introduce to algorithm
introduce to algorithm
- 1710. 卡车上的最大单元数
- 1711. 大餐计数
- 1720. 解码异或后的数组
- 1721. 交换链表中的节点
- 1722. 执行交换操作后的最小汉明距离
- 1725. 可以形成最大正方形的矩形数目
- 1726. 同积元组
- 1727. 重新排列后的最大子矩阵
- 1732. 找到最高海拔
- 1733. 需要教语言的最少人数
- 1734. 解码异或后的排列
- 1736. 替换隐藏数字得到的最晚时间
- 1737. 满足三条件之一需改变的最少字符数
- 1738. 找出第 K 大的异或坐标值
- 1739. 放置盒子
- 5654. 盒子中小球的最大数量
- 5665. 从相邻元素对还原数组
- 生成一个适合你的列表
- 创建一个表格
- 设定内容居中、居左、居右
- SmartyPants
- 创建一个自定义列表
- 如何创建一个注脚
- 注释也是必不可少的
- KaTeX数学公式
- 新的甘特图功能,丰富你的文章
- UML 图表
- FLowchart流程图
- 导出与导入
- 导出
- 导入
1710. 卡车上的最大单元数
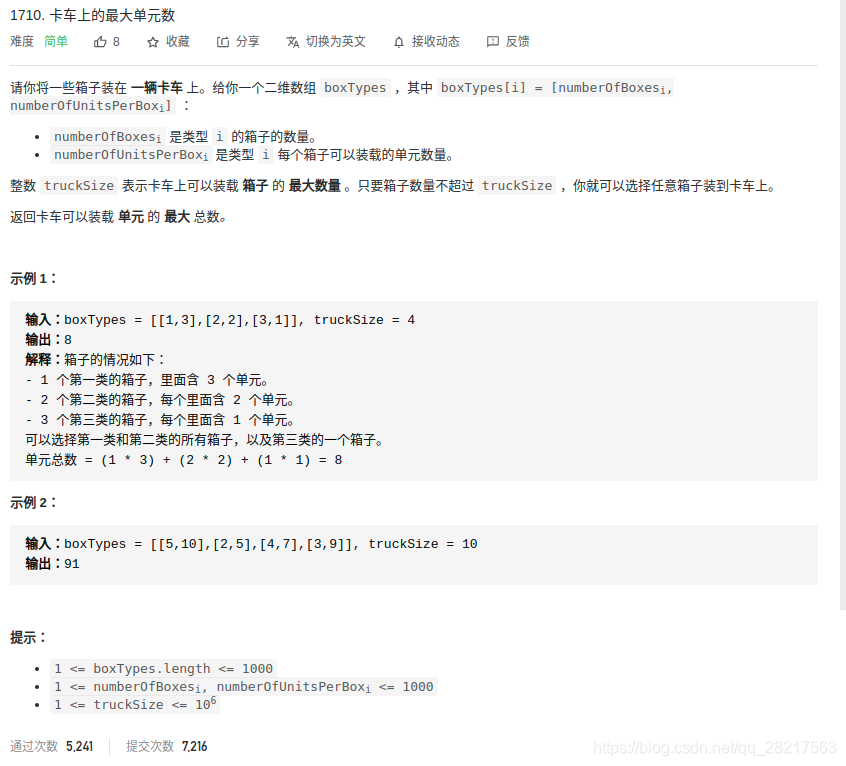
#define debug(args...) //printf(args)int compare11(const void *a, const void *b)
{int *elem1 = (int *)a;int *elem2 = (int *)b;return *(elem2 + 1) - *(elem1 + 1);
}int maximumUnits(int** boxTypes, int boxTypesSize, int* boxTypesColSize, int truckSize)
{int cur_boxsize = 0;int max_elem = 0;int tmp;int *box = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2 * boxTypesSize);for (int i = 0; i < boxTypesSize; ++i) {box[i << 1] = boxTypes[i][0];box[(i << 1) + 1] = boxTypes[i][1];}qsort(box, boxTypesSize, sizeof(int) << 1, compare11);for (int i = 0; i < boxTypesSize; ++i) {debug("%d %d\n", box[i << 1], box[(i << 1) + 1]);}for (int i = 0; i < boxTypesSize; ++i) {tmp = box[i << 1];for (int j = 0; j < tmp; ++j) {if (cur_boxsize >= truckSize)goto out;debug("max_elem = %d box[%d] = %d\n", max_elem, i, box[(i << 1) + 1]);max_elem += box[(i << 1) + 1];cur_boxsize++;}}out:return max_elem;
}1711. 大餐计数

class Solution {
private:const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;public:int countPairs(vector<int>& deliciousness) {int sum = 0;unordered_map<int, int> map;for (int i : deliciousness) {for (int j = 0; j < 22; ++j) {int ans = pow(2, j) - i;if (ans < 0)continue;if (map.count(ans)) {sum += map[ans];sum %= MOD;}}map[i]++;}return sum;}
};
1720. 解码异或后的数组
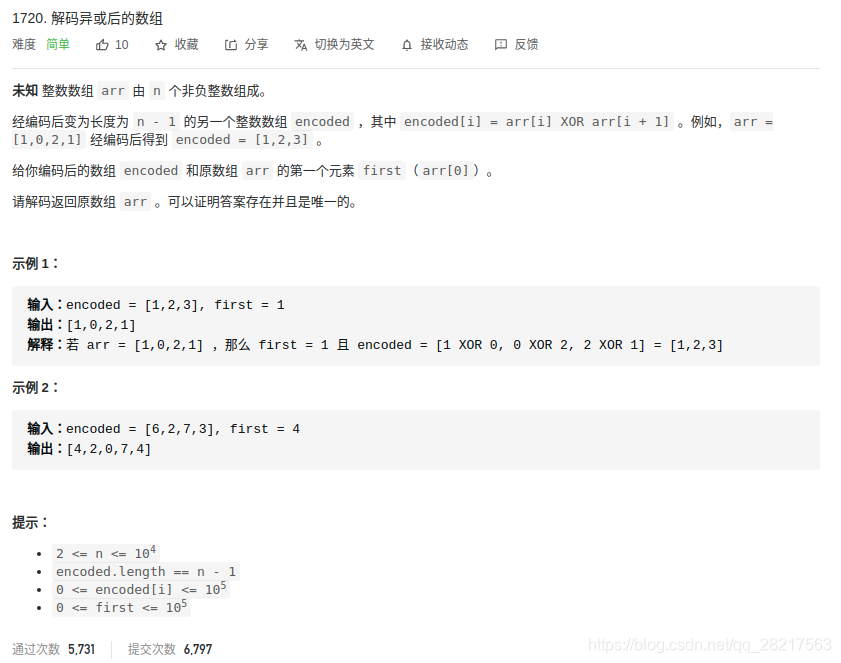
/*** Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().*/
int* decode(int* encoded, int encodedSize, int first, int* returnSize)
{int *arr = malloc(sizeof(int) * (encodedSize + 1));if (!arr)return NULL;*returnSize = encodedSize + 1;arr[0] = first;for (int i = 1; i < *returnSize; i++) {arr[i] = arr[i - 1] ^ encoded[i - 1];}return arr;
}
1721. 交换链表中的节点
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/struct ListNode* swapNodes(struct ListNode* head, int k)
{int node_cnt = 0;struct ListNode *node = head;int val_l, val_r, k_r;int i;while (node) {node_cnt++;if (node_cnt == k)val_l = node->val;node = node->next;}k_r = node_cnt - k + 1;i = 0;node = head;while (node) {i++;if (i == k_r) {val_r = node->val;node->val = val_l;break;}node = node->next;}i = 0;node = head;while (node) {i++;if (i == k) {node->val = val_r;break;}node = node->next;}return head;
}
1722. 执行交换操作后的最小汉明距离
- using bfs to do Add Collect
class Solution {
public:int minimumHammingDistance(vector<int>& source, vector<int>& target, vector<vector<int>>& allowedSwaps) {int size = source.size();int same = 0;unordered_map<int, vector<int>> graph;for (auto e : allowedSwaps) {graph[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);graph[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);}vector<int> vis(size, 0);for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {if (vis[i])continue;vector<int> s, t;queue<int> q;q.push(i);vis[i] = 1;while (not q.empty()) {int c = q.front();q.pop();s.push_back(source[c]);t.push_back(target[c]);for (auto u : graph[c]) {if (vis[u])continue;q.push(u);vis[u] = 1;}}sort(s.begin(), s.end());sort(t.begin(), t.end());for (int si = 0, ti = 0; si < s.size() && ti < t.size(); ) {if (s[si] > t[ti]) {ti++;} else if (s[si] < t[ti]) {si++;} else {si++;ti++;same++;}} }return size - same;}
};
* Add Collect
```cpp
/* version 1 */
class Solution {
public:int minimumHammingDistance(vector<int>& source, vector<int>& target, vector<vector<int>>& allowedSwaps) {int n = source.size();unordered_map<int, vector<int>> G;for(auto e : allowedSwaps){G[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);G[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);}vector<int> vis(n);int ans = n;for(int i = 0; i < n; i += 1) if(not vis[i]){queue<int> q;vector<int> A, B;q.push(i);vis[i] = 1;while(not q.empty()){int u = q.front();q.pop();A.push_back(source[u]);B.push_back(target[u]);for(int v : G[u]) if(not vis[v]){vis[v] = 1;q.push(v);}}sort(A.begin(), A.end());sort(B.begin(), B.end());for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < A.size() and j < B.size();){if(A[i] == B[j]){ans -= 1;i += 1;j += 1;}else if(A[i] < B[j]) i += 1;else j += 1;}}return ans;}
};
/* version 2 */
class Solution {
private:int getf(vector<int> &f, int x){while (1) {if (f[x] == x)return x;x = f[x];}}void init(vector<int> &f, vector<int> &rack){int size = f.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {f[i] = i;rack[i] = 1;}}void merge(vector<int> &f, vector<int> &rack, int a, int b){int x = getf(f, a);int y = getf(f, b);if (rack[x] <= rack[y])f[x] = y;elsef[y] = x;if (rack[x] == rack[y] && x != y)rack[y]++;}public:int minimumHammingDistance(vector<int>& source, vector<int>& target, vector<vector<int>>& allowedSwaps)/* {int size = source.size();vector fa(size);vector rack(size);int same = 0;init(fa, rack);for (auto a : allowedSwaps)merge(fa, rack, a[0], a[1]);unordered_map> map;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {int f = getf(fa, i);map[f].push_back(i);}for (auto [root, group] : map) {unordered_map s, t;for (auto i : group) {s[source[i]]++;t[target[i]]++;}for (auto [index, value] : t) {same += min(value, s[index]);}}return size - same;}*/ {int size = source.size();vector<int> fa(size);vector<int> rack(size);int ans = 0;init(fa, rack);for (auto a : allowedSwaps)merge(fa, rack, a[0], a[1]);unordered_map<int, unordered_multiset<int>> s_map;unordered_map<int, unordered_multiset<int>> t_map;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {int f = getf(fa, i);s_map[f].insert(source[i]);t_map[f].insert(target[i]);}for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {if (s_map.find(i) == s_map.end())continue;for (int a : s_map[i]) {if (t_map[i].find(a) == t_map[i].end())ans++;elset_map[i].erase(t_map[i].find(a));}}return ans;}
};
1725. 可以形成最大正方形的矩形数目
class Solution {
public:int countGoodRectangles(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles) {unordered_map<int, int> map;int max_index = 0;int min_side;for (auto &i : rectangles) {min_side = min(i[0], i[1]);map[min_side]++;max_index = max(max_index, min_side);}return map[max_index];}
};1726. 同积元组
class Solution {
public:int tupleSameProduct(vector<int>& nums) {int size = nums.size();unordered_map <int, int> map;int num = 0;for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) {map[nums[i] * nums[j]]++;}}for (auto a : map) {num += a.second * (a.second - 1);}return num << 2;}
};
class Solution {
public:int tupleSameProduct(vector<int>& nums) {unordered_map<int, int> count;int n = nums.size();int result = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {int& val = count[nums[i] * nums[j]];result += val;++val;}}return result * 8;}
};
1727. 重新排列后的最大子矩阵
class Solution {
public:int largestSubmatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {int row_size = matrix.size();int column_size = matrix[0].size();vector<int> count(column_size, 0);int ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < row_size; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < column_size; ++j) {count[j] = matrix[i][j] ? count[j] + 1 : 0;}vector<int> temp = count;sort(temp.rbegin(), temp.rend());for (int j = 0; j < column_size; ++j) {ans = max(ans, temp[j] * (j + 1));}}return ans;}
};class Solution {
public:int largestSubmatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {int row_size = matrix.size();int column_size = matrix[0].size();vector<vector<int>> count = matrix;int ans = 0;for (int i = 1; i < row_size; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < column_size; ++j) {if (matrix[i][j])count[i][j] = count[i - 1][j] + 1;}}for (int i = 0; i < row_size; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < column_size; ++j) {cout << count[i][j];}}cout << endl;for (int i = 0; i < row_size; ++i) {sort(count[i].rbegin(), count[i].rend());for (int j = 0; j < column_size; ++j) {ans = max(ans, count[i][j] * (j + 1));}}return ans;}
};
1732. 找到最高海拔
class Solution {
public:int largestAltitude(vector<int>& gain) {int highest = 0;int cur = 0;for (auto i : gain) {cur += i;highest = max(cur, highest);}return highest;}
};
1733. 需要教语言的最少人数
class Solution {
private:bool is_connect(vector<vector<int>>& a, int e0, int e1){for (auto i : a[e0 - 1]) {for (auto j : a[e1 - 1]) {if (i == j)return true;}}return false;}public:int minimumTeachings(int n, vector<vector<int>>& a, vector<vector<int>>& e) {unordered_set<int> nc;unordered_map<int, int> common_language;int most = 0;for (auto &i : e) {if (!is_connect(a, i[0], i[1])) {nc.insert(i[0] - 1);nc.insert(i[1] - 1);}}for (auto &i : nc) {for (auto &j : a[i])common_language[j]++;}for (auto &i : common_language) {most = max(most, i.second);}return nc.size() - most;}
};class Solution {
public:int minimumTeachings(int n, vector<vector<int>>& languages, vector<vector<int>>& friendships) {int ans = languages.size();unordered_map<int, unordered_set<int>> map;vector<vector<int>> find(ans, vector<int>(ans));for (int i = 0; i < ans; ++i) {for (int &j : languages[i])map[i].insert(j);}for (auto &e : friendships) {for (auto &i : languages[e[0] - 1]) {if (map[e[1] - 1].count(i)) {find[e[0] - 1][e[1] - 1] = 1;break;}}//cout << find[e[0] - 1][e[1] - 1] << endl;}for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {unordered_set<int> set1;for (auto &e : friendships) {if (find[e[0] - 1][e[1] - 1])continue;if (map[e[0] - 1].count(i) == 0)set1.insert(e[0] - 1);if (map[e[1] - 1].count(i) == 0)set1.insert(e[1] - 1);}ans = min(ans, (int)set1.size());// cout << ans <}return ans;}
};
1734. 解码异或后的排列
class Solution {
public:vector<int> decode(vector<int>& encoded) {int perm_size = encoded.size() + 1;int all = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= perm_size; ++i)all ^= i;for (int i = 0; i < perm_size - 2; i += 2)all ^= encoded[i];encoded.push_back(all);for (int i = perm_size - 2; i >= 0; --i)encoded[i] = encoded[i + 1] ^ encoded[i];return encoded;}
};
1736. 替换隐藏数字得到的最晚时间
class Solution {
public:string maximumTime(string time) {if (time[3] == '?')time[3] = '5';if (time[4] == '?')time[4] = '9';if (time[0] == '?') {if (time[1] == '?') {time[0] = '2';time[1] = '3';} else if (time[1] > '3' && time[1] <= '9')time[0] = '1';elsetime[0] = '2';} else {if (time[1] == '?') {if (time[0] < '2')time[1] = '9';elsetime[1] = '3';}}return time;}
};
1737. 满足三条件之一需改变的最少字符数
class Solution {
public:int minCharacters(string a, string b) {vector<int> count_a(26, 0);vector<int> count_b(26, 0);int a_sum = 0;int b_sum = 0;int asize = a.size();int bsize = b.size();int ans = asize + bsize;for (char i : a)count_a[i - 'a']++;for (char i : b)count_b[i - 'a']++;for (int i = 0; i < 25; ++i) {a_sum += count_a[i];b_sum += count_b[i];ans = min(min(ans, asize + bsize - count_a[i] - count_b[i]), min(asize - a_sum + b_sum, bsize - b_sum + a_sum));}ans = min(ans, asize + bsize - count_a[25] - count_b[25]);return ans;}
};
1738. 找出第 K 大的异或坐标值
class Solution {
public:int kthLargestValue(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int k) {int row = matrix.size();int column = matrix[0].size();vector<int> arr;for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j < column; ++j) {int c = matrix[i][j];if (j > 0)c ^= matrix[i][j - 1];if (i > 0)c ^= matrix[i - 1][j];if (i > 0 && j > 0)c ^= matrix[i - 1][j - 1];matrix[i][j] = c;arr.push_back(c);}}k = arr.size() - k;nth_element(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + k, arr.end());return arr[k];}
};
1739. 放置盒子
class Solution {
public:int minimumBoxes(int n) {int ans = 0;int b = 0;for (int i = 1; ans < n; ++i) {for (int j = 1; j < i && ans < n; ++j) {b++;ans += j;}}return b;}
};class Solution1 {
public:int minimumBoxes(int n) {//使用体积公式确定能够涵盖n个方块的完美三角锥边长//体积公式:V=a(a+1)(a+2)/6;long edge=floor(pow(6.0*n,1.0/3))+1;//由于是对三次方程近似求解,所以可能略大一点,往低试探走两步if((edge-1)*edge*(edge+1)>=6.0*n)edge--;if((edge-1)*edge*(edge+1)>=6.0*n)edge--;//求得edge即为边长//考虑到完美三角锥的方块个数all>=n个,考虑拆除若干方块long all=edge*(edge+1)*(edge+2)/6;long bottom=edge*(edge+1)/2;//考虑到稳定性,所以只能从上往下拆除//经过观察,发现第一次需要拆edge块,才会让底面积减一//下一次需要拆edge-1块,才会让底面积减一//每次让底面积减一所需的拆除块数为edge,edge-1,edge-2,...//设拆除last块后发现剩余块数不够n//则从edge到last共拆除(edge+last)*(edge-last+1)/2//last^2 < edge^2+edge+last-2*(all-n)//last约等于(edge*edge+edge-2*(all-n))^0.5long last=pow(edge*edge+edge-2*(all-n),0.5);//估算可能使预估值偏小,需要往大试探走两步if(all-(edge+last)*(edge-last+1)/2<n)last++;if(all-(edge+last)*(edge-last+1)/2<n)last++;return bottom-(edge-last+1);}
};
5654. 盒子中小球的最大数量
class Solution {
private:inline int calc_box(int a){int ans = 0;while (a) {ans += a % 10;a = a / 10;}return ans;}
public:int countBalls(int l, int h) {vector<int> box(100);for (int i = l; i <= h; ++i)box[calc_box(i)]++;return *max_element(box.begin(), box.end());}
};class Solution {
private:int calc_box(int a){int ans = 0;while (a) {ans += a % 10;a = a / 10;}return ans;}
public:int countBalls(int l, int h) {unordered_map<int, int> box;int ans = 0;for (int i = l; i <= h; ++i)box[calc_box(i)]++;for (auto b : box)ans = max(b.second, ans);return ans;}
};
5665. 从相邻元素对还原数组
class Solution {
public:vector<int> restoreArray(vector<vector<int>>& adjacentPairs) {vector<int> ans;int size = adjacentPairs.size() + 1;unordered_map<int, vector<int>> h;int rear, front;for (auto &e : adjacentPairs) {h[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);h[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);}for (auto &e : h) {if (e.second.size() == 1) {rear = e.first;front = e.second[0];}}ans.push_back(rear);ans.push_back(front);while (ans.size() < size) {auto &it = h[front];for (auto i : it) {if (i != rear) {ans.push_back(i);rear = front;front = i;break;}}}return ans;}
};class Solution {
private:
#define print_v(v, h) /*\for (auto &i : v) \cout << i << " "; \\cout << endl; \\for (auto &e : h) { \cout << e.first << " "; \for (auto &i : e.second) \cout << i << " "; \cout << endl; \}
*/
public:vector<int> restoreArray(vector<vector<int>>& adjacentPairs) {vector<int> ans;int size = adjacentPairs.size() + 1;unordered_map<int, vector<int>> h;unordered_set<int> use;int front, rear;int tmp1;for (auto &e : adjacentPairs) {h[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);h[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);}for (auto &i : h) {if (i.second.size() == 1) {rear = i.first;front = i.second[0];}}use.insert(rear);ans.push_back(rear);ans.push_back(front);while (ans.size() < size) {//if (h[front].size() == 1 && use.count(h[front][0])) {} else {print_v(ans, h);//cout << "front: " << front << " " << h[front].size() << endl;auto &tmp = h[front];//cout << "use: " << tmp[0] << use.count(tmp[0]) << " " << tmp.size() << use.count(tmp[tmp.size() - 1]) << endl;if (not use.count(tmp[0])) {ans.push_back(tmp[0]);use.insert(front);front = tmp[0];} else if (tmp.size() > 1 && not use.count(tmp[1])) {ans.push_back(tmp[1]);use.insert(front);front = tmp[1];}}}return ans;}
};
生成一个适合你的列表
- 项目
- 项目
- 项目
- 项目
- 项目1
- 项目2
- 项目3
- 计划任务
- 完成任务
创建一个表格
一个简单的表格是这么创建的:
| 项目 | Value |
|---|---|
| 电脑 | $1600 |
| 手机 | $12 |
| 导管 | $1 |
设定内容居中、居左、居右
使用:---------:居中
使用:----------居左
使用----------:居右
| 第一列 | 第二列 | 第三列 |
|---|---|---|
| 第一列文本居中 | 第二列文本居右 | 第三列文本居左 |
SmartyPants
SmartyPants将ASCII标点字符转换为“智能”印刷标点HTML实体。例如:
| TYPE | ASCII | HTML |
|---|---|---|
| Single backticks | 'Isn't this fun?' | ‘Isn’t this fun?’ |
| Quotes | "Isn't this fun?" | “Isn’t this fun?” |
| Dashes | -- is en-dash, --- is em-dash | – is en-dash, — is em-dash |
创建一个自定义列表
- Markdown
- Text-to- HTML conversion tool Authors
- John
- Luke
如何创建一个注脚
一个具有注脚的文本。1
注释也是必不可少的
Markdown将文本转换为 HTML。
KaTeX数学公式
您可以使用渲染LaTeX数学表达式 KaTeX:
Gamma公式展示 Γ ( n ) = ( n − 1 ) ! ∀ n ∈ N \Gamma(n) = (n-1)!\quad\forall n\in\mathbb N Γ(n)=(n−1)!∀n∈N 是通过欧拉积分
Γ ( z ) = ∫ 0 ∞ t z − 1 e − t d t . \Gamma(z) = \int_0^\infty t^{z-1}e^{-t}dt\,. Γ(z)=∫0∞tz−1e−tdt.
你可以找到更多关于的信息 LaTeX 数学表达式here.
新的甘特图功能,丰富你的文章
- 关于 甘特图 语法,参考 这儿,
UML 图表
可以使用UML图表进行渲染。 Mermaid. 例如下面产生的一个序列图:
这将产生一个流程图。:
- 关于 Mermaid 语法,参考 这儿,
FLowchart流程图
我们依旧会支持flowchart的流程图:
- 关于 Flowchart流程图 语法,参考 这儿.
导出与导入
导出
如果你想尝试使用此编辑器, 你可以在此篇文章任意编辑。当你完成了一篇文章的写作, 在上方工具栏找到 文章导出 ,生成一个.md文件或者.html文件进行本地保存。
导入
如果你想加载一篇你写过的.md文件,在上方工具栏可以选择导入功能进行对应扩展名的文件导入,
继续你的创作。
注脚的解释 ↩︎
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!