(List dest, List src):将src中的内容复制到dest中// 拷贝要注意 ,拷贝后的集合dest的元素个数要>=被拷贝集合arrayList// 一般情况在初始化dest指定大小和arrayList相同//ArrayList dest = new ArrayList(); // java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsExceptionArrayList dest = new ArrayList();for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {dest.add(i);}dest.add("Copy");dest.add("Paste");Collections.copy(dest, arrayList);System.out.println("dest集合元素:");System.out.println(dest);ArrayList arrayList1 = new ArrayList(10); // 指的是容量(达到后下次扩容成当前的1.5倍)System.out.println("arrayList1.size(): " + arrayList1.size());//boolean replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal):使用新值替换List对象的所有旧值System.out.println("boolean replaceAll(List list, Object oldVal, Object newVal):使用新值替换List对象的所有旧值 ");Collections.replaceAll(dest, "周润发", "金喜善"); // 如果有周润发就替换成金喜善System.out.println(dest);}
课后作业
课后作业1:

package com.HomeWork;import org.junit.Test;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;public class HomeWork01 {@Testpublic void HomeWork() {ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add(new News("新闻一:新冠确诊病例超过千万,数以万计印度教徒赶赴恒河"));arrayList.add(new News("新闻二:男子突然想起2个月前钓的鱼还在网兜"));System.out.println("----倒序遍历----");Collections.reverse(arrayList);for (Object o : arrayList) {// 先实例化对象News news = (News) o;if (news.getTitle().length() > 15) {System.out.println(news.getTitle().substring(0, 15) + "…………");} else {System.out.println(news.getTitle());}}}@Testpublic void HomeWork01_Teacher() {ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add(new News("新闻一:新冠确诊病例超过千万,数以万计印度教徒赶赴恒河"));arrayList.add(new News("新闻二:男子突然想起2个月前钓的鱼还在网兜"));System.out.println("----倒序遍历----");for (int i = arrayList.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {News news = (News) arrayList.get(i);System.out.println(substrTitle(news.getTitle()));}}public String substrTitle(String title) {if (null == title || "".equals(title)) {return "";}if (title.length() > 15) {return title.substring(0, 15) + "…………";} else {return title;}}
}class News {private String title;private String text;public String getTitle() {return title;}public void setTitle(String title) {this.title = title;}public String getText() {return text;}public void setText(String text) {this.text = text;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "News{" +"title='" + title + '\'' +'}';}public News(String title) {this.title = title;}
}
课后习题2

package com.HomeWork;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;public class HomeWork02 {@Testpublic void getHomeWork02() {List list = new ArrayList();Car car1 = new Car("宝马", 400000);Car car2 = new Car("宾利", 5000000);Car car3 = new Car("劳斯莱斯", 60000000);Car car4 = new Car("法拉利", 70000000);list.add(car1);list.add(car2);System.out.println(list);list.remove(car1);System.out.println(list);System.out.println(list.contains(car2));System.out.println(list.size());System.out.println(list.isEmpty());list.clear();System.out.println(list);List list2 = new ArrayList();list2.add(car1);list2.add(car2);list2.add(car3);list2.add(car4);list.addAll(list2);System.out.println("----list.addAll(list2)----");System.out.println(list);System.out.println(list2.containsAll(list));list2.removeAll(list);System.out.println(list2);System.out.println("list增强for循环");for (Object o : list) {System.out.println(o);}System.out.println("list迭代器");Iterator iterator = list.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(next);}}
}class Car {private String name;private double price;public Car(String name, double price) {this.name = name;this.price = price;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Car{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", price=" + price +'}';}
}
课后习题3

package com.HomeWork;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.*;public class HomeWork03 {@Testpublic void getHomeWork03() {Map map = new HashMap();map.put("1", new Worker("jack", 650));map.put("2", new Worker("tom", 1200));map.put("3", new Worker("smith", 2900));System.out.println("正常情况");Set set = map.keySet();for (Object o : set) {Worker worker = (Worker) map.get(o);System.out.println(worker);}// jack更改为2600元System.out.println("----更改工资和加薪后----");map.put("1", new Worker("jack", 2600));System.out.println(map);// 为所有员工加薪100元Set set1 = map.entrySet();Iterator iterator = set1.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) next;Worker worker = (Worker) entry.getValue();// 加薪worker.setSal(worker.getSal() + 100);//System.out.println(worker.getSal() + 100);System.out.println(worker);}System.out.println("----遍历工资----");// 把工资遍历出来Collection values = map.values();for (Object value : values) {Worker worker = (Worker) value;System.out.println(worker.getSal());}}
}class Worker {private String name;private double sal;public Worker(String name, double sal) {this.name = name;this.sal = sal;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return name + "————" + sal + "元";}public double getSal() {return sal;}public void setSal(double sal) {this.sal = sal;}
}
简答题
试分析HashSet和TreeSet分别是如何实现去重的
- HashSet的去重机制:hashCode() + equals(),底层先通过存入对象,进行运算得到一个hash值,通过hash值得到对应的索引,如果发现table索引所在的位置,没有数据,就直接存放,如果有数据,就进行equals比较[遍历比较],如果比较后不相同就加入,否则就不加入。
- TreeSet的去重机制:如果你传入了一个Comparator匿名对象,就使用实现的compare去重,如果方法返回0,就认为是相同的元素/数据,就不添加,如果你没有传入一个Comparator匿名对象,则以你添加的对象实现的Comparator接口的compareTo去重。
课后作业5:
package com.HomeWork;import org.junit.Test;import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.TreeSet;public class HomeWork05 {@Testpublic void getHomeWorker05() {TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();treeSet.add(new Person()); // java.lang.ClassCastException 报错// 错误原因:treeSet在add时候会执行/*** final int compare(Object var1, Object var2) {* return this.comparator == null ? ((Comparable)var1).compareTo(var2) : this.comparator.compare(var1, var2);* }** 会把加入的元素var1 转换成(Comparable) 对象,所以Person必须实现Comparable接口才行*/}
}class Person implements Comparable { // 实现之后再添加就不会报错了/***TreeSet的去重机制:如果你传入了一个Comparator匿名对象,就使用实现的compare去重,如果方法返回 0,就认为是相同的元素/数据,就不添加,如果你没有传入一个Comparator匿名对象,则以你添加的对象实现的Comparator接口的compareTo去重。* final int compare(Object var1, Object var2) {* return this.comparator == null ? ((Comparable)var1).compareTo(var2) : this.comparator.compare(var1, var2);* }* @param o* @return*/@Overridepublic int compareTo(Object o) {return 0;}
}
课后作业6
Vector和ArrayList比较
底层结构 版本 线程安全(同步)效率 扩容倍数
ArrayList 可变数组 1.2 线程不安全,效率高 无参第一次扩容至10,从第二次开始按照1.5倍扩容Vector 可变数组 1.0 线程安全,效率低 无参第一次扩容至10,从第二次开始按照2倍扩容
| 名称 | 底层结构 | 版本 | 线程安全(同步) | 效率 | 扩容倍数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayList | 可变数组 | 1.2 | 线程不安全 | 高 | 无参第一次扩容至10,从第二次开始按照1.5倍扩容 |
| Vector | 可变数组 | 1.0 | 线程安全 | 低 | 无参第一次扩容至10,从第二次开始按照2倍扩容 |
集合总结
最后,我把本章所有的集合整理了一下,整合了一个excel文件,需要的可以自行下载。当然,你也可以根据自己的理解整理,这里仅供参考
集合excel整理本章所有集合
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!