client-go源码
注 本文源码基于分支release-1.19
client
restclient
RESTClient是最基础的,相当于的底层基础结构,封装底层http rest请求。可以直接通过 是RESTClient提供的RESTful方法如Get(),Put(),Post(),Delete()进行交互,同时支持Json 和 protobuf。支持所有原生资源和crd,为了更为优雅的处理,需要进一步封装,通过Clientset封装RESTClient,然后再对外提供接口和服务。
源码示例
type RESTClient struct {// base is the root URL for all invocations of the clientbase *url.URL// versionedAPIPath is a path segment connecting the base URL to the resource rootversionedAPIPath string// content describes how a RESTClient encodes and decodes responses.content ClientContentConfig// creates BackoffManager that is passed to requests.createBackoffMgr func() BackoffManager// rateLimiter is shared among all requests created by this client unless specifically// overridden.rateLimiter flowcontrol.RateLimiter// warningHandler is shared among all requests created by this client.// If not set, defaultWarningHandler is used.warningHandler WarningHandler// Set specific behavior of the client. If not set http.DefaultClient will be used.Client *http.Client
}
func (c *RESTClient) Verb(verb string) *Request {return NewRequest(c).Verb(verb)
}// Post begins a POST request. Short for c.Verb("POST").
func (c *RESTClient) Post() *Request {return c.Verb("POST")
}// Put begins a PUT request. Short for c.Verb("PUT").
func (c *RESTClient) Put() *Request {return c.Verb("PUT")
}// Patch begins a PATCH request. Short for c.Verb("Patch").
func (c *RESTClient) Patch(pt types.PatchType) *Request {return c.Verb("PATCH").SetHeader("Content-Type", string(pt))
}// Get begins a GET request. Short for c.Verb("GET").
func (c *RESTClient) Get() *Request {return c.Verb("GET")
}// Delete begins a DELETE request. Short for c.Verb("DELETE").
func (c *RESTClient) Delete() *Request {return c.Verb("DELETE")
}
clientset
Clientset是调用Kubernetes资源对象最常用的client,可以操作所有的资源对象,包含RESTClient。需要指定Group、指定Version,然后根据Resource获取,每种内置的gvk都有对应client-go中一个informer、clientset、list,在staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/路径中。自定义的资源的clientset需要通过codegen自动生成。最优雅的客户端方式。
使用示例:
func main() {var kubeconfig *stringif home := homedir.HomeDir(); home != "" {kubeconfig = flag.String("kubeconfig", filepath.Join(home, ".kube", "config"), "(optional) absolute path to the kubeconfig file")} else {kubeconfig = flag.String("kubeconfig", "", "absolute path to the kubeconfig file")}flag.Parse()config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", *kubeconfig)if err != nil {panic(err)}clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)if err != nil {panic(err)}deploymentsClient := clientset.AppsV1().Deployments(apiv1.NamespaceDefault)deployment := &appsv1.Deployment{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "demo-deployment",},Spec: appsv1.DeploymentSpec{Replicas: int32Ptr(2),Selector: &metav1.LabelSelector{MatchLabels: map[string]string{"app": "demo",},},Template: apiv1.PodTemplateSpec{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Labels: map[string]string{"app": "demo",},},Spec: apiv1.PodSpec{Containers: []apiv1.Container{{Name: "web",Image: "nginx:1.12",Ports: []apiv1.ContainerPort{{Name: "http",Protocol: apiv1.ProtocolTCP,ContainerPort: 80,},},},},},},},}// Create Deploymentfmt.Println("Creating deployment...")result, err := deploymentsClient.Create(context.TODO(), deployment, metav1.CreateOptions{})if err != nil {panic(err)}fmt.Printf("Created deployment %q.\n", result.GetObjectMeta().GetName())// Update Deploymentprompt()fmt.Println("Updating deployment...")retryErr := retry.RetryOnConflict(retry.DefaultRetry, func() error {// Retrieve the latest version of Deployment before attempting update// RetryOnConflict uses exponential backoff to avoid exhausting the apiserverresult, getErr := deploymentsClient.Get(context.TODO(), "demo-deployment", metav1.GetOptions{})if getErr != nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("Failed to get latest version of Deployment: %v", getErr))}result.Spec.Replicas = int32Ptr(1) // reduce replica countresult.Spec.Template.Spec.Containers[0].Image = "nginx:1.13" // change nginx version_, updateErr := deploymentsClient.Update(context.TODO(), result, metav1.UpdateOptions{})return updateErr})if retryErr != nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("Update failed: %v", retryErr))}fmt.Println("Updated deployment...")// List Deploymentsprompt()fmt.Printf("Listing deployments in namespace %q:\n", apiv1.NamespaceDefault)list, err := deploymentsClient.List(context.TODO(), metav1.ListOptions{})if err != nil {panic(err)}for _, d := range list.Items {fmt.Printf(" * %s (%d replicas)\n", d.Name, *d.Spec.Replicas)}// Delete Deploymentprompt()fmt.Println("Deleting deployment...")deletePolicy := metav1.DeletePropagationForegroundif err := deploymentsClient.Delete(context.TODO(), "demo-deployment", metav1.DeleteOptions{PropagationPolicy: &deletePolicy,}); err != nil {panic(err)}fmt.Println("Deleted deployment.")
}func prompt() {fmt.Printf("-> Press Return key to continue.")scanner := bufio.NewScanner(os.Stdin)for scanner.Scan() {break}if err := scanner.Err(); err != nil {panic(err)}fmt.Println()
}func int32Ptr(i int32) *int32 { return &i }
dynamicclient
Dynamic client 是一种动态的 客户端,它能处理 kubernetes 所有的资源包括内置资源和crd资源。不同于 clientset,dynamic client 返回的对象是一个 map[string]interface{}数据结构,如果一个 controller 中需要控制所有的 API,可以使用dynamic client,目前它在 garbage collector 和 namespace controller中被使用。只支持JSON。
使用示例:
func main() {var kubeconfig *stringif home := homedir.HomeDir(); home != "" {kubeconfig = flag.String("kubeconfig", filepath.Join(home, ".kube", "config"), "(optional) absolute path to the kubeconfig file")} else {kubeconfig = flag.String("kubeconfig", "", "absolute path to the kubeconfig file")}flag.Parse()namespace := "default"config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", *kubeconfig)if err != nil {panic(err)}client, err := dynamic.NewForConfig(config)if err != nil {panic(err)}deploymentRes := schema.GroupVersionResource{Group: "apps", Version: "v1", Resource: "deployments"}deployment := &unstructured.Unstructured{Object: map[string]interface{}{"apiVersion": "apps/v1","kind": "Deployment","metadata": map[string]interface{}{"name": "demo-deployment",},"spec": map[string]interface{}{"replicas": 2,"selector": map[string]interface{}{"matchLabels": map[string]interface{}{"app": "demo",},},"template": map[string]interface{}{"metadata": map[string]interface{}{"labels": map[string]interface{}{"app": "demo",},},"spec": map[string]interface{}{"containers": []map[string]interface{}{{"name": "web","image": "nginx:1.12","ports": []map[string]interface{}{{"name": "http","protocol": "TCP","containerPort": 80,},},},},},},},},}// Create Deploymentfmt.Println("Creating deployment...")result, err := client.Resource(deploymentRes).Namespace(namespace).Create(context.TODO(), deployment, metav1.CreateOptions{})if err != nil {panic(err)}fmt.Printf("Created deployment %q.\n", result.GetName())// Update Deploymentprompt()fmt.Println("Updating deployment...")retryErr := retry.RetryOnConflict(retry.DefaultRetry, func() error {// Retrieve the latest version of Deployment before attempting update// RetryOnConflict uses exponential backoff to avoid exhausting the apiserverresult, getErr := client.Resource(deploymentRes).Namespace(namespace).Get(context.TODO(), "demo-deployment", metav1.GetOptions{})if getErr != nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("failed to get latest version of Deployment: %v", getErr))}// update replicas to 1if err := unstructured.SetNestedField(result.Object, int64(1), "spec", "replicas"); err != nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("failed to set replica value: %v", err))}// extract spec containerscontainers, found, err := unstructured.NestedSlice(result.Object, "spec", "template", "spec", "containers")if err != nil || !found || containers == nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("deployment containers not found or error in spec: %v", err))}// update container[0] imageif err := unstructured.SetNestedField(containers[0].(map[string]interface{}), "nginx:1.13", "image"); err != nil {panic(err)}if err := unstructured.SetNestedField(result.Object, containers, "spec", "template", "spec", "containers"); err != nil {panic(err)}_, updateErr := client.Resource(deploymentRes).Namespace(namespace).Update(context.TODO(), result, metav1.UpdateOptions{})return updateErr})if retryErr != nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("update failed: %v", retryErr))}fmt.Println("Updated deployment...")// List Deploymentsprompt()fmt.Printf("Listing deployments in namespace %q:\n", apiv1.NamespaceDefault)list, err := client.Resource(deploymentRes).Namespace(namespace).List(context.TODO(), metav1.ListOptions{})if err != nil {panic(err)}for _, d := range list.Items {replicas, found, err := unstructured.NestedInt64(d.Object, "spec", "replicas")if err != nil || !found {fmt.Printf("Replicas not found for deployment %s: error=%s", d.GetName(), err)continue}fmt.Printf(" * %s (%d replicas)\n", d.GetName(), replicas)}// Delete Deploymentprompt()fmt.Println("Deleting deployment...")deletePolicy := metav1.DeletePropagationForegrounddeleteOptions := metav1.DeleteOptions{PropagationPolicy: &deletePolicy,}if err := client.Resource(deploymentRes).Namespace(namespace).Delete(context.TODO(), "demo-deployment", deleteOptions); err != nil {panic(err)}fmt.Println("Deleted deployment.")
}func prompt() {fmt.Printf("-> Press Return key to continue.")scanner := bufio.NewScanner(os.Stdin)for scanner.Scan() {break}if err := scanner.Err(); err != nil {panic(err)}fmt.Println()
}
discoveryclient
DiscoveryClient是发现客户端,主要用于发现Kubernetes API Server所支持的资源组、资源版本、资源信息gvk信息。除此之外,还可以将这些信息存储到本地磁盘,用户本地缓存cache memory,以减轻对Kubernetes API Server访问的压力。kubectl的api-versions和api-resources命令查看支持的api资源信息的输出是通过DiscoversyClient实现的。
源码位置
源码
目录
-
deprecated 废弃
-
discovery:gvk资源的客户端
-
dynamic:动态客户端,支持任何资源类型 map[string]interface{}
-
informers:内置 各种api资源的Informer接口
-
kubernetes: group下每种资源不同api资源的 clientset客户端
-
listers:每种资源的lister,在上述informers中使用
-
metadata
-
pkg
-
plugin
-
rest:最底层的restclient 封装http请求
-
restmapper
-
scale
-
tools:主要包括cache等。。。见下
-
transport
-
util:包括自定义控制器用的各种队列。。。见下
rest
-
fake
-
watch:
-
client.go:拼装restclient结构
-
config.go:配置包括:http请求、gv、tls等
-
plugin.go
-
request.go:封装http rest请求 restclient的底层调用
-
transport.go
-
url_utils.go
-
urlbackoff.go
-
warnings.go:警告 放到http header Warning
restclient的底层核心实现request.go
// POST PUT DELETE ...
func (r *Request) request(ctx context.Context, fn func(*http.Request, *http.Response)) error {//Metrics for total request latencystart := time.Now()defer func() {metrics.RequestLatency.Observe(r.verb, r.finalURLTemplate(), time.Since(start))}()if r.err != nil {klog.V(4).Infof("Error in request: %v", r.err)return r.err}if err := r.requestPreflightCheck(); err != nil {return err}client := r.c.Clientif client == nil {client = http.DefaultClient}// Throttle the first try before setting up the timeout configured on the// client. We don't want a throttled client to return timeouts to callers// before it makes a single request.if err := r.tryThrottle(ctx); err != nil {return err}if r.timeout > 0 {var cancel context.CancelFuncctx, cancel = context.WithTimeout(ctx, r.timeout)defer cancel()}// Right now we make about ten retry attempts if we get a Retry-After response.retries := 0for {url := r.URL().String()req, err := http.NewRequest(r.verb, url, r.body)if err != nil {return err}req = req.WithContext(ctx)req.Header = r.headersr.backoff.Sleep(r.backoff.CalculateBackoff(r.URL()))if retries > 0 {// We are retrying the request that we already send to apiserver// at least once before.// This request should also be throttled with the client-internal rate limiter.if err := r.tryThrottle(ctx); err != nil {return err}}resp, err := client.Do(req)updateURLMetrics(r, resp, err)if err != nil {r.backoff.UpdateBackoff(r.URL(), err, 0)} else {r.backoff.UpdateBackoff(r.URL(), err, resp.StatusCode)}if err != nil {// "Connection reset by peer" or "apiserver is shutting down" are usually a transient errors.// Thus in case of "GET" operations, we simply retry it.// We are not automatically retrying "write" operations, as// they are not idempotent.if r.verb != "GET" {return err}// For connection errors and apiserver shutdown errors retry.if net.IsConnectionReset(err) || net.IsProbableEOF(err) {// For the purpose of retry, we set the artificial "retry-after" response.// TODO: Should we clean the original response if it exists?resp = &http.Response{StatusCode: http.StatusInternalServerError,Header: http.Header{"Retry-After": []string{"1"}},Body: ioutil.NopCloser(bytes.NewReader([]byte{})),}} else {return err}}done := func() bool {// Ensure the response body is fully read and closed// before we reconnect, so that we reuse the same TCP// connection.defer func() {const maxBodySlurpSize = 2 << 10if resp.ContentLength <= maxBodySlurpSize {io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, &io.LimitedReader{R: resp.Body, N: maxBodySlurpSize})}resp.Body.Close()}()retries++if seconds, wait := checkWait(resp); wait && retries <= r.maxRetries {if seeker, ok := r.body.(io.Seeker); ok && r.body != nil {_, err := seeker.Seek(0, 0)if err != nil {klog.V(4).Infof("Could not retry request, can't Seek() back to beginning of body for %T", r.body)fn(req, resp)return true}}klog.V(4).Infof("Got a Retry-After %ds response for attempt %d to %v", seconds, retries, url)r.backoff.Sleep(time.Duration(seconds) * time.Second)return false}fn(req, resp)return true}()if done {return nil}}
}// watch
func (r *Request) Watch(ctx context.Context) (watch.Interface, error) {// We specifically don't want to rate limit watches, so we// don't use r.rateLimiter here.if r.err != nil {return nil, r.err}url := r.URL().String()req, err := http.NewRequest(r.verb, url, r.body)if err != nil {return nil, err}req = req.WithContext(ctx)req.Header = r.headersclient := r.c.Clientif client == nil {client = http.DefaultClient}r.backoff.Sleep(r.backoff.CalculateBackoff(r.URL()))resp, err := client.Do(req)updateURLMetrics(r, resp, err)if r.c.base != nil {if err != nil {r.backoff.UpdateBackoff(r.c.base, err, 0)} else {r.backoff.UpdateBackoff(r.c.base, err, resp.StatusCode)}}if err != nil {// The watch stream mechanism handles many common partial data errors, so closed// connections can be retried in many cases.if net.IsProbableEOF(err) || net.IsTimeout(err) {return watch.NewEmptyWatch(), nil}return nil, err}if resp.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {defer resp.Body.Close()if result := r.transformResponse(resp, req); result.err != nil {return nil, result.err}return nil, fmt.Errorf("for request %s, got status: %v", url, resp.StatusCode)}contentType := resp.Header.Get("Content-Type")mediaType, params, err := mime.ParseMediaType(contentType)if err != nil {klog.V(4).Infof("Unexpected content type from the server: %q: %v", contentType, err)}objectDecoder, streamingSerializer, framer, err := r.c.content.Negotiator.StreamDecoder(mediaType, params)if err != nil {return nil, err}handleWarnings(resp.Header, r.warningHandler)frameReader := framer.NewFrameReader(resp.Body)watchEventDecoder := streaming.NewDecoder(frameReader, streamingSerializer)return watch.NewStreamWatcher(restclientwatch.NewDecoder(watchEventDecoder, objectDecoder),// use 500 to indicate that the cause of the error is unknown - other error codes// are more specific to HTTP interactions, and set a reasonerrors.NewClientErrorReporter(http.StatusInternalServerError, r.verb, "ClientWatchDecoding"),), nil
}
tools
-
auth
-
cache:informer的实现 见下
-
clientcmd
-
events
-
leaderelection
-
metrics:指标 度量告警性能?
-
pager:分页器
-
portforward
-
record
-
reference
-
remotecommand
-
watch
util
-
cert
-
certificate
-
connrotation
-
exec
-
flowcontrol
-
homedir
-
jsonpath
-
keyutil
-
retry
-
testing
-
workqueue 各种队列的实现 见下
workqueue
概念
client-go 中实现了多种队列,包括通用队列、延时队列、限速队列 。
-
default_rate_limiters.go
-
default_rate_limiters_test.go
-
delaying_queue.go
-
delaying_queue_test.go
-
doc.go
-
main_test.go
-
metrics.go
-
metrics_test.go
-
parallelizer.go
-
parallelizer_test.go
-
queue.go
-
queue_test.go
-
rate_limiting_queue.go
-
rate_limiting_queue_test.go
延时队列与优先级队列
延迟队列可以看成一个使用时间作为优先级的优先级队列。
优先级队列虽然也叫队列,但是和普通的队列还是有差别的。普通队列出队顺序只取决于入队顺序,而优先级队列的出队顺序总是按照元素自身的优先级。换句话说,优先级队列是一个自动排序的队列。元素自身的优先级可以根据入队时间,也可以根据其他因素来确定,因此非常灵活。优先级队列的内部实现可以通过有序数组、无序数组和堆等。
限速队列
限速队列是扩展的延迟队列 。用延迟队列的特性,延迟某个元素的插入时间来达到限速的目的。
延迟队列
引用:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU4NjcwMTk1Ng==&mid=2247483864&idx=1&sn=2fe734d9913936c59e0b2dd0d6ad0403&chksm=fdf60c33ca8185253f9a9000dcc790bce459beaef96a49626489ffd8f34a7e6c0a4eaadbe3bb&scene=21#wechat_redirect
基础通用队列
// 通用队列接口定义
type Interface interface {Add(item interface{}) // 向队列中添加一个元素Len() int // 获取队列长度Get() (item interface{}, shutdown bool) // 获取队列头部的元素,第二个返回值表示队列是否已经关闭Done(item interface{}) // 标记队列中元素已经处理完ShutDown() // 关闭队列ShuttingDown() bool // 队列是否正在关闭
}// New constructs a new work queue (see the package comment).
func New() *Type {return NewNamed("")
}func NewNamed(name string) *Type {rc := clock.RealClock{}return newQueue(rc,globalMetricsFactory.newQueueMetrics(name, rc),defaultUnfinishedWorkUpdatePeriod,)
}func newQueue(c clock.Clock, metrics queueMetrics, updatePeriod time.Duration) *Type {t := &Type{clock: c,dirty: set{},processing: set{},cond: sync.NewCond(&sync.Mutex{}),metrics: metrics,unfinishedWorkUpdatePeriod: updatePeriod,}go t.updateUnfinishedWorkLoop()return t
}const defaultUnfinishedWorkUpdatePeriod = 500 * time.Millisecond// Type is a work queue (see the package comment).
type Type struct {// queue defines the order in which we will work on items. Every// element of queue should be in the dirty set and not in the// processing set.queue []t// dirty defines all of the items that need to be processed.dirty set// Things that are currently being processed are in the processing set.// These things may be simultaneously in the dirty set. When we finish// processing something and remove it from this set, we'll check if// it's in the dirty set, and if so, add it to the queue.processing setcond *sync.CondshuttingDown boolmetrics queueMetricsunfinishedWorkUpdatePeriod time.Durationclock clock.Clock
}type empty struct{}
type t interface{}
type set map[t]emptyfunc (s set) has(item t) bool {_, exists := s[item]return exists
}func (s set) insert(item t) {s[item] = empty{}
}func (s set) delete(item t) {delete(s, item)
}// Add marks item as needing processing.
func (q *Type) Add(item interface{}) {q.cond.L.Lock()defer q.cond.L.Unlock()if q.shuttingDown {return}if q.dirty.has(item) {return}q.metrics.add(item)q.dirty.insert(item)if q.processing.has(item) {return}q.queue = append(q.queue, item)q.cond.Signal()
}// Len returns the current queue length, for informational purposes only. You
// shouldn't e.g. gate a call to Add() or Get() on Len() being a particular
// value, that can't be synchronized properly.
func (q *Type) Len() int {q.cond.L.Lock()defer q.cond.L.Unlock()return len(q.queue)
}// Get blocks until it can return an item to be processed. If shutdown = true,
// the caller should end their goroutine. You must call Done with item when you
// have finished processing it.
func (q *Type) Get() (item interface{}, shutdown bool) {q.cond.L.Lock()defer q.cond.L.Unlock()for len(q.queue) == 0 && !q.shuttingDown {q.cond.Wait()}if len(q.queue) == 0 {// We must be shutting down.return nil, true}item, q.queue = q.queue[0], q.queue[1:]q.metrics.get(item)q.processing.insert(item)q.dirty.delete(item)return item, false
}// Done marks item as done processing, and if it has been marked as dirty again
// while it was being processed, it will be re-added to the queue for
// re-processing.
func (q *Type) Done(item interface{}) {q.cond.L.Lock()defer q.cond.L.Unlock()q.metrics.done(item)q.processing.delete(item)if q.dirty.has(item) {q.queue = append(q.queue, item)q.cond.Signal()}
}// ShutDown will cause q to ignore all new items added to it. As soon as the
// worker goroutines have drained the existing items in the queue, they will be
// instructed to exit.
func (q *Type) ShutDown() {q.cond.L.Lock()defer q.cond.L.Unlock()q.shuttingDown = trueq.cond.Broadcast()
}func (q *Type) ShuttingDown() bool {q.cond.L.Lock()defer q.cond.L.Unlock()return q.shuttingDown
}func (q *Type) updateUnfinishedWorkLoop() {t := q.clock.NewTicker(q.unfinishedWorkUpdatePeriod)defer t.Stop()for range t.C() {if !func() bool {q.cond.L.Lock()defer q.cond.L.Unlock()if !q.shuttingDown {q.metrics.updateUnfinishedWork()return true}return false}() {return}}
}延时队列实现
// DelayingInterface is an Interface that can Add an item at a later time. This makes it easier to
// requeue items after failures without ending up in a hot-loop.
type DelayingInterface interface {Interface// AddAfter adds an item to the workqueue after the indicated duration has passedAddAfter(item interface{}, duration time.Duration)
}// 对外暴露的实例化函数
// NewDelayingQueue constructs a new workqueue with delayed queuing ability
func NewDelayingQueue() DelayingInterface {return NewDelayingQueueWithCustomClock(clock.RealClock{}, "")
}// NewDelayingQueueWithCustomQueue constructs a new workqueue with ability to
// inject custom queue Interface instead of the default one
func NewDelayingQueueWithCustomQueue(q Interface, name string) DelayingInterface {return newDelayingQueue(clock.RealClock{}, q, name)
}// NewNamedDelayingQueue constructs a new named workqueue with delayed queuing ability
func NewNamedDelayingQueue(name string) DelayingInterface {return NewDelayingQueueWithCustomClock(clock.RealClock{}, name)
}// NewDelayingQueueWithCustomClock constructs a new named workqueue
// with ability to inject real or fake clock for testing purposes
func NewDelayingQueueWithCustomClock(clock clock.Clock, name string) DelayingInterface {return newDelayingQueue(clock, NewNamed(name), name)
}func newDelayingQueue(clock clock.Clock, q Interface, name string) *delayingType {ret := &delayingType{Interface: q,clock: clock,heartbeat: clock.NewTicker(maxWait),stopCh: make(chan struct{}),waitingForAddCh: make(chan *waitFor, 1000),metrics: newRetryMetrics(name),}// 后台循环任务处理延时消息的消费和添加go ret.waitingLoop()return ret
}// delayingType wraps an Interface and provides delayed re-enquing
type delayingType struct {// 一个通用队列Interface// clock tracks time for delayed firingclock clock.Clock// stopCh lets us signal a shutdown to the waiting loopstopCh chan struct{}// stopOnce guarantees we only signal shutdown a single timestopOnce sync.Once// heartbeat ensures we wait no more than maxWait before firingheartbeat clock.Ticker// waitingForAddCh is a buffered channel that feeds waitingForAdd//buffered channel,将延迟添加的元素封装成 waitFor 放到通道中,当到了指定的时间后就将元素添加到通用队列中去进行处理,还没有到时间的话就放到这个缓冲通道中waitingForAddCh chan *waitFor// metrics counts the number of retriesmetrics retryMetrics
}// waitFor holds the data to add and the time it should be added
type waitFor struct {data treadyAt time.Time// index in the priority queue (heap)index int
}// waitForPriorityQueue implements a priority queue for waitFor items.
//
// waitForPriorityQueue implements heap.Interface. The item occurring next in
// time (i.e., the item with the smallest readyAt) is at the root (index 0).
// Peek returns this minimum item at index 0. Pop returns the minimum item after
// it has been removed from the queue and placed at index Len()-1 by
// container/heap. Push adds an item at index Len(), and container/heap
// percolates it into the correct location.
// 把需要延迟的元素放到一个队列中,然后在队列中按照元素的延时添加时间(readyAt)从小到大排序
// 其实这个优先级队列就是实现的 go内置的 container/heap/heap.go 中的 Interface 接口。heap.Init时会根据实现的函数排序。最终实现的队列就是 waitForPriorityQueue 这个集合是有序的,按照时间从小到大进行排列
type waitForPriorityQueue []*waitForfunc (pq waitForPriorityQueue) Len() int {return len(pq)
}
func (pq waitForPriorityQueue) Less(i, j int) bool {return pq[i].readyAt.Before(pq[j].readyAt)
}
func (pq waitForPriorityQueue) Swap(i, j int) {pq[i], pq[j] = pq[j], pq[i]pq[i].index = ipq[j].index = j
}// Push adds an item to the queue. Push should not be called directly; instead,
// use `heap.Push`.
func (pq *waitForPriorityQueue) Push(x interface{}) {n := len(*pq)item := x.(*waitFor)item.index = n*pq = append(*pq, item)
}// Pop removes an item from the queue. Pop should not be called directly;
// instead, use `heap.Pop`.
func (pq *waitForPriorityQueue) Pop() interface{} {n := len(*pq)item := (*pq)[n-1]item.index = -1*pq = (*pq)[0:(n - 1)]return item
}// Peek returns the item at the beginning of the queue, without removing the
// item or otherwise mutating the queue. It is safe to call directly.
func (pq waitForPriorityQueue) Peek() interface{} {return pq[0]
}// ShutDown stops the queue. After the queue drains, the returned shutdown bool
// on Get() will be true. This method may be invoked more than once.
func (q *delayingType) ShutDown() {q.stopOnce.Do(func() {q.Interface.ShutDown()close(q.stopCh)q.heartbeat.Stop()})
}// AddAfter adds the given item to the work queue after the given delay
func (q *delayingType) AddAfter(item interface{}, duration time.Duration) {// don't add if we're already shutting downif q.ShuttingDown() {return}q.metrics.retry()// 延时时间小于0直接放到通用队列中if duration <= 0 {q.Add(item)return}select {case <-q.stopCh:// unblock if ShutDown() is called// 把元素封装成 waitFor 传给 waitingForAddChcase q.waitingForAddCh <- &waitFor{data: item, readyAt: q.clock.Now().Add(duration)}:}
}// maxWait keeps a max bound on the wait time. It's just insurance against weird things happening.
// Checking the queue every 10 seconds isn't expensive and we know that we'll never end up with an
// expired item sitting for more than 10 seconds.
const maxWait = 10 * time.Second// waitingLoop runs until the workqueue is shutdown and keeps a check on the list of items to be added.
func (q *delayingType) waitingLoop() {defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()// Make a placeholder channel to use when there are no items in our listnever := make(<-chan time.Time)// Make a timer that expires when the item at the head of the waiting queue is readyvar nextReadyAtTimer clock.Timer// 构造一个优先级队列waitingForQueue := &waitForPriorityQueue{}// container/heap堆实现优先级队列heap.Init(waitingForQueue)// 用来避免元素重复添加,如果重复添加了就只更新时间waitingEntryByData := map[t]*waitFor{}// 死循环for {if q.Interface.ShuttingDown() {return}now := q.clock.Now()// 如果优先队列中有元素的话for waitingForQueue.Len() > 0 {// 获取第一个元素entry := waitingForQueue.Peek().(*waitFor)// 如果第一个元素指定的时间还没到时间,则跳出当前循环 因为第一个元素是时间最小的。直到优先队列中元素都需要等待if entry.readyAt.After(now) {break}// 时间已经过了,那就把它从优先队列中拿出来放入通用队列中// 同时要把元素从上面提到的 map 中删除,因为不用再判断重复添加了entry = heap.Pop(waitingForQueue).(*waitFor)q.Add(entry.data)delete(waitingEntryByData, entry.data)}// 如果优先队列中还有元素,那就用第一个元素指定的时间减去当前时间作为等待时间// 因为优先队列是用时间排序的,后面的元素需要等待的时间更长,所以先处理排序靠前面的元素nextReadyAt := neverif waitingForQueue.Len() > 0 {if nextReadyAtTimer != nil {nextReadyAtTimer.Stop()}entry := waitingForQueue.Peek().(*waitFor)// 第一个元素的时间减去当前时间作为等待时间nextReadyAtTimer = q.clock.NewTimer(entry.readyAt.Sub(now))nextReadyAt = nextReadyAtTimer.C()}select {case <-q.stopCh:return// 定时器,每过一段时间没有任何数据,那就再执行一次大循环case <-q.heartbeat.C():// continue the loop, which will add ready items// 上面的等待时间信号,时间到了就有信号 激活这个case,然后继续循环case <-nextReadyAt:// continue the loop, which will add ready items
// AddAfter 函数中放入到通道中的元素,这里从通道中获取数据case waitEntry := <-q.waitingForAddCh:// 如果时间已经过了就直接放入通用队列,没过就插入到有序队列if waitEntry.readyAt.After(q.clock.Now()) {insert(waitingForQueue, waitingEntryByData, waitEntry)} else {q.Add(waitEntry.data)}// 下面就是把channel里面的元素全部取出来 如果没有数据了就直接退出drained := falsefor !drained {select {case waitEntry := <-q.waitingForAddCh:if waitEntry.readyAt.After(q.clock.Now()) {insert(waitingForQueue, waitingEntryByData, waitEntry)} else {q.Add(waitEntry.data)}default:drained = true}}}}
}// 插入元素到有序队列,如果已经存在了则更新时间
func insert(q *waitForPriorityQueue, knownEntries map[t]*waitFor, entry *waitFor) {// if the entry already exists, update the time only if it would cause the item to be queued soonerexisting, exists := knownEntries[entry.data]if exists {if existing.readyAt.After(entry.readyAt) {existing.readyAt = entry.readyAtheap.Fix(q, existing.index)}return}heap.Push(q, entry)knownEntries[entry.data] = entry
}
延时队列原理:
优先级有序队列+通用队列。按照时间的先后顺序来构造一个优先级队列,优先级队列中的元素时间到了的话就把这个元素放到通用队列中去进行正常的处理就行,没到则继续等待。
限速队列
引用:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1709073
限速队列实现
// RateLimitingInterface is an interface that rate limits items being added to the queue.
type RateLimitingInterface interface {DelayingInterface// 在限速器说ok后,将元素item添加到工作队列中AddRateLimited(item interface{})// Forget indicates that an item is finished being retried. Doesn't matter whether it's for perm failing// or for success, we'll stop the rate limiter from tracking it. This only clears the `rateLimiter`, you// still have to call `Done` on the queue.// 丢弃指定的元素Forget(item interface{})// NumRequeues returns back how many times the item was requeued// 查询元素放入队列的次数NumRequeues(item interface{}) int
}// NewRateLimitingQueue constructs a new workqueue with rateLimited queuing ability
// Remember to call Forget! If you don't, you may end up tracking failures forever.
// 限速器 + 延时队列
func NewRateLimitingQueue(rateLimiter RateLimiter) RateLimitingInterface {return &rateLimitingType{DelayingInterface: NewDelayingQueue(),rateLimiter: rateLimiter,}
}func NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(rateLimiter RateLimiter, name string) RateLimitingInterface {return &rateLimitingType{DelayingInterface: NewNamedDelayingQueue(name),rateLimiter: rateLimiter,}
}// rateLimitingType wraps an Interface and provides rateLimited re-enquing
type rateLimitingType struct {DelayingInterfacerateLimiter RateLimiter
}// 通过限速器获取延迟时间,然后加入到延时队列
func (q *rateLimitingType) AddRateLimited(item interface{}) {q.DelayingInterface.AddAfter(item, q.rateLimiter.When(item))
}
// 直接通过限速器获取元素放入队列的次数
func (q *rateLimitingType) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {return q.rateLimiter.NumRequeues(item)
}
// 直接通过限速器丢弃指定的元素
func (q *rateLimitingType) Forget(item interface{}) {q.rateLimiter.Forget(item)
}
不同限速器实现
限流器类型
- BucketRateLimiter
- ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter
- ItemFastSlowRateLimiter
- MaxOfRateLimiter
1 BucketRateLimiter
BucketRateLimiter(令牌桶限速器),这是一个固定速率(qps)的限速器,该限速器是利用
golang.org/x/time/rate库来实现的,令牌桶算法内部实现了一个存放 token(令牌)的“桶”,初始时“桶”是空的,token 会以固定速率往“桶”里填充,直到将其填满为止,多余的 token 会被丢弃。每个元素都会从令牌桶得到一个 token,只有得到 token 的元素才允许通过,而没有得到 token 的元素处于等待状态。令牌桶算法通过控制发放 token 来达到限速目的。令牌桶是有一个固定大小的桶,系统会以恒定的速率向桶中放 Token,桶满了就暂时不放了,而用户则从桶中取 Token,如果有剩余的 Token 就可以一直取,如果没有剩余的 Token,则需要等到系统中放置了 Token 才行。比如抽奖、抢优惠、投票、报名……等场景,在面对突然到来的上百倍流量峰值,除了消息队列预留容量以外,可以考虑做峰值限流。因为对于大部分营销类活动,消息限流(对被限流的消息直接丢弃并直接回复:“系统繁忙,请稍后再试。”)并不会对营销的结果有太大影响。
2 ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter
ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(指数增长限速器) 是比较常用的限速器,从字面意思解释是元素错误次数指数递增限速器,他会根据元素错误次数逐渐累加等待时间。
3 ItemFastSlowRateLimiter
ItemFastSlowRateLimiter (快慢限速器)和 ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter 很像,都是用于错误尝试的,但是 ItemFastSlowRateLimiter 的限速策略是尝试次数超过阈值用长延迟,否则用短延迟,不过该限速器很少使用。
4 MaxOfRateLimiter
MaxOfRateLimiter 也可以叫混合限速器,他内部有多个限速器,选择所有限速器中速度最慢(延迟最大)的一种方案。比如内部有三个限速器,When() 接口返回的就是三个限速器里面延迟最大的。在 Kubernetes 中默认的控制器限速器初始化就是使用的混合限速器:
type RateLimiter interface {// When gets an item and gets to decide how long that item should waitWhen(item interface{}) time.Duration// Forget indicates that an item is finished being retried. Doesn't matter whether its for perm failing// or for success, we'll stop tracking itForget(item interface{})// NumRequeues returns back how many failures the item has hadNumRequeues(item interface{}) int
}// DefaultControllerRateLimiter is a no-arg constructor for a default rate limiter for a workqueue. It has
// both overall and per-item rate limiting. The overall is a token bucket and the per-item is exponential
func DefaultControllerRateLimiter() RateLimiter {return NewMaxOfRateLimiter(NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(5*time.Millisecond, 1000*time.Second),// 10 qps, 100 bucket size. This is only for retry speed and its only the overall factor (not per item)&BucketRateLimiter{Limiter: rate.NewLimiter(rate.Limit(10), 100)},)
}// BucketRateLimiter adapts a standard bucket to the workqueue ratelimiter API
type BucketRateLimiter struct {*rate.Limiter
}var _ RateLimiter = &BucketRateLimiter{}func (r *BucketRateLimiter) When(item interface{}) time.Duration {// 获取需要等待的时间(延迟),而且这个延迟是一个相对固定的周期return r.Limiter.Reserve().Delay()
}func (r *BucketRateLimiter) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {return 0
}func (r *BucketRateLimiter) Forget(item interface{}) {
}// ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter does a simple baseDelay*2^ limit
// dealing with max failures and expiration are up to the caller
type ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter struct {failuresLock sync.Mutexfailures map[interface{}]intbaseDelay time.DurationmaxDelay time.Duration
}var _ RateLimiter = &ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter{}func NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(baseDelay time.Duration, maxDelay time.Duration) RateLimiter {return &ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter{failures: map[interface{}]int{},baseDelay: baseDelay,maxDelay: maxDelay,}
}func DefaultItemBasedRateLimiter() RateLimiter {return NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(time.Millisecond, 1000*time.Second)
}func (r *ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter) When(item interface{}) time.Duration {r.failuresLock.Lock()defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()exp := r.failures[item]r.failures[item] = r.failures[item] + 1// The backoff is capped such that 'calculated' value never overflows.backoff := float64(r.baseDelay.Nanoseconds()) * math.Pow(2, float64(exp))if backoff > math.MaxInt64 {return r.maxDelay}calculated := time.Duration(backoff)if calculated > r.maxDelay {return r.maxDelay}return calculated
}func (r *ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {r.failuresLock.Lock()defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()return r.failures[item]
}func (r *ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter) Forget(item interface{}) {r.failuresLock.Lock()defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()delete(r.failures, item)
}// ItemFastSlowRateLimiter does a quick retry for a certain number of attempts, then a slow retry after that
type ItemFastSlowRateLimiter struct {failuresLock sync.Mutexfailures map[interface{}]intmaxFastAttempts intfastDelay time.DurationslowDelay time.Duration
}var _ RateLimiter = &ItemFastSlowRateLimiter{}func NewItemFastSlowRateLimiter(fastDelay, slowDelay time.Duration, maxFastAttempts int) RateLimiter {return &ItemFastSlowRateLimiter{failures: map[interface{}]int{},fastDelay: fastDelay,slowDelay: slowDelay,maxFastAttempts: maxFastAttempts,}
}func (r *ItemFastSlowRateLimiter) When(item interface{}) time.Duration {r.failuresLock.Lock()defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()r.failures[item] = r.failures[item] + 1if r.failures[item] <= r.maxFastAttempts {return r.fastDelay}return r.slowDelay
}func (r *ItemFastSlowRateLimiter) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {r.failuresLock.Lock()defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()return r.failures[item]
}func (r *ItemFastSlowRateLimiter) Forget(item interface{}) {r.failuresLock.Lock()defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()delete(r.failures, item)
}// MaxOfRateLimiter calls every RateLimiter and returns the worst case response
// When used with a token bucket limiter, the burst could be apparently exceeded in cases where particular items
// were separately delayed a longer time.
type MaxOfRateLimiter struct {limiters []RateLimiter
}func (r *MaxOfRateLimiter) When(item interface{}) time.Duration {ret := time.Duration(0)for _, limiter := range r.limiters {curr := limiter.When(item)if curr > ret {ret = curr}}return ret
}func NewMaxOfRateLimiter(limiters ...RateLimiter) RateLimiter {return &MaxOfRateLimiter{limiters: limiters}
}func (r *MaxOfRateLimiter) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {ret := 0for _, limiter := range r.limiters {curr := limiter.NumRequeues(item)if curr > ret {ret = curr}}return ret
}func (r *MaxOfRateLimiter) Forget(item interface{}) {for _, limiter := range r.limiters {limiter.Forget(item)}
}
应用
informer 自定义控制器 workqueue应用
func NewController(queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface, indexer cache.Indexer, informer cache.Controller) *Controller {return &Controller{informer: informer,indexer: indexer,queue: queue,}
}func (c *Controller) processNextItem() bool {// Wait until there is a new item in the working queuekey, quit := c.queue.Get()if quit {return false}// Tell the queue that we are done with processing this key. This unblocks the key for other workers// This allows safe parallel processing because two pods with the same key are never processed in// parallel.defer c.queue.Done(key)// Invoke the method containing the business logicerr := c.syncToStdout(key.(string))// Handle the error if something went wrong during the execution of the business logicc.handleErr(err, key)return true
}// syncToStdout is the business logic of the controller. In this controller it simply prints
// information about the pod to stdout. In case an error happened, it has to simply return the error.
// The retry logic should not be part of the business logic.
func (c *Controller) syncToStdout(key string) error {obj, exists, err := c.indexer.GetByKey(key)if err != nil {klog.Errorf("Fetching object with key %s from store failed with %v", key, err)return err}if !exists {// Below we will warm up our cache with a Pod, so that we will see a delete for one podfmt.Printf("Pod %s does not exist anymore\n", key)} else {// Note that you also have to check the uid if you have a local controlled resource, which// is dependent on the actual instance, to detect that a Pod was recreated with the same namefmt.Printf("Sync/Add/Update for Pod %s\n", obj.(*v1.Pod).GetName())}return nil
}// handleErr checks if an error happened and makes sure we will retry later.
func (c *Controller) handleErr(err error, key interface{}) {if err == nil {// Forget about the #AddRateLimited history of the key on every successful synchronization.// This ensures that future processing of updates for this key is not delayed because of// an outdated error history.c.queue.Forget(key)return}// This controller retries 5 times if something goes wrong. After that, it stops trying.if c.queue.NumRequeues(key) < 5 {klog.Infof("Error syncing pod %v: %v", key, err)// Re-enqueue the key rate limited. Based on the rate limiter on the// queue and the re-enqueue history, the key will be processed later again.c.queue.AddRateLimited(key)return}c.queue.Forget(key)// Report to an external entity that, even after several retries, we could not successfully process this keyruntime.HandleError(err)klog.Infof("Dropping pod %q out of the queue: %v", key, err)
}func (c *Controller) Run(threadiness int, stopCh chan struct{}) {defer runtime.HandleCrash()// Let the workers stop when we are donedefer c.queue.ShutDown()klog.Info("Starting Pod controller")go c.informer.Run(stopCh)// Wait for all involved caches to be synced, before processing items from the queue is startedif !cache.WaitForCacheSync(stopCh, c.informer.HasSynced) {runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Timed out waiting for caches to sync"))return}for i := 0; i < threadiness; i++ {go wait.Until(c.runWorker, time.Second, stopCh)}<-stopChklog.Info("Stopping Pod controller")
}func (c *Controller) runWorker() {for c.processNextItem() {}
}func main() {var kubeconfig stringvar master stringflag.StringVar(&kubeconfig, "kubeconfig", "", "absolute path to the kubeconfig file")flag.StringVar(&master, "master", "", "master url")flag.Parse()// creates the connectionconfig, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags(master, kubeconfig)if err != nil {klog.Fatal(err)}// creates the clientsetclientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)if err != nil {klog.Fatal(err)}// create the pod watcherpodListWatcher := cache.NewListWatchFromClient(clientset.CoreV1().RESTClient(), "pods", v1.NamespaceDefault, fields.Everything())// create the workqueue// 默认的限速队列queue := workqueue.NewRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter())// Bind the workqueue to a cache with the help of an informer. This way we make sure that// whenever the cache is updated, the pod key is added to the workqueue.// Note that when we finally process the item from the workqueue, we might see a newer version// of the Pod than the version which was responsible for triggering the update.indexer, informer := cache.NewIndexerInformer(podListWatcher, &v1.Pod{}, 0, cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {key, err := cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj)if err == nil {queue.Add(key)}},UpdateFunc: func(old interface{}, new interface{}) {key, err := cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(new)if err == nil {queue.Add(key)}},DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}) {// IndexerInformer uses a delta queue, therefore for deletes we have to use this// key function.key, err := cache.DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj)if err == nil {queue.Add(key)}},}, cache.Indexers{})controller := NewController(queue, indexer, informer)// We can now warm up the cache for initial synchronization.// Let's suppose that we knew about a pod "mypod" on our last run, therefore add it to the cache.// If this pod is not there anymore, the controller will be notified about the removal after the// cache has synchronized.indexer.Add(&v1.Pod{ObjectMeta: meta_v1.ObjectMeta{Name: "mypod",Namespace: v1.NamespaceDefault,},})// Now let's start the controllerstop := make(chan struct{})defer close(stop)go controller.Run(1, stop)// Wait foreverselect {}
}
informer
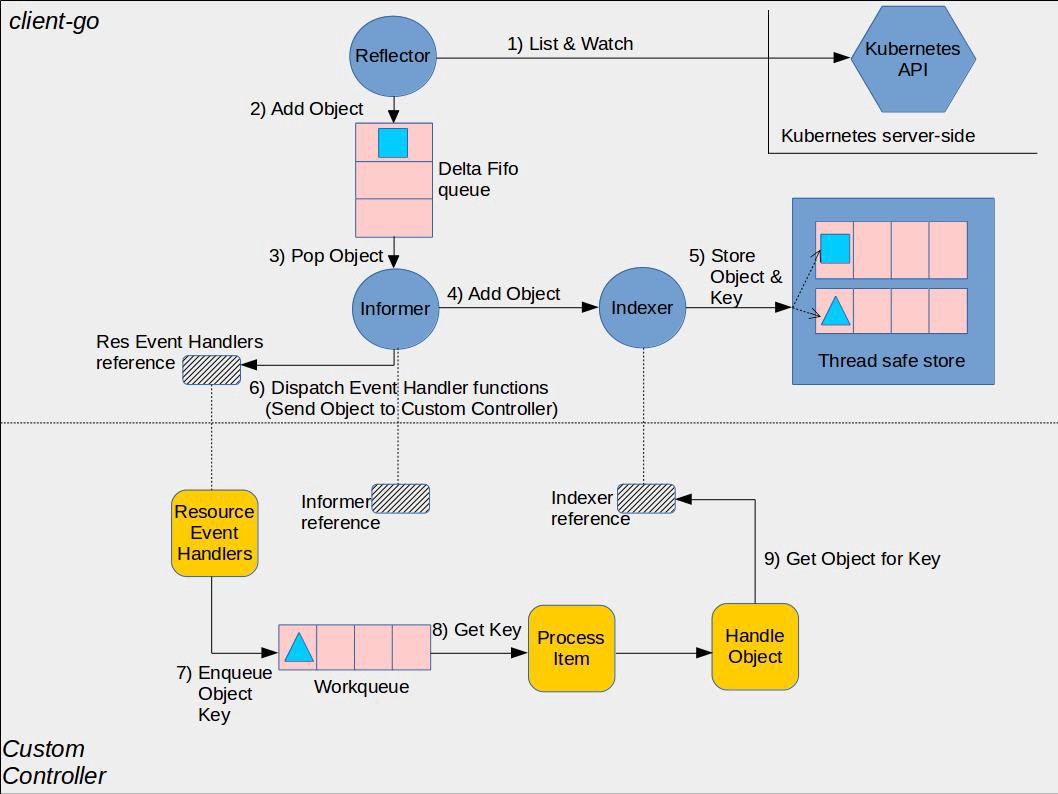
Informer模块是Kubernetes中的基础组件,负责各组件与Apiserver的资源与事件同步。List/Watch机制是Kubernetes中实现集群控制模块最核心的设计之一,它采用统一的异步消息处理机制,保证了消息的实时性、可靠性、顺序性和性能等,为声明式风格的API奠定了良好的基础。
应用
引用:https://www.jianshu.com/p/61f2d1d884a9
pod的informer
package mainimport ("fmt"clientset "k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes""k8s.io/client-go/rest""k8s.io/client-go/informers""k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache""k8s.io/api/core/v1""k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/labels""time"
)func main() {config := &rest.Config{Host: "http://172.21.0.16:8080",}client := clientset.NewForConfigOrDie(config)// 生成一个SharedInformerFactory// 工厂方法factory := informers.NewSharedInformerFactory(client, 5 * time.Second)// 生成一个PodInformer// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/informers// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/listerspodInformer := factory.Core().V1().Pods()// 获得一个cache.SharedIndexInformer 单例模式sharedInformer := podInformer.Informer()// 用户自定义控制器逻辑sharedInformer.AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {fmt.Printf("add: %v\n", obj.(*v1.Pod).Name)},UpdateFunc: func(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {fmt.Printf("update: %v\n", newObj.(*v1.Pod).Name)},DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}){fmt.Printf("delete: %v\n", obj.(*v1.Pod).Name)},})stopCh := make(chan struct{})// 第一种方式// 可以这样启动 也可以按照下面的方式启动// go sharedInformer.Run(stopCh)// 需要等待2秒钟才调用list方法, 因为如果不sleep, 有可能获得的是空的.// time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)// 第二种方式factory.Start(stopCh)// 该方法是等待所有已经启动的informers完成同步. 因为不等到同步完成的时候, 本地缓存中是没有数据的, 如果直接就运行逻辑代码, 有些调用list方法就会获取不到, 因为服务器端是有数据的, 所以就会产生一定的偏差, 因此一般都是等到服务器端数据同步到本地缓存完了才开始运行用户自己的逻辑.factory.WaitForCacheSync(stopCh)// Lister()就是从本地缓存中取数据, 而不是直接去服务器端(k8s)上获得数据.pods, _ := podInformer.Lister().Pods("default").List(labels.Everything())for _, p := range pods {fmt.Printf("list pods: %v\n", p.Name)}<- stopCh
}
原理图
尽在图中
目录
-
controller.go
-
expiration_cache.go
-
heap.go
-
index.go
-
listers.go:从本地缓存中结合index读取资源的列表数据
-
listwatch.go:listwatch接口的定义,底层对应不同资源的restclient实现list watch
-
mutation_cache.go
-
mutation_detector.go
-
reflector.go list watch apiserver将事件放到delta queue中
-
reflector_metrics.go
-
shared_informer.go
-
store.go:fifo.go中的Queue接口继承store.go中的Store接口,deltafifo、fifo实现了接口queue;store.go中的cache结构体,装配ThreadSafeStore本地缓存实现Store接口。其中的cache是本地缓存的实现结构,cache中通过ThreadSafeStore实现具体的逻辑。
-
fifo.go
-
delta_fifo.go 一级队列缓存
-
thread_safe_store.go 二级本地缓存
-
undelta_store.go
queue
作为一级缓存,reflector listwatch的缓存后端。
- fifo队列
- deltafifo:有具体增删改查事件动作的队列
引用:https://www.jianshu.com/p/095de3ee5f7b
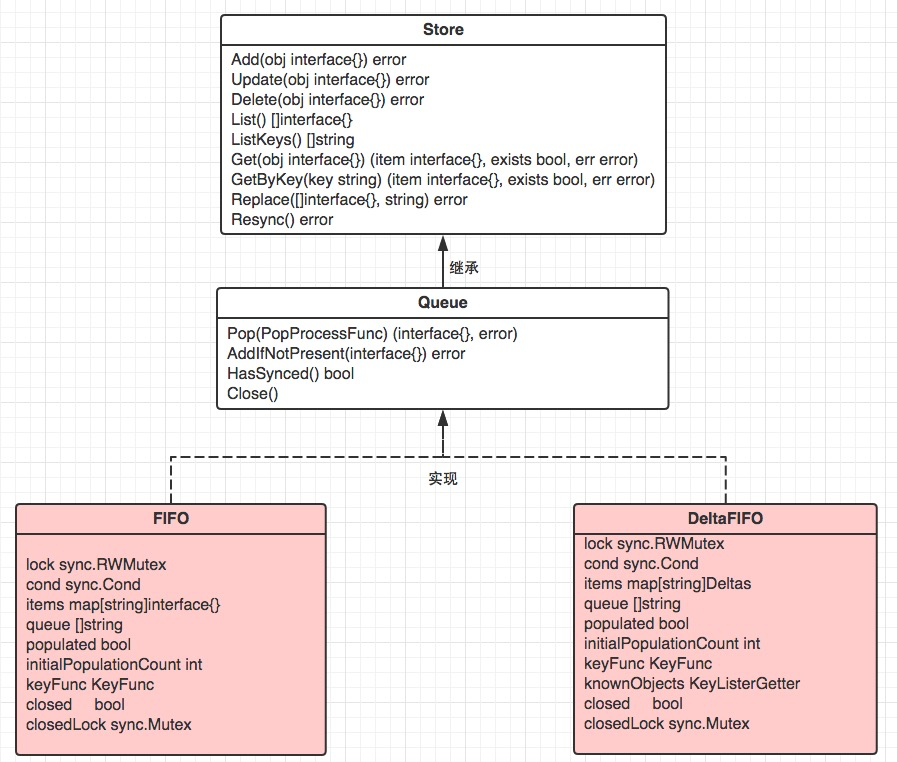
实现接口与实现关系:
fifo
引用 https://www.jianshu.com/p/9e75976a9f3c
源码
// PopProcessFunc is passed to Pop() method of Queue interface.
// It is supposed to process the accumulator popped from the queue.
type PopProcessFunc func(interface{}) error// ErrRequeue may be returned by a PopProcessFunc to safely requeue
// the current item. The value of Err will be returned from Pop.
type ErrRequeue struct {// Err is returned by the Pop functionErr error
}// ErrFIFOClosed used when FIFO is closed
var ErrFIFOClosed = errors.New("DeltaFIFO: manipulating with closed queue")func (e ErrRequeue) Error() string {if e.Err == nil {return "the popped item should be requeued without returning an error"}return e.Err.Error()
}// Queue extends Store with a collection of Store keys to "process".
// Every Add, Update, or Delete may put the object's key in that collection.
// A Queue has a way to derive the corresponding key given an accumulator.
// A Queue can be accessed concurrently from multiple goroutines.
// A Queue can be "closed", after which Pop operations return an error.
type Queue interface {// 继承Store// Pop blocks until there is at least one key to process or the// Queue is closed. In the latter case Pop returns with an error.// In the former case Pop atomically picks one key to process,// removes that (key, accumulator) association from the Store, and// processes the accumulator. Pop returns the accumulator that// was processed and the result of processing. The PopProcessFunc// may return an ErrRequeue{inner} and in this case Pop will (a)// return that (key, accumulator) association to the Queue as part// of the atomic processing and (b) return the inner error from// Pop. 从队列弹出元素Pop(PopProcessFunc) (interface{}, error)// AddIfNotPresent puts the given accumulator into the Queue (in// association with the accumulator's key) if and only if that key// is not already associated with a non-empty accumulator.//不存在添加AddIfNotPresent(interface{}) error// HasSynced returns true if the first batch of keys have all been// popped. The first batch of keys are those of the first Replace// operation if that happened before any Add, AddIfNotPresent,// Update, or Delete; otherwise the first batch is empty.HasSynced() bool// Close the queueClose()
}// Pop is helper function for popping from Queue.
// WARNING: Do NOT use this function in non-test code to avoid races
// unless you really really really really know what you are doing.
func Pop(queue Queue) interface{} {var result interface{}queue.Pop(func(obj interface{}) error {result = objreturn nil})return result
}type FIFO struct {//队列的增删改锁lock sync.RWMutex//队列pop时没有元素,等待增改改的广播消息cond sync.Cond// We depend on the property that every key in `items` is also in `queue`// 1个map存id元素 一个切片存iditems map[string]interface{}queue []string// populated is true if the first batch of items inserted by Replace() has been populated// or Delete/Add/Update was called first.populated bool// initialPopulationCount is the number of items inserted by the first call of Replace()// 最初replace时 队列中元素个数initialPopulationCount int// keyFunc is used to make the key used for queued item insertion and retrieval, and// should be deterministic.// 对obj哈希函数取的idkeyFunc KeyFunc// Indication the queue is closed.// Used to indicate a queue is closed so a control loop can exit when a queue is empty.// Currently, not used to gate any of CRED operations.closed bool
}var (// if impl interface Queue_ = Queue(&FIFO{}) // FIFO is a Queue
)// Close the queue.
func (f *FIFO) Close() {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()f.closed = truef.cond.Broadcast()
}// HasSynced returns true if an Add/Update/Delete/AddIfNotPresent are called first,
// or the first batch of items inserted by Replace() has been popped.
// !!!!!!! 队列中的元素个数为0+已经调用了Replace;场景:队列中的元素已经被消息完了,即已经同步完成
// 假设此时FIFQ刚刚初始化.
//1. 如果啥方法都没有调用, 那么HasSynced返回false, 因为populated=false.
//2. 如果先调用Add/Update/AddIfNotPresent/Delete后(后面调用什么函数都不用管了), 那么HasSynced返回true, 因为populated=true并且initialPopulationCount == 0.
//3. 如果先调用Replace(后面调用什么函数都不用管了), 那么必须要等待该replace方法加入元素的个数全部pop之后, HasSynced才会返回true, 因为只有全部pop完了之后initialPopulationCount才减为0
func (f *FIFO) HasSynced() bool {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()return f.populated && f.initialPopulationCount == 0
}// Add inserts an item, and puts it in the queue. The item is only enqueued
// if it doesn't already exist in the set.
func (f *FIFO) Add(obj interface{}) error {id, err := f.keyFunc(obj)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()f.populated = trueif _, exists := f.items[id]; !exists {f.queue = append(f.queue, id)}f.items[id] = objf.cond.Broadcast()return nil
}// AddIfNotPresent inserts an item, and puts it in the queue. If the item is already
// present in the set, it is neither enqueued nor added to the set.
//
// This is useful in a single producer/consumer scenario so that the consumer can
// safely retry items without contending with the producer and potentially enqueueing
// stale items.
func (f *FIFO) AddIfNotPresent(obj interface{}) error {id, err := f.keyFunc(obj)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()f.addIfNotPresent(id, obj)return nil
}// addIfNotPresent assumes the fifo lock is already held and adds the provided
// item to the queue under id if it does not already exist.
func (f *FIFO) addIfNotPresent(id string, obj interface{}) {f.populated = trueif _, exists := f.items[id]; exists {return}f.queue = append(f.queue, id)f.items[id] = objf.cond.Broadcast()
}// Update is the same as Add in this implementation.
func (f *FIFO) Update(obj interface{}) error {return f.Add(obj)
}// Delete removes an item. It doesn't add it to the queue, because
// this implementation assumes the consumer only cares about the objects,
// not the order in which they were created/added.
//Delete方法可以看到只是从items中删除, 并没有从queue中删除该obj的key., 不过这不会有影响, 在pop方法的时候, 如果从queue里面出来的key在items中找不到, 就认为该obj已经删除了, 就不做处理了. 所以items里面的数据是安全的, queue里面的数据有可能是已经被删除了的.
func (f *FIFO) Delete(obj interface{}) error {id, err := f.keyFunc(obj)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()f.populated = truedelete(f.items, id)return err
}// List returns a list of all the items.
func (f *FIFO) List() []interface{} {f.lock.RLock()defer f.lock.RUnlock()list := make([]interface{}, 0, len(f.items))for _, item := range f.items {list = append(list, item)}return list
}// ListKeys returns a list of all the keys of the objects currently
// in the FIFO.
func (f *FIFO) ListKeys() []string {f.lock.RLock()defer f.lock.RUnlock()list := make([]string, 0, len(f.items))for key := range f.items {list = append(list, key)}return list
}// Get returns the requested item, or sets exists=false.
func (f *FIFO) Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) {key, err := f.keyFunc(obj)if err != nil {return nil, false, KeyError{obj, err}}return f.GetByKey(key)
}// GetByKey returns the requested item, or sets exists=false.
func (f *FIFO) GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) {f.lock.RLock()defer f.lock.RUnlock()item, exists = f.items[key]return item, exists, nil
}// IsClosed checks if the queue is closed
func (f *FIFO) IsClosed() bool {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()if f.closed {return true}return false
}// Pop waits until an item is ready and processes it. If multiple items are
// ready, they are returned in the order in which they were added/updated.
// The item is removed from the queue (and the store) before it is processed,
// so if you don't successfully process it, it should be added back with
// AddIfNotPresent(). process function is called under lock, so it is safe
// update data structures in it that need to be in sync with the queue.
func (f *FIFO) Pop(process PopProcessFunc) (interface{}, error) {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()for {for len(f.queue) == 0 {// When the queue is empty, invocation of Pop() is blocked until new item is enqueued.// When Close() is called, the f.closed is set and the condition is broadcasted.// Which causes this loop to continue and return from the Pop().// 如果队列已经关闭 则直接返回错误if f.IsClosed() {return nil, ErrFIFOClosed}// 等待 有元素了之后会通知f.cond.Wait()}id := f.queue[0]f.queue = f.queue[1:]// 如果initialPopulationCount > 0 表明Replace是比Add/Update/AddIfNotPresent/Delete先调用 然后设置了initialPopulationCountif f.initialPopulationCount > 0 {f.initialPopulationCount--}item, ok := f.items[id]if !ok {// 如果已经删除了 不做处理// Item may have been deleted subsequently.continue}// 从items中删除iddelete(f.items, id)// 消息处理err := process(item)if e, ok := err.(ErrRequeue); ok {// 如果用户处理逻辑返回错误是ErrRequeue// 那么表明需要重新加回到queue里面去f.addIfNotPresent(id, item)err = e.Err}return item, err}
}// Replace will delete the contents of 'f', using instead the given map.
// 'f' takes ownership of the map, you should not reference the map again
// after calling this function. f's queue is reset, too; upon return, it
// will contain the items in the map, in no particular order.
//informer list的时候会调用这个接口,刷新队列中的所有元素和资源版本
func (f *FIFO) Replace(list []interface{}, resourceVersion string) error {items := make(map[string]interface{}, len(list))for _, item := range list {key, err := f.keyFunc(item)if err != nil {return KeyError{item, err}}items[key] = item}f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()if !f.populated {f.populated = true// 最初的元素数量 f.initialPopulationCount = len(items)}f.items = itemsf.queue = f.queue[:0]for id := range items {f.queue = append(f.queue, id)}if len(f.queue) > 0 {f.cond.Broadcast()}return nil
}// Resync will ensure that every object in the Store has its key in the queue.
// This should be a no-op, because that property is maintained by all operations.
// id切片列表去重
// id切片列表增加 元素map中没有的id
func (f *FIFO) Resync() error {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()inQueue := sets.NewString()for _, id := range f.queue {inQueue.Insert(id)}for id := range f.items {if !inQueue.Has(id) {f.queue = append(f.queue, id)}}if len(f.queue) > 0 {f.cond.Broadcast()}return nil
}// NewFIFO returns a Store which can be used to queue up items to
// process.
func NewFIFO(keyFunc KeyFunc) *FIFO {f := &FIFO{items: map[string]interface{}{},queue: []string{},keyFunc: keyFunc,}f.cond.L = &f.lockreturn f
}
deltafifo
引用:https://www.jianshu.com/p/095de3ee5f7b
与FIFO相比, 主要有以下几点不同:
- items中的value不再只存着该key对应的obj, 而是obj的一系列变化, 用一个数组来表示. 包括添加/更新/删除等等. 因此衍生出来了很多结构体和方法, 包括Deltas, Delta等等.
- 增加了本地缓存knownObjects KeyListerGetter, KeyListerGetter提供了两个方法分别是从本地缓存中获得所有的key和根据key找到对应的obj. 当程序中错过了某些event, 比如deletion event, 会造成服务器数据库中没有该obj, 而本地缓存中有该obj, 从而造成数据不一致, 那么在同步的过程中会有所操作. (其实KeyListerGetter在informers体系中是一个Indexer. )或许有人会疑惑会为什么需要用另外一个属性来缓存呢? items属性不就可以当做缓存了吗? 理由是: items只是暂时性存储, 当调用pop的时候对应的数据就会从items中删除了, 而knownObjects会维护本地缓存.
- DeletedFinalStateUnknown: 当一个obj被删除了, 但是这个程序这边由于某种原因miss了这次deletion event, 那么假如在做同步操作时, 从服务器获取的列表中已经没有了这个obj, 因为该程序没有接收到deletion event, 所以该obj在本地缓存中依然存在, 所以此时会给这个obj构造成这个DeletedFinalStateUnknown类型.
源码
// 对象的hash key函数 如获取对象的id
// 对象的二级本地缓存
// replace的是sync还是replace事件?
func NewDeltaFIFO(keyFunc KeyFunc, knownObjects KeyListerGetter) *DeltaFIFO {return NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{KeyFunction: keyFunc,KnownObjects: knownObjects,})
}// DeltaFIFOOptions is the configuration parameters for DeltaFIFO. All are
// optional.
type DeltaFIFOOptions struct {// KeyFunction is used to figure out what key an object should have. (It's// exposed in the returned DeltaFIFO's KeyOf() method, with additional// handling around deleted objects and queue state).// Optional, the default is MetaNamespaceKeyFunc.KeyFunction KeyFunc// KnownObjects is expected to return a list of keys that the consumer of// this queue "knows about". It is used to decide which items are missing// when Replace() is called; 'Deleted' deltas are produced for the missing items.// KnownObjects may be nil if you can tolerate missing deletions on Replace().KnownObjects KeyListerGetter// EmitDeltaTypeReplaced indicates that the queue consumer// understands the Replaced DeltaType. Before the `Replaced` event type was// added, calls to Replace() were handled the same as Sync(). For// backwards-compatibility purposes, this is false by default.// When true, `Replaced` events will be sent for items passed to a Replace() call.// When false, `Sync` events will be sent instead.EmitDeltaTypeReplaced bool
}// NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions returns a Queue which can be used to process changes to
// items. See also the comment on DeltaFIFO.
func NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(opts DeltaFIFOOptions) *DeltaFIFO {if opts.KeyFunction == nil {opts.KeyFunction = MetaNamespaceKeyFunc}f := &DeltaFIFO{items: map[string]Deltas{},queue: []string{},keyFunc: opts.KeyFunction,knownObjects: opts.KnownObjects,emitDeltaTypeReplaced: opts.EmitDeltaTypeReplaced,}f.cond.L = &f.lockreturn f
}type DeltaFIFO struct {// lock/cond protects access to 'items' and 'queue'.lock sync.RWMutexcond sync.Cond// `items` maps keys to Deltas.// `queue` maintains FIFO order of keys for consumption in Pop().// We maintain the property that keys in the `items` and `queue` are// strictly 1:1 mapping, and that all Deltas in `items` should have// at least one Delta.// items里面存的是key 以及该key对应的pod的变化// queue中存的是key 即出队列的顺序。消息的顺序性保证items map[string]Deltasqueue []string// populated is true if the first batch of items inserted by Replace() has been populated// or Delete/Add/Update/AddIfNotPresent was called first.populated bool// initialPopulationCount is the number of items inserted by the first call of Replace()initialPopulationCount int// keyFunc is used to make the key used for queued item// insertion and retrieval, and should be deterministic.keyFunc KeyFunc// knownObjects list keys that are "known" --- affecting Delete(),// Replace(), and Resync()// 说白了就是本地缓存 是一个indexerknownObjects KeyListerGetter// Used to indicate a queue is closed so a control loop can exit when a queue is empty.// Currently, not used to gate any of CRED operations.closed bool// emitDeltaTypeReplaced is whether to emit the Replaced or Sync// DeltaType when Replace() is called (to preserve backwards compat).emitDeltaTypeReplaced bool
}// 用于判断DeltaFIFO是否实现了接口Queue,若没有实现则编译失败
var (_ = Queue(&DeltaFIFO{}) // DeltaFIFO is a Queue
)var (// ErrZeroLengthDeltasObject is returned in a KeyError if a Deltas// object with zero length is encountered (should be impossible,// but included for completeness).ErrZeroLengthDeltasObject = errors.New("0 length Deltas object; can't get key")
)// Close the queue.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Close() {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()f.closed = truef.cond.Broadcast()
}// KeyOf exposes f's keyFunc, but also detects the key of a Deltas object or
// DeletedFinalStateUnknown objects.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) KeyOf(obj interface{}) (string, error) {if d, ok := obj.(Deltas); ok {if len(d) == 0 {return "", KeyError{obj, ErrZeroLengthDeltasObject}}obj = d.Newest().Object}if d, ok := obj.(DeletedFinalStateUnknown); ok {return d.Key, nil}return f.keyFunc(obj)
}// HasSynced returns true if an Add/Update/Delete/AddIfNotPresent are called first,
// or the first batch of items inserted by Replace() has been popped.
// 1. 如果啥方法都没有调用, 那么HasSynced返回false, 因为populated=false.
//2. 如果先调用Add/Update/AddIfNotPresent/Delete后(后面调用什么函数都不用管了), 那么HasSynced返回true, 因为populated=true并且initialPopulationCount == 0.
//3. 如果先调用Replace(后面调用什么函数都不用管了), 那么必须要等待该replace方法加入元素的个数和DeletedFinalStateUnknown(也就是那些本地缓存上有服务器上没有的元素)全部pop之后, HasSynced才会返回true, 因为只有全部pop完了之后initialPopulationCount才减为0.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) HasSynced() bool {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()return f.populated && f.initialPopulationCount == 0
}// Add inserts an item, and puts it in the queue. The item is only enqueued
// if it doesn't already exist in the set.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Add(obj interface{}) error {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()f.populated = truereturn f.queueActionLocked(Added, obj)
}// Update is just like Add, but makes an Updated Delta.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Update(obj interface{}) error {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()f.populated = truereturn f.queueActionLocked(Updated, obj)
}// Delete is just like Add, but makes a Deleted Delta. If the given
// object does not already exist, it will be ignored. (It may have
// already been deleted by a Replace (re-list), for example.) In this
// method `f.knownObjects`, if not nil, provides (via GetByKey)
// _additional_ objects that are considered to already exist.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Delete(obj interface{}) error {id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()f.populated = trueif f.knownObjects == nil {if _, exists := f.items[id]; !exists {// Presumably, this was deleted when a relist happened.// Don't provide a second report of the same deletion.return nil}} else {// We only want to skip the "deletion" action if the object doesn't// exist in knownObjects and it doesn't have corresponding item in items.// Note that even if there is a "deletion" action in items, we can ignore it,// because it will be deduped automatically in "queueActionLocked"_, exists, err := f.knownObjects.GetByKey(id)_, itemsExist := f.items[id]if err == nil && !exists && !itemsExist {// Presumably, this was deleted when a relist happened.// Don't provide a second report of the same deletion.return nil}}// exist in items and/or KnownObjectsreturn f.queueActionLocked(Deleted, obj)
}// AddIfNotPresent inserts an item, and puts it in the queue. If the item is already
// present in the set, it is neither enqueued nor added to the set.
//
// This is useful in a single producer/consumer scenario so that the consumer can
// safely retry items without contending with the producer and potentially enqueueing
// stale items.
//
// Important: obj must be a Deltas (the output of the Pop() function). Yes, this is
// different from the Add/Update/Delete functions.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) AddIfNotPresent(obj interface{}) error {deltas, ok := obj.(Deltas)if !ok {return fmt.Errorf("object must be of type deltas, but got: %#v", obj)}id, err := f.KeyOf(deltas.Newest().Object)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()f.addIfNotPresent(id, deltas)return nil
}// addIfNotPresent inserts deltas under id if it does not exist, and assumes the caller
// already holds the fifo lock.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) addIfNotPresent(id string, deltas Deltas) {f.populated = trueif _, exists := f.items[id]; exists {return}f.queue = append(f.queue, id)f.items[id] = deltasf.cond.Broadcast()
}// re-listing and watching can deliver the same update multiple times in any
// order. This will combine the most recent two deltas if they are the same.
// 后两位去重?
func dedupDeltas(deltas Deltas) Deltas {n := len(deltas)if n < 2 {return deltas}a := &deltas[n-1]b := &deltas[n-2]if out := isDup(a, b); out != nil {// `a` and `b` are duplicates. Only keep the one returned from isDup().// TODO: This extra array allocation and copy seems unnecessary if// all we do to dedup is compare the new delta with the last element// in `items`, which could be done by mutating `items` directly.// Might be worth profiling and investigating if it is safe to optimize.d := append(Deltas{}, deltas[:n-2]...)return append(d, *out)}return deltas
}// If a & b represent the same event, returns the delta that ought to be kept.
// Otherwise, returns nil.
// TODO: is there anything other than deletions that need deduping?
func isDup(a, b *Delta) *Delta {if out := isDeletionDup(a, b); out != nil {return out}// TODO: Detect other duplicate situations? Are there any?return nil
}// keep the one with the most information if both are deletions.
func isDeletionDup(a, b *Delta) *Delta {if b.Type != Deleted || a.Type != Deleted {return nil}// Do more sophisticated checks, or is this sufficient?if _, ok := b.Object.(DeletedFinalStateUnknown); ok {return a}return b
}// queueActionLocked appends to the delta list for the object.
// Caller must lock first.
// 增删改 同步替换事件入队
func (f *DeltaFIFO) queueActionLocked(actionType DeltaType, obj interface{}) error {id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}newDeltas := append(f.items[id], Delta{actionType, obj})// 判断最后两个元素是不是都是delete, 如果是则将前面去掉只保留最后两个其一newDeltas = dedupDeltas(newDeltas)if len(newDeltas) > 0 {if _, exists := f.items[id]; !exists {f.queue = append(f.queue, id)}f.items[id] = newDeltasf.cond.Broadcast()} else {// This never happens, because dedupDeltas never returns an empty list// when given a non-empty list (as it is here).// But if somehow it ever does return an empty list, then// We need to remove this from our map (extra items in the queue are// ignored if they are not in the map).delete(f.items, id)}return nil
}// List returns a list of all the items; it returns the object
// from the most recent Delta.
// You should treat the items returned inside the deltas as immutable.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) List() []interface{} {f.lock.RLock()defer f.lock.RUnlock()return f.listLocked()
}func (f *DeltaFIFO) listLocked() []interface{} {list := make([]interface{}, 0, len(f.items))for _, item := range f.items {list = append(list, item.Newest().Object)}return list
}// ListKeys returns a list of all the keys of the objects currently
// in the FIFO.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) ListKeys() []string {f.lock.RLock()defer f.lock.RUnlock()list := make([]string, 0, len(f.items))for key := range f.items {list = append(list, key)}return list
}// Get returns the complete list of deltas for the requested item,
// or sets exists=false.
// You should treat the items returned inside the deltas as immutable.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) {key, err := f.KeyOf(obj)if err != nil {return nil, false, KeyError{obj, err}}return f.GetByKey(key)
}// GetByKey returns the complete list of deltas for the requested item,
// setting exists=false if that list is empty.
// You should treat the items returned inside the deltas as immutable.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) {f.lock.RLock()defer f.lock.RUnlock()d, exists := f.items[key]if exists {// Copy item's slice so operations on this slice// won't interfere with the object we return.d = copyDeltas(d)}return d, exists, nil
}// IsClosed checks if the queue is closed
func (f *DeltaFIFO) IsClosed() bool {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()return f.closed
}// Pop blocks until an item is added to the queue, and then returns it. If
// multiple items are ready, they are returned in the order in which they were
// added/updated. The item is removed from the queue (and the store) before it
// is returned, so if you don't successfully process it, you need to add it back
// with AddIfNotPresent().
// process function is called under lock, so it is safe to update data structures
// in it that need to be in sync with the queue (e.g. knownKeys). The PopProcessFunc
// may return an instance of ErrRequeue with a nested error to indicate the current
// item should be requeued (equivalent to calling AddIfNotPresent under the lock).
// process should avoid expensive I/O operation so that other queue operations, i.e.
// Add() and Get(), won't be blocked for too long.
//
// Pop returns a 'Deltas', which has a complete list of all the things
// that happened to the object (deltas) while it was sitting in the queue.
// 从items中弹出对象事件
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Pop(process PopProcessFunc) (interface{}, error) {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()for {for len(f.queue) == 0 {// When the queue is empty, invocation of Pop() is blocked until new item is enqueued.// When Close() is called, the f.closed is set and the condition is broadcasted.// Which causes this loop to continue and return from the Pop().if f.closed {return nil, ErrFIFOClosed}f.cond.Wait()}id := f.queue[0]f.queue = f.queue[1:]if f.initialPopulationCount > 0 {f.initialPopulationCount--}item, ok := f.items[id]if !ok {// Item may have been deleted subsequently.continue}delete(f.items, id)// 调用消息的处理函数,包括1 从一级缓存deta queue同步到二级缓存indexer;2 添加消息到用户自定义处理器的queue中err := process(item)if e, ok := err.(ErrRequeue); ok {f.addIfNotPresent(id, item)err = e.Err}// Don't need to copyDeltas here, because we're transferring// ownership to the caller.return item, err}
}// Replace atomically does two things: (1) it adds the given objects
// using the Sync or Replace DeltaType and then (2) it does some deletions.
// In particular: for every pre-existing key K that is not the key of
// an object in `list` there is the effect of
// `Delete(DeletedFinalStateUnknown{K, O})` where O is current object
// of K. If `f.knownObjects == nil` then the pre-existing keys are
// those in `f.items` and the current object of K is the `.Newest()`
// of the Deltas associated with K. Otherwise the pre-existing keys
// are those listed by `f.knownObjects` and the current object of K is
// what `f.knownObjects.GetByKey(K)` returns.
// 两件事 1 将list到的对象列表 加上事件类型【sync replaced】入队;2 将list中没有 二级缓存中有的对象 加上事件类型【DeletedFinalStateUnknown informer漏掉的删除事件】入队
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Replace(list []interface{}, resourceVersion string) error {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()keys := make(sets.String, len(list))// keep backwards compat for old clientsaction := Syncif f.emitDeltaTypeReplaced {action = Replaced}// Add Sync/Replaced action for each new item.for _, item := range list {key, err := f.KeyOf(item)if err != nil {return KeyError{item, err}}keys.Insert(key)if err := f.queueActionLocked(action, item); err != nil {return fmt.Errorf("couldn't enqueue object: %v", err)}}if f.knownObjects == nil {// Do deletion detection against our own list.queuedDeletions := 0for k, oldItem := range f.items {if keys.Has(k) {continue}// Delete pre-existing items not in the new list.// This could happen if watch deletion event was missed while// disconnected from apiserver.var deletedObj interface{}if n := oldItem.Newest(); n != nil {deletedObj = n.Object}queuedDeletions++if err := f.queueActionLocked(Deleted, DeletedFinalStateUnknown{k, deletedObj}); err != nil {return err}}if !f.populated {f.populated = true// While there shouldn't be any queued deletions in the initial// population of the queue, it's better to be on the safe side.f.initialPopulationCount = len(list) + queuedDeletions}return nil}// Detect deletions not already in the queue.knownKeys := f.knownObjects.ListKeys()queuedDeletions := 0for _, k := range knownKeys {if keys.Has(k) {continue}deletedObj, exists, err := f.knownObjects.GetByKey(k)if err != nil {deletedObj = nilklog.Errorf("Unexpected error %v during lookup of key %v, placing DeleteFinalStateUnknown marker without object", err, k)} else if !exists {deletedObj = nilklog.Infof("Key %v does not exist in known objects store, placing DeleteFinalStateUnknown marker without object", k)}queuedDeletions++if err := f.queueActionLocked(Deleted, DeletedFinalStateUnknown{k, deletedObj}); err != nil {return err}}if !f.populated {f.populated = truef.initialPopulationCount = len(list) + queuedDeletions}return nil
}// Resync adds, with a Sync type of Delta, every object listed by
// `f.knownObjects` whose key is not already queued for processing.
// If `f.knownObjects` is `nil` then Resync does nothing.
// 将二级缓存重新同步到一级缓存队列中,其中事件类型为synctor
// reflector listwatch中会调用
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Resync() error {f.lock.Lock()defer f.lock.Unlock()if f.knownObjects == nil {return nil}keys := f.knownObjects.ListKeys()for _, k := range keys {if err := f.syncKeyLocked(k); err != nil {return err}}return nil
}func (f *DeltaFIFO) syncKeyLocked(key string) error {obj, exists, err := f.knownObjects.GetByKey(key)if err != nil {klog.Errorf("Unexpected error %v during lookup of key %v, unable to queue object for sync", err, key)return nil} else if !exists {klog.Infof("Key %v does not exist in known objects store, unable to queue object for sync", key)return nil}// If we are doing Resync() and there is already an event queued for that object,// we ignore the Resync for it. This is to avoid the race, in which the resync// comes with the previous value of object (since queueing an event for the object// doesn't trigger changing the underlying store . id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}if len(f.items[id]) > 0 {return nil}if err := f.queueActionLocked(Sync, obj); err != nil {return fmt.Errorf("couldn't queue object: %v", err)}return nil
}// A KeyListerGetter is anything that knows how to list its keys and look up by key.
// 实现为indexer
type KeyListerGetter interface {KeyListerKeyGetter
}// A KeyLister is anything that knows how to list its keys.
type KeyLister interface {ListKeys() []string
}// A KeyGetter is anything that knows how to get the value stored under a given key.
type KeyGetter interface {// GetByKey returns the value associated with the key, or sets exists=false.GetByKey(key string) (value interface{}, exists bool, err error)
}// DeltaType is the type of a change (addition, deletion, etc)
type DeltaType string// Change type definition
// 增删改
// 替换、同步在队列函数replace、resync中使用
const (Added DeltaType = "Added"Updated DeltaType = "Updated"Deleted DeltaType = "Deleted"// Replaced is emitted when we encountered watch errors and had to do a// relist. We don't know if the replaced object has changed.//// NOTE: Previous versions of DeltaFIFO would use Sync for Replace events// as well. Hence, Replaced is only emitted when the option// EmitDeltaTypeReplaced is true.Replaced DeltaType = "Replaced"// Sync is for synthetic events during a periodic resync.Sync DeltaType = "Sync"
)// Delta is the type stored by a DeltaFIFO. It tells you what change
// happened, and the object's state after* that change.
//
// [*] Unless the change is a deletion, and then you'll get the final
// state of the object before it was deleted.
// delta的数据结构,带有事件类型和obj
// delta queue中的元素为delta列表,其中按顺序分为最新、最老
type Delta struct {Type DeltaTypeObject interface{}
}// Deltas is a list of one or more 'Delta's to an individual object.
// The oldest delta is at index 0, the newest delta is the last one.
type Deltas []Delta// Oldest is a convenience function that returns the oldest delta, or
// nil if there are no deltas.
func (d Deltas) Oldest() *Delta {if len(d) > 0 {return &d[0]}return nil
}// Newest is a convenience function that returns the newest delta, or
// nil if there are no deltas.
// 对象最新的操作
func (d Deltas) Newest() *Delta {if n := len(d); n > 0 {return &d[n-1]}return nil
}// copyDeltas returns a shallow copy of d; that is, it copies the slice but not
// the objects in the slice. This allows Get/List to return an object that we
// know won't be clobbered by a subsequent modifications.
func copyDeltas(d Deltas) Deltas {d2 := make(Deltas, len(d))copy(d2, d)return d2
}// DeletedFinalStateUnknown is placed into a DeltaFIFO in the case where an object
// was deleted but the watch deletion event was missed while disconnected from
// apiserver. In this case we don't know the final "resting" state of the object, so
// there's a chance the included `Obj` is stale.
// 由于删除事件丢失 远端服务对象已删除 本地二级缓存对象还存在
type DeletedFinalStateUnknown struct {Key stringObj interface{}
}
应用
// test fake KeyFunc
func testFifoObjectKeyFunc(obj interface{}) (string, error) {return obj.(testFifoObject).name, nil
}
type testFifoObject struct {name stringval interface{}
}
func mkFifoObj(name string, val interface{}) testFifoObject {return testFifoObject{name: name, val: val}
}
// helper function to reduce stuttering
func testPop(f *DeltaFIFO) testFifoObject {return Pop(f).(Deltas).Newest().Object.(testFifoObject)
}// keyLookupFunc adapts a raw function to be a KeyLookup.
// test fake KeyListerGetter
type keyLookupFunc func() []testFifoObject// ListKeys just calls kl.
func (kl keyLookupFunc) ListKeys() []string {result := []string{}for _, fifoObj := range kl() {result = append(result, fifoObj.name)}return result
}// GetByKey returns the key if it exists in the list returned by kl.
func (kl keyLookupFunc) GetByKey(key string) (interface{}, bool, error) {for _, v := range kl() {if v.name == key {return v, true, nil}}return nil, false, nil
}// delta fifo
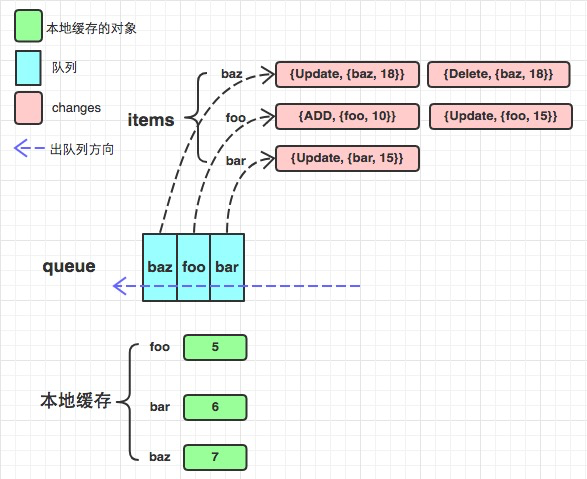
f := NewDeltaFIFO(testFifoObjectKeyFunc,keyLookupFunc(func() []testFifoObject {return []testFifoObject{mkFifoObj("foo", 5), mkFifoObj("bar", 6), mkFifoObj("baz", 7)}}),)f.Update(mkFifoObj("baz", 18))f.Add(mkFifoObj("foo", 10))f.Update(mkFifoObj("bar", 15))f.Update(mkFifoObj("foo", 15))f.Delete(mkFifoObj("baz", 18))//staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/controller.go
func newInformer(lw ListerWatcher,objType runtime.Object,resyncPeriod time.Duration,h ResourceEventHandler,clientState Store,
) Controller {// clientState就是本地缓存 对应的knownObjectsfifo := NewDeltaFIFO(MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, clientState)cfg := &Config{Queue: fifo,ListerWatcher: lw,ObjectType: objType,FullResyncPeriod: resyncPeriod,RetryOnError: false,Process: func(obj interface{}) error {// from oldest to newest 出队列的数组 一个一个操作for _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {// 从一级缓存delta队列中的元素switch d.Type {case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:// 本地缓存存在 更新本地缓存if old, exists, err := clientState.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {if err := clientState.Update(d.Object); err != nil {return err}h.OnUpdate(old, d.Object)} else {// 本地缓存不存在 添加到本地缓存if err := clientState.Add(d.Object); err != nil {return err}h.OnAdd(d.Object)}case Deleted:// 删除本地缓存if err := clientState.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {return err}h.OnDelete(d.Object)}}return nil},}return New(cfg)
}
最终的结果如下:
队列pop出队列的是baz, 然后通过上述的informer中的process 依次对它的两个变化{Update, {baz, 18}}和{Delete, {baz, 20}}进行操作。
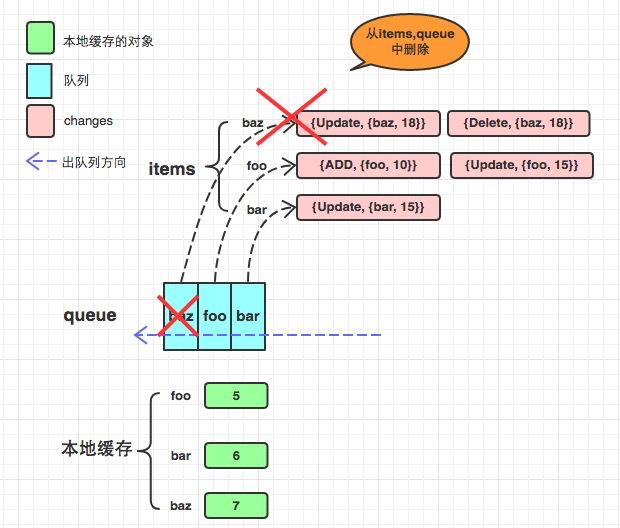
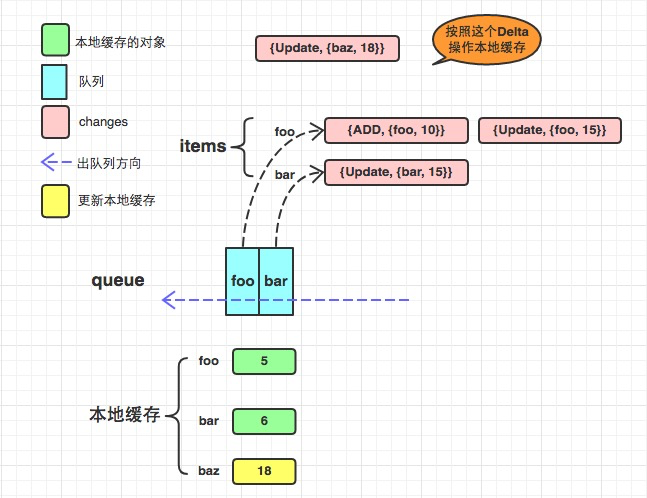
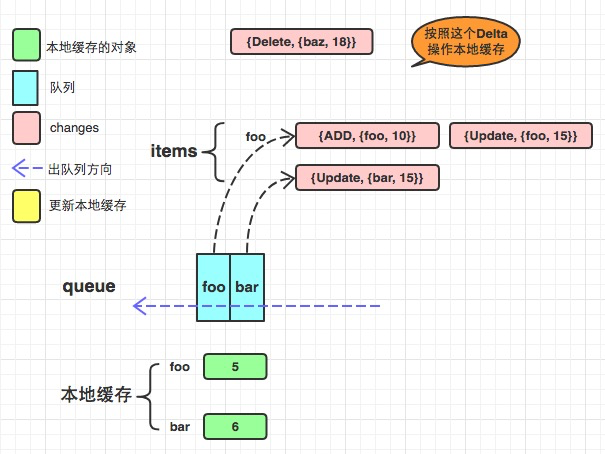
store和index
作为二级缓存,本地缓存存储kv时,保存到到item同时也去更新index。cache实现了indexer接口,其中使用threasafestore实现,其中维护两个数据结构一个item map[string]obj,一个indices,map[string]map[string]set
引用:https://www.jianshu.com/p/76e7b1a57d2c
store和index的实现如下,涉及源码路径如下,接口实现类关系如下。
staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/store.go
staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/index.go
staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
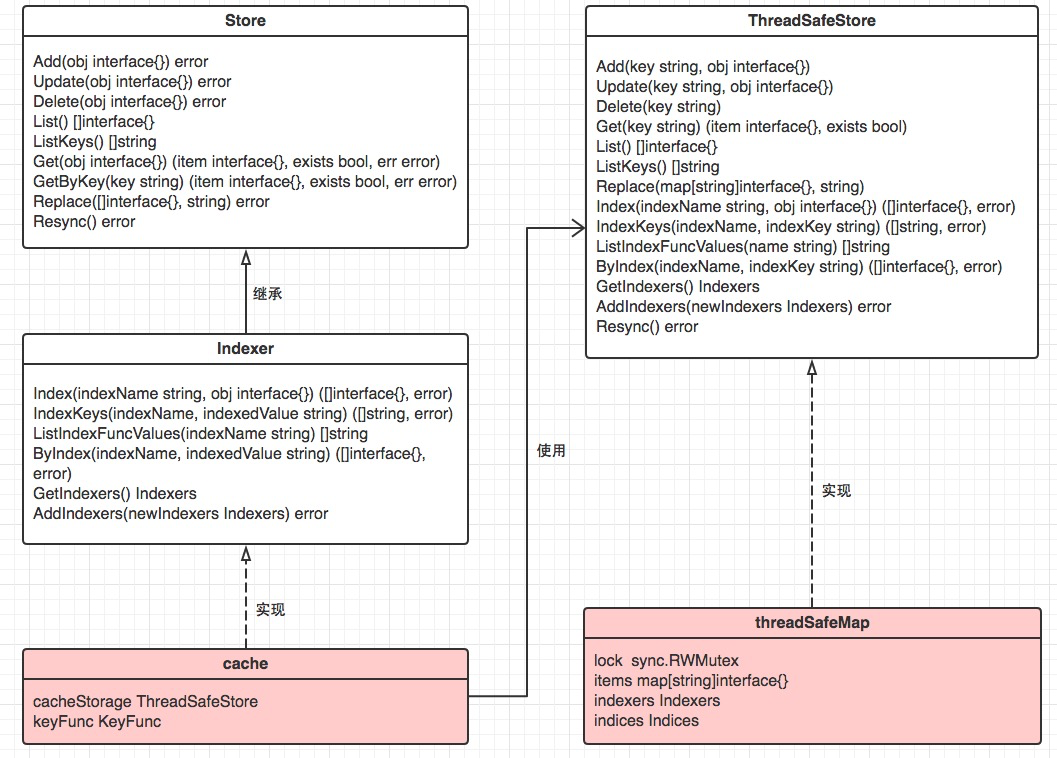
应用
index应用示例:
func testUsersIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {pod := obj.(*v1.Pod)usersString := pod.Annotations["users"]return strings.Split(usersString, ","), nil
}func TestMultiIndexKeys(t *testing.T) {index := NewIndexer(MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, Indexers{"byUser": testUsersIndexFunc})//pod1 := &v1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "one", Annotations: map[string]string{"users": "ernie,bert"}}}pod2 := &v1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "two", Annotations: map[string]string{"users": "bert,oscar"}}}pod3 := &v1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Name: "tre", Annotations: map[string]string{"users": "ernie,elmo"}}}index.Add(pod1)index.Add(pod2)index.Add(pod3)
}add,最终加入pod1, pod2 和pod3,本地缓存生成的数据结构如下,一个map item,key obj;一个indices,索引器名称对应,map,索引函数生成的所有串作为map的key,value为key组成的set。
通过索引名称和索引的key查询,可以看到其实就是取indices["byUser"]["ernie"], 所以返回值就是["one", "tre"]
index.ByIndex("byUser", "ernie")
// tools/cache/store.go
func (c *cache) ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error) {return c.cacheStorage.ByIndex(indexName, indexKey)
}
// tools/cache/thread_safe_store.go
func (c *threadSafeMap) ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error) {c.lock.RLock()defer c.lock.RUnlock()indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]if indexFunc == nil {return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)}index := c.indices[indexName]set := index[indexKey]list := make([]interface{}, 0, set.Len())for key := range set {list = append(list, c.items[key])}return list, nil
}index.Index("byUser", pod1)
// obj的index值对应的所有其他的obj pod1 po2 pod3
// Index returns a list of items that match the given object on the index function.
// Index is thread-safe so long as you treat all items as immutable.
func (c *threadSafeMap) Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error) {c.lock.RLock()defer c.lock.RUnlock()indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]if indexFunc == nil {return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)}indexedValues, err := indexFunc(obj)if err != nil {return nil, err}index := c.indices[indexName]var storeKeySet sets.Stringif len(indexedValues) == 1 {// In majority of cases, there is exactly one value matching.// Optimize the most common path - deduping is not needed here.storeKeySet = index[indexedValues[0]]} else {// Need to de-dupe the return list.// Since multiple keys are allowed, this can happen.storeKeySet = sets.String{}for _, indexedValue := range indexedValues {for key := range index[indexedValue] {storeKeySet.Insert(key)}}}list := make([]interface{}, 0, storeKeySet.Len())for storeKey := range storeKeySet {list = append(list, c.items[storeKey])}return list, nil
}
源码
store源码:
type Store interface {// Add adds the given object to the accumulator associated with the given object's keyAdd(obj interface{}) error// Update updates the given object in the accumulator associated with the given object's keyUpdate(obj interface{}) error// Delete deletes the given object from the accumulator associated with the given object's keyDelete(obj interface{}) error// List returns a list of all the currently non-empty accumulatorsList() []interface{}// ListKeys returns a list of all the keys currently associated with non-empty accumulatorsListKeys() []string// Get returns the accumulator associated with the given object's keyGet(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)// GetByKey returns the accumulator associated with the given keyGetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)// Replace will delete the contents of the store, using instead the// given list. Store takes ownership of the list, you should not reference// it after calling this function.Replace([]interface{}, string) error// Resync is meaningless in the terms appearing here but has// meaning in some implementations that have non-trivial// additional behavior (e.g., DeltaFIFO).Resync() error
}// KeyFunc knows how to make a key from an object. Implementations should be deterministic.
type KeyFunc func(obj interface{}) (string, error)// KeyError will be returned any time a KeyFunc gives an error; it includes the object
// at fault.
type KeyError struct {Obj interface{}Err error
}// Error gives a human-readable description of the error.
func (k KeyError) Error() string {return fmt.Sprintf("couldn't create key for object %+v: %v", k.Obj, k.Err)
}// ExplicitKey can be passed to MetaNamespaceKeyFunc if you have the key for
// the object but not the object itself.
type ExplicitKey string// MetaNamespaceKeyFunc is a convenient default KeyFunc which knows how to make
// keys for API objects which implement meta.Interface.
// The key uses the format / unless is empty, then
// it's just .
//
// TODO: replace key-as-string with a key-as-struct so that this
// packing/unpacking won't be necessary.
// 默认的key func取对象的ns/name
func MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj interface{}) (string, error) {if key, ok := obj.(ExplicitKey); ok {return string(key), nil}meta, err := meta.Accessor(obj)if err != nil {return "", fmt.Errorf("object has no meta: %v", err)}if len(meta.GetNamespace()) > 0 {return meta.GetNamespace() + "/" + meta.GetName(), nil}return meta.GetName(), nil
}// SplitMetaNamespaceKey returns the namespace and name that
// MetaNamespaceKeyFunc encoded into key.
//
// TODO: replace key-as-string with a key-as-struct so that this
// packing/unpacking won't be necessary.
func SplitMetaNamespaceKey(key string) (namespace, name string, err error) {parts := strings.Split(key, "/")switch len(parts) {case 1:// name only, no namespacereturn "", parts[0], nilcase 2:// namespace and namereturn parts[0], parts[1], nil}return "", "", fmt.Errorf("unexpected key format: %q", key)
}// `*cache` implements Indexer in terms of a ThreadSafeStore and an
// associated KeyFunc.
// 对外暴露的二级本地缓存 真正实现逻辑在ThreadSafeStore中
type cache struct {// cacheStorage bears the burden of thread safety for the cachecacheStorage ThreadSafeStore// keyFunc is used to make the key for objects stored in and retrieved from items, and// should be deterministic.keyFunc KeyFunc
}// 判断是否实现Store接口否则编译失败
var _ Store = &cache{}// Add inserts an item into the cache.
func (c *cache) Add(obj interface{}) error {key, err := c.keyFunc(obj)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}c.cacheStorage.Add(key, obj)return nil
}// Update sets an item in the cache to its updated state.
func (c *cache) Update(obj interface{}) error {key, err := c.keyFunc(obj)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}c.cacheStorage.Update(key, obj)return nil
}// Delete removes an item from the cache.
func (c *cache) Delete(obj interface{}) error {key, err := c.keyFunc(obj)if err != nil {return KeyError{obj, err}}c.cacheStorage.Delete(key)return nil
}// List returns a list of all the items.
// List is completely threadsafe as long as you treat all items as immutable.
func (c *cache) List() []interface{} {return c.cacheStorage.List()
}// ListKeys returns a list of all the keys of the objects currently
// in the cache.
func (c *cache) ListKeys() []string {return c.cacheStorage.ListKeys()
}// GetIndexers returns the indexers of cache
func (c *cache) GetIndexers() Indexers {return c.cacheStorage.GetIndexers()
}// Index returns a list of items that match on the index function
// Index is thread-safe so long as you treat all items as immutable
func (c *cache) Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error) {return c.cacheStorage.Index(indexName, obj)
}func (c *cache) IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error) {return c.cacheStorage.IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey)
}// ListIndexFuncValues returns the list of generated values of an Index func
func (c *cache) ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string {return c.cacheStorage.ListIndexFuncValues(indexName)
}func (c *cache) ByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error) {return c.cacheStorage.ByIndex(indexName, indexKey)
}func (c *cache) AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error {return c.cacheStorage.AddIndexers(newIndexers)
}// Get returns the requested item, or sets exists=false.
// Get is completely threadsafe as long as you treat all items as immutable.
func (c *cache) Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) {key, err := c.keyFunc(obj)if err != nil {return nil, false, KeyError{obj, err}}return c.GetByKey(key)
}// GetByKey returns the request item, or exists=false.
// GetByKey is completely threadsafe as long as you treat all items as immutable.
func (c *cache) GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error) {item, exists = c.cacheStorage.Get(key)return item, exists, nil
}// Replace will delete the contents of 'c', using instead the given list.
// 'c' takes ownership of the list, you should not reference the list again
// after calling this function.
func (c *cache) Replace(list []interface{}, resourceVersion string) error {items := make(map[string]interface{}, len(list))for _, item := range list {key, err := c.keyFunc(item)if err != nil {return KeyError{item, err}}items[key] = item}c.cacheStorage.Replace(items, resourceVersion)return nil
}// Resync is meaningless for one of these
func (c *cache) Resync() error {return nil
}// NewStore returns a Store implemented simply with a map and a lock.
// 不带索引函数的二级缓存
func NewStore(keyFunc KeyFunc) Store {return &cache{cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(Indexers{}, Indices{}),keyFunc: keyFunc,}
}// NewIndexer returns an Indexer implemented simply with a map and a lock.
// 带索引函数的二级缓存
func NewIndexer(keyFunc KeyFunc, indexers Indexers) Indexer {return &cache{cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(indexers, Indices{}),keyFunc: keyFunc,}
}
二级本地缓存的主逻辑实现代码:
type ThreadSafeStore interface {Add(key string, obj interface{})Update(key string, obj interface{})Delete(key string)Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool)List() []interface{}ListKeys() []stringReplace(map[string]interface{}, string)Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)IndexKeys(indexName, indexKey string) ([]string, error)ListIndexFuncValues(name string) []stringByIndex(indexName, indexKey string) ([]interface{}, error)GetIndexers() Indexers// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data// in the store, the results are undefined.AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error// Resync is a no-op and is deprecatedResync() error
}// threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore
type threadSafeMap struct {lock sync.RWMutexitems map[string]interface{}// indexers maps a name to an IndexFuncindexers Indexers// indices maps a name to an Indexindices Indices
}func (c *threadSafeMap) Add(key string, obj interface{}) {c.lock.Lock()defer c.lock.Unlock()oldObject := c.items[key]c.items[key] = objc.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key)
}func (c *threadSafeMap) Update(key string, obj interface{}) {c.lock.Lock()defer c.lock.Unlock()oldObject := c.items[key]c.items[key] = objc.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key)
}func (c *threadSafeMap) Delete(key string) {c.lock.Lock()defer c.lock.Unlock()if obj, exists := c.items[key]; exists {c.deleteFromIndices(obj, key)delete(c.items, key)}
}func (c *threadSafeMap) Get(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool) {c.lock.RLock()defer c.lock.RUnlock()item, exists = c.items[key]return item, exists
}func (c *threadSafeMap) List() []interface{} {c.lock.RLock()defer c.lock.RUnlock()list := make([]interface{}, 0, len(c.items))for _, item := range c.items {list = append(list, item)}return list
}// ListKeys returns a list of all the keys of the objects currently
// in the threadSafeMap.
func (c *threadSafeMap) ListKeys() []string {c.lock.RLock()defer c.lock.RUnlock()list := make([]string, 0, len(c.items))for key := range c.items {list = append(list, key)}return list
}func (c *threadSafeMap) Replace(items map[string]interface{}, resourceVersion string) {c.lock.Lock()defer c.lock.Unlock()c.items = items// rebuild any indexc.indices = Indices{}for key, item := range c.items {c.updateIndices(nil, item, key)}
}// Index returns a list of items that match the given object on the index function.
// Index is thread-safe so long as you treat all items as immutable.
func (c *threadSafeMap) Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error) {c.lock.RLock()defer c.lock.RUnlock()indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]if indexFunc == nil {return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)}indexedValues, err := indexFunc(obj)if err != nil {return nil, err}index := c.indices[indexName]var storeKeySet sets.Stringif len(indexedValues) == 1 {// In majority of cases, there is exactly one value matching.// Optimize the most common path - deduping is not needed here.storeKeySet = index[indexedValues[0]]} else {// Need to de-dupe the return list.// Since multiple keys are allowed, this can happen.storeKeySet = sets.String{}for _, indexedValue := range indexedValues {for key := range index[indexedValue] {storeKeySet.Insert(key)}}}list := make([]interface{}, 0, storeKeySet.Len())for storeKey := range storeKeySet {list = append(list, c.items[storeKey])}return list, nil
}// ByIndex returns a list of the items whose indexed values in the given index include the given indexed value
func (c *threadSafeMap) ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error) {c.lock.RLock()defer c.lock.RUnlock()indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]if indexFunc == nil {return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)}index := c.indices[indexName]set := index[indexedValue]list := make([]interface{}, 0, set.Len())for key := range set {list = append(list, c.items[key])}return list, nil
}// IndexKeys returns a list of the Store keys of the objects whose indexed values in the given index include the given indexed value.
// IndexKeys is thread-safe so long as you treat all items as immutable.
func (c *threadSafeMap) IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error) {c.lock.RLock()defer c.lock.RUnlock()indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]if indexFunc == nil {return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)}index := c.indices[indexName]set := index[indexedValue]return set.List(), nil
}func (c *threadSafeMap) ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string {c.lock.RLock()defer c.lock.RUnlock()index := c.indices[indexName]names := make([]string, 0, len(index))for key := range index {names = append(names, key)}return names
}func (c *threadSafeMap) GetIndexers() Indexers {return c.indexers
}func (c *threadSafeMap) AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error {c.lock.Lock()defer c.lock.Unlock()if len(c.items) > 0 {return fmt.Errorf("cannot add indexers to running index")}oldKeys := sets.StringKeySet(c.indexers)newKeys := sets.StringKeySet(newIndexers)if oldKeys.HasAny(newKeys.List()...) {return fmt.Errorf("indexer conflict: %v", oldKeys.Intersection(newKeys))}for k, v := range newIndexers {c.indexers[k] = v}return nil
}// updateIndices modifies the objects location in the managed indexes, if this is an update, you must provide an oldObj
// updateIndices must be called from a function that already has a lock on the cache
func (c *threadSafeMap) updateIndices(oldObj interface{}, newObj interface{}, key string) {// if we got an old object, we need to remove it before we add it againif oldObj != nil {c.deleteFromIndices(oldObj, key)}for name, indexFunc := range c.indexers {indexValues, err := indexFunc(newObj)if err != nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("unable to calculate an index entry for key %q on index %q: %v", key, name, err))}index := c.indices[name]if index == nil {index = Index{}c.indices[name] = index}for _, indexValue := range indexValues {set := index[indexValue]if set == nil {set = sets.String{}index[indexValue] = set}set.Insert(key)}}
}// deleteFromIndices removes the object from each of the managed indexes
// it is intended to be called from a function that already has a lock on the cache
func (c *threadSafeMap) deleteFromIndices(obj interface{}, key string) {for name, indexFunc := range c.indexers {indexValues, err := indexFunc(obj)if err != nil {panic(fmt.Errorf("unable to calculate an index entry for key %q on index %q: %v", key, name, err))}index := c.indices[name]if index == nil {continue}for _, indexValue := range indexValues {set := index[indexValue]if set != nil {set.Delete(key)// If we don't delete the set when zero, indices with high cardinality// short lived resources can cause memory to increase over time from// unused empty sets. See `kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/84959`.if len(set) == 0 {delete(index, indexValue)}}}}
}func (c *threadSafeMap) Resync() error {// Nothing to doreturn nil
}// NewThreadSafeStore creates a new instance of ThreadSafeStore.
func NewThreadSafeStore(indexers Indexers, indices Indices) ThreadSafeStore {return &threadSafeMap{items: map[string]interface{}{},indexers: indexers,indices: indices,}
}reflector
原理
reflector通过ListerWatcher封装rest api去list watch 某个k8s的资源,将事件入delta队列中。
reflector属于一个反射器, 上面对接从k8s api获得信息的ListWatcher, 下面对接DeltaFIFO, 也就是把k8s api获得的信息通过reflector存储到DeltaFIFO中.
reflector中有一个listerWatcher ListerWatcher, 该对象是从api-server中获得元素和监控. 也有一个store Store对象, 这个在informers体系中是DeltaFIFO的一个对象,一级缓存.
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/79194ca934e5
resourceVersion
参考:https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/reference/using-api/api-concepts/
为了使客户端能够构造一个模型来表达集群的当前状态,所有 Kubernetes 对象资源类型 都需要支持一致的列表和一个称作 watch 的增量变更通知信源(feed)。 每个 Kubernetes 对象都有一个 resourceVersion 字段,代表该资源在下层数据库中 存储的版本。检视资源集合(名字空间作用域或集群作用域)时,服务器返回的响应 中会包含 resourceVersion 值,可用来向服务器发起 watch 请求。 服务器会返回所提供的 resourceVersion 之后发生的所有变更(创建、删除和更新)。 这使得客户端能够取回当前的状态并监视其变更,且不会错过任何变更事件。 客户端的监视连接被断开时,可以从最后返回的 resourceVersion 重启新的监视连接, 或者执行一个新的集合请求之后从头开始监视操作。k8s的并发操作是通过ResourceVersion来实现的, 在api-server该对象有一次改动, ResourceVersion就会加1。
给定的 Kubernetes 服务器只会保留一定的时间内发生的历史变更列表。 使用 etcd3 的集群默认保存过去 5 分钟内发生的变更。 当所请求的 watch 操作因为资源的历史版本不存在而失败,客户端必须能够处理 因此而返回的状态代码 410 Gone,清空其本地的缓存,重新执行 list 操作, 并基于新的 list 操作所返回的 resourceVersion 来开始新的 watch 操作。 大多数客户端库都能够提供某种形式的、包含此逻辑的工具。 (在 Go 语言客户端库中,这一设施称作 Reflector,位于 k8s.io/client-go/cache 包中。)
listwatch
参考 https://www.jianshu.com/p/79194ca934e5
listwatch apiserver的消息,同步到delta queue。
整个
reflector所做的工作就是从list中获得所有对象, 然后根据当时拿到的resouceVersion开始进行监控后面的一系列操作, 然后加入到deltaFIFO中.
然后负责工作的是
WatchHandler, 当该方法中出现不是nil的错误时, 会重新调用WatchList方法重新获得list并replace对接的deltaFIFO. 如果出现的错误是nil, 这种情况是因为watch被关闭了, 这个时候watchHandler会返回到WatchList重新再次生成一个watch对象重新调用watchHandler进行监控.
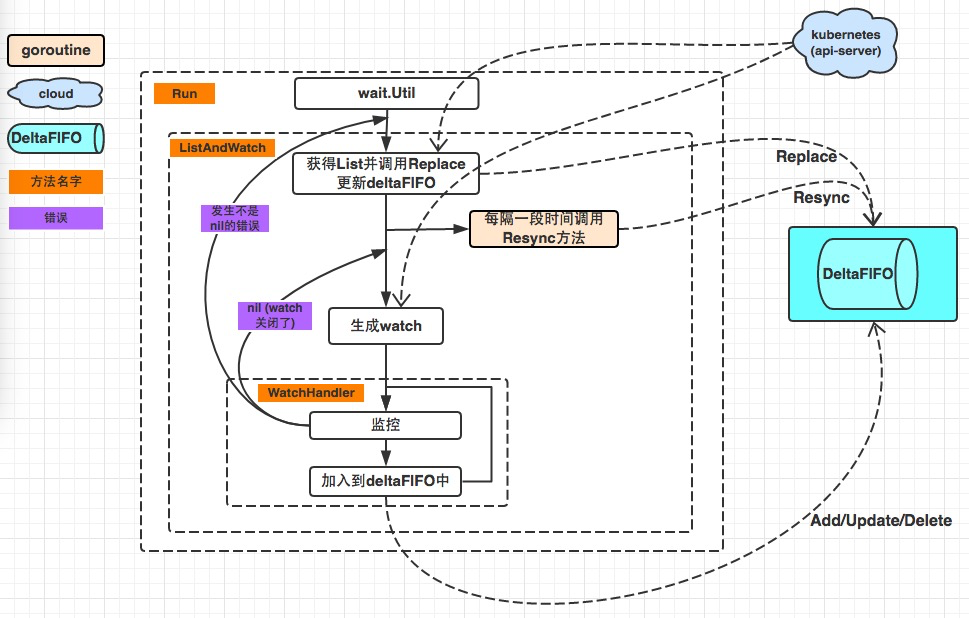
源码
const defaultExpectedTypeName = "" // Reflector watches a specified resource and causes all changes to be reflected in the given store.
type Reflector struct {// name identifies this reflector. By default it will be a file:line if possible.name string// The name of the type we expect to place in the store. The name// will be the stringification of expectedGVK if provided, and the// stringification of expectedType otherwise. It is for display// only, and should not be used for parsing or comparison.expectedTypeName string// An example object of the type we expect to place in the store.// Only the type needs to be right, except that when that is// `unstructured.Unstructured` the object's `"apiVersion"` and// `"kind"` must also be right.expectedType reflect.Type// The GVK of the object we expect to place in the store if unstructured.expectedGVK *schema.GroupVersionKind// The destination to sync up with the watch source// 存储的一级缓存DeltaFIFO队列store Store// listerWatcher is used to perform lists and watches.listerWatcher ListerWatcher// backoff manages backoff of ListWatchbackoffManager wait.BackoffManagerresyncPeriod time.Duration// ShouldResync is invoked periodically and whenever it returns `true` the Store's Resync operation is invokedShouldResync func() bool// clock allows tests to manipulate timeclock clock.Clock// paginatedResult defines whether pagination should be forced for list calls.// It is set based on the result of the initial list call.paginatedResult bool// lastSyncResourceVersion is the resource version token last// observed when doing a sync with the underlying store// it is thread safe, but not synchronized with the underlying store// 最后一次sync的resourceversionlastSyncResourceVersion string// isLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable is true if the previous list or watch request with// lastSyncResourceVersion failed with an "expired" or "too large resource version" error.isLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable bool// lastSyncResourceVersionMutex guards read/write access to lastSyncResourceVersionlastSyncResourceVersionMutex sync.RWMutex// WatchListPageSize is the requested chunk size of initial and resync watch lists.// If unset, for consistent reads (RV="") or reads that opt-into arbitrarily old data// (RV="0") it will default to pager.PageSize, for the rest (RV != "" && RV != "0")// it will turn off pagination to allow serving them from watch cache.// NOTE: It should be used carefully as paginated lists are always served directly from// etcd, which is significantly less efficient and may lead to serious performance and// scalability problems.WatchListPageSize int64// Called whenever the ListAndWatch drops the connection with an error.watchErrorHandler WatchErrorHandler
}// The WatchErrorHandler is called whenever ListAndWatch drops the
// connection with an error. After calling this handler, the informer
// will backoff and retry.
//
// The default implementation looks at the error type and tries to log
// the error message at an appropriate level.
//
// Implementations of this handler may display the error message in other
// ways. Implementations should return quickly - any expensive processing
// should be offloaded.
type WatchErrorHandler func(r *Reflector, err error)// DefaultWatchErrorHandler is the default implementation of WatchErrorHandler
func DefaultWatchErrorHandler(r *Reflector, err error) {switch {case isExpiredError(err):// Don't set LastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable - LIST call with ResourceVersion=RV already// has a semantic that it returns data at least as fresh as provided RV.// So first try to LIST with setting RV to resource version of last observed object.klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v closed with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)case err == io.EOF:// watch closed normallycase err == io.ErrUnexpectedEOF:klog.V(1).Infof("%s: Watch for %v closed with unexpected EOF: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)default:utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: Failed to watch %v: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err))}
}var (// We try to spread the load on apiserver by setting timeouts for// watch requests - it is random in [minWatchTimeout, 2*minWatchTimeout].minWatchTimeout = 5 * time.Minute
)// NewNamespaceKeyedIndexerAndReflector creates an Indexer and a Reflector
// The indexer is configured to key on namespace
func NewNamespaceKeyedIndexerAndReflector(lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, resyncPeriod time.Duration) (indexer Indexer, reflector *Reflector) {indexer = NewIndexer(MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, Indexers{NamespaceIndex: MetaNamespaceIndexFunc})reflector = NewReflector(lw, expectedType, indexer, resyncPeriod)return indexer, reflector
}// NewReflector creates a new Reflector object which will keep the
// given store up to date with the server's contents for the given
// resource. Reflector promises to only put things in the store that
// have the type of expectedType, unless expectedType is nil. If
// resyncPeriod is non-zero, then the reflector will periodically
// consult its ShouldResync function to determine whether to invoke
// the Store's Resync operation; `ShouldResync==nil` means always
// "yes". This enables you to use reflectors to periodically process
// everything as well as incrementally processing the things that
// change.
func NewReflector(lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {return NewNamedReflector(naming.GetNameFromCallsite(internalPackages...), lw, expectedType, store, resyncPeriod)
}// NewNamedReflector same as NewReflector, but with a specified name for logging
func NewNamedReflector(name string, lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {realClock := &clock.RealClock{}r := &Reflector{name: name,listerWatcher: lw,store: store,// We used to make the call every 1sec (1 QPS), the goal here is to achieve ~98% traffic reduction when// API server is not healthy. With these parameters, backoff will stop at [30,60) sec interval which is// 0.22 QPS. If we don't backoff for 2min, assume API server is healthy and we reset the backoff.backoffManager: wait.NewExponentialBackoffManager(800*time.Millisecond, 30*time.Second, 2*time.Minute, 2.0, 1.0, realClock),resyncPeriod: resyncPeriod,clock: realClock,watchErrorHandler: WatchErrorHandler(DefaultWatchErrorHandler),}r.setExpectedType(expectedType)return r
}func (r *Reflector) setExpectedType(expectedType interface{}) {r.expectedType = reflect.TypeOf(expectedType)if r.expectedType == nil {r.expectedTypeName = defaultExpectedTypeNamereturn}r.expectedTypeName = r.expectedType.String()if obj, ok := expectedType.(*unstructured.Unstructured); ok {// Use gvk to check that watch event objects are of the desired type.gvk := obj.GroupVersionKind()if gvk.Empty() {klog.V(4).Infof("Reflector from %s configured with expectedType of *unstructured.Unstructured with empty GroupVersionKind.", r.name)return}r.expectedGVK = &gvkr.expectedTypeName = gvk.String()}
}// internalPackages are packages that ignored when creating a default reflector name. These packages are in the common
// call chains to NewReflector, so they'd be low entropy names for reflectors
var internalPackages = []string{"client-go/tools/cache/"}// Run repeatedly uses the reflector's ListAndWatch to fetch all the
// objects and subsequent deltas.
// Run will exit when stopCh is closed.
func (r *Reflector) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {klog.V(2).Infof("Starting reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)// 循环执行list watch 直到stopch,一个执行完才执行下一个// BackoffUntil loops until stop channel is closed, run f every duration given by BackoffManager.wait.BackoffUntil(func() {if err := r.ListAndWatch(stopCh); err != nil {r.watchErrorHandler(r, err)}}, r.backoffManager, true, stopCh)klog.V(2).Infof("Stopping reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
}var (// nothing will ever be sent down this channelneverExitWatch <-chan time.Time = make(chan time.Time)// Used to indicate that watching stopped because of a signal from the stop// channel passed in from a client of the reflector.errorStopRequested = errors.New("Stop requested")
)// resyncChan returns a channel which will receive something when a resync is
// required, and a cleanup function.
func (r *Reflector) resyncChan() (<-chan time.Time, func() bool) {if r.resyncPeriod == 0 {return neverExitWatch, func() bool { return false }}// The cleanup function is required: imagine the scenario where watches// always fail so we end up listing frequently. Then, if we don't// manually stop the timer, we could end up with many timers active// concurrently.t := r.clock.NewTimer(r.resyncPeriod)return t.C(), t.Stop
}// ListAndWatch first lists all items and get the resource version at the moment of call,
// and then use the resource version to watch.
// It returns error if ListAndWatch didn't even try to initialize watch.
// 主要逻辑
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {klog.V(3).Infof("Listing and watching %v from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.name)var resourceVersion stringoptions := metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()}// LIST 将获取到的资源list和资源版本刷新替换本地缓存// resourceVersion page continue...if err := func() error {initTrace := trace.New("Reflector ListAndWatch", trace.Field{"name", r.name})defer initTrace.LogIfLong(10 * time.Second)var list runtime.Objectvar paginatedResult boolvar err errorlistCh := make(chan struct{}, 1)panicCh := make(chan interface{}, 1)go func() {defer func() {if r := recover(); r != nil {panicCh <- r}}()// Attempt to gather list in chunks, if supported by listerWatcher, if not, the first// list request will return the full response.// list 的分页pager := pager.New(pager.SimplePageFunc(func(opts metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {return r.listerWatcher.List(opts)}))switch {case r.WatchListPageSize != 0:pager.PageSize = r.WatchListPageSizecase r.paginatedResult:// We got a paginated result initially. Assume this resource and server honor// paging requests (i.e. watch cache is probably disabled) and leave the default// pager size set.case options.ResourceVersion != "" && options.ResourceVersion != "0":// User didn't explicitly request pagination.//// With ResourceVersion != "", we have a possibility to list from watch cache,// but we do that (for ResourceVersion != "0") only if Limit is unset.// To avoid thundering herd on etcd (e.g. on master upgrades), we explicitly// switch off pagination to force listing from watch cache (if enabled).// With the existing semantic of RV (result is at least as fresh as provided RV),// this is correct and doesn't lead to going back in time.//// We also don't turn off pagination for ResourceVersion="0", since watch cache// is ignoring Limit in that case anyway, and if watch cache is not enabled// we don't introduce regression.pager.PageSize = 0}list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), options)if isExpiredError(err) || isTooLargeResourceVersionError(err) {r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(true)// Retry immediately if the resource version used to list is unavailable.// The pager already falls back to full list if paginated list calls fail due to an "Expired" error on// continuation pages, but the pager might not be enabled, the full list might fail because the// resource version it is listing at is expired or the cache may not yet be synced to the provided// resource version. So we need to fallback to resourceVersion="" in all to recover and ensure// the reflector makes forward progress.// listlist, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()})}close(listCh)}()select {case <-stopCh:return nilcase r := <-panicCh:panic(r)case <-listCh:}if err != nil {return fmt.Errorf("failed to list %v: %v", r.expectedTypeName, err)}// We check if the list was paginated and if so set the paginatedResult based on that.// However, we want to do that only for the initial list (which is the only case// when we set ResourceVersion="0"). The reasoning behind it is that later, in some// situations we may force listing directly from etcd (by setting ResourceVersion="")// which will return paginated result, even if watch cache is enabled. However, in// that case, we still want to prefer sending requests to watch cache if possible.//// Paginated result returned for request with ResourceVersion="0" mean that watch// cache is disabled and there are a lot of objects of a given type. In such case,// there is no need to prefer listing from watch cache.if options.ResourceVersion == "0" && paginatedResult {r.paginatedResult = true}r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(false) // list was successfulinitTrace.Step("Objects listed")listMetaInterface, err := meta.ListAccessor(list)if err != nil {return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v: %v", list, err)}resourceVersion = listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion()initTrace.Step("Resource version extracted")items, err := meta.ExtractList(list)if err != nil {return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v (%v)", list, err)}initTrace.Step("Objects extracted")// 将获取到的资源list和资源版本刷新替换一级缓存Deltafifoif err := r.syncWith(items, resourceVersion); err != nil {return fmt.Errorf("unable to sync list result: %v", err)}initTrace.Step("SyncWith done")r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion)initTrace.Step("Resource version updated")return nil}(); err != nil {return err}// ????// 这里主要是启动一个异步goroutine 每隔r.resyncPeriod时间调用DeltaFIFO的Resyncresyncerrc := make(chan error, 1)cancelCh := make(chan struct{})defer close(cancelCh)go func() {resyncCh, cleanup := r.resyncChan()defer func() {cleanup() // Call the last one written into cleanup}()for {select {case <-resyncCh:case <-stopCh:returncase <-cancelCh:return}if r.ShouldResync == nil || r.ShouldResync() {klog.V(4).Infof("%s: forcing resync", r.name)// 调用DeltaFIFO的Resync 将二级缓存同步到一级缓存delta queue中if err := r.store.Resync(); err != nil {resyncerrc <- errreturn}}cleanup()resyncCh, cleanup = r.resyncChan()}}()// WATCH watch资源,将资源的增删改事件存到delta queue// 根据当前的ResourceVersion生成一个watch// 监控该ResourceVersion后面的一系列变化 然后对应加入到DeltaFIFO中for {// give the stopCh a chance to stop the loop, even in case of continue statements further down on errorsselect {case <-stopCh:return nildefault:}timeoutSeconds := int64(minWatchTimeout.Seconds() * (rand.Float64() + 1.0))options = metav1.ListOptions{// 资源版本 超时时间5-10分钟ResourceVersion: resourceVersion,// We want to avoid situations of hanging watchers. Stop any wachers that do not// receive any events within the timeout window.TimeoutSeconds: &timeoutSeconds,// To reduce load on kube-apiserver on watch restarts, you may enable watch bookmarks.// Reflector doesn't assume bookmarks are returned at all (if the server do not support// watch bookmarks, it will ignore this field).AllowWatchBookmarks: true,}// start the clock before sending the request, since some proxies won't flush headers until after the first watch event is sentstart := r.clock.Now()w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)if err != nil {// If this is "connection refused" error, it means that most likely apiserver is not responsive.// It doesn't make sense to re-list all objects because most likely we will be able to restart// watch where we ended.// If that's the case wait and resend watch request.if utilnet.IsConnectionRefused(err) {time.Sleep(time.Second)continue}return err}if err := r.watchHandler(start, w, &resourceVersion, resyncerrc, stopCh); err != nil {if err != errorStopRequested {switch {case isExpiredError(err):// Don't set LastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable - LIST call with ResourceVersion=RV already// has a semantic that it returns data at least as fresh as provided RV.// So first try to LIST with setting RV to resource version of last observed object.klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v closed with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)default:klog.Warningf("%s: watch of %v ended with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)}}return nil}}
}// syncWith replaces the store's items with the given list.
func (r *Reflector) syncWith(items []runtime.Object, resourceVersion string) error {found := make([]interface{}, 0, len(items))for _, item := range items {found = append(found, item)}return r.store.Replace(found, resourceVersion)
}// watchHandler watches w and keeps *resourceVersion up to date.
// 承上,listwatch的子函数,watch到的事件的增删改处理
func (r *Reflector) watchHandler(start time.Time, w watch.Interface, resourceVersion *string, errc chan error, stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {eventCount := 0// Stopping the watcher should be idempotent and if we return from this function there's no way// we're coming back in with the same watch interface.defer w.Stop()loop:for {select {// stopCh被close了 退出watchHandler方法case <-stopCh:// DeltaFIFO的Resync出现错误,退出watchHandler方法return errorStopRequestedcase err := <-errc:return errcase event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():if !ok {// watch这个channel已经被关闭 跳出loopbreak loop}if event.Type == watch.Error {return apierrors.FromObject(event.Object)}if r.expectedType != nil {// 得到的对象类型与该reflector监控的类型不一致// 比如该reflector负责的是pod对象 来了一个Service对象if e, a := r.expectedType, reflect.TypeOf(event.Object); e != a {utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected type %v, but watch event object had type %v", r.name, e, a))continue}}if r.expectedGVK != nil {if e, a := *r.expectedGVK, event.Object.GetObjectKind().GroupVersionKind(); e != a {utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected gvk %v, but watch event object had gvk %v", r.name, e, a))continue}}meta, err := meta.Accessor(event.Object)if err != nil {utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))continue}// 获得新的ResourceVersionnewResourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()switch event.Type {case watch.Added:// 往Delta添加一个对象err := r.store.Add(event.Object)if err != nil {utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))}case watch.Modified:// 往Delta更新一个对象err := r.store.Update(event.Object)if err != nil {utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to update watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))}case watch.Deleted:// TODO: Will any consumers need access to the "last known// state", which is passed in event.Object? If so, may need// to change this.// 往Delta删除一个对象err := r.store.Delete(event.Object)if err != nil {utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to delete watch event object (%#v) from store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))}case watch.Bookmark:// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersiondefault:utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))}*resourceVersion = newResourceVersionr.setLastSyncResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)eventCount++}}watchDuration := r.clock.Since(start)// 如果该watch一个event都没有处理 并且1秒钟都不到// 那有可能问题 所以会返回一个错误 此时退出watchHandler后, 会整个退出ListAndWatch, Run中的util会再次调用ListAndWatch方法.if watchDuration < 1*time.Second && eventCount == 0 {return fmt.Errorf("very short watch: %s: Unexpected watch close - watch lasted less than a second and no items received", r.name)}klog.V(4).Infof("%s: Watch close - %v total %v items received", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, eventCount)return nil
}// LastSyncResourceVersion is the resource version observed when last sync with the underlying store
// The value returned is not synchronized with access to the underlying store and is not thread-safe
func (r *Reflector) LastSyncResourceVersion() string {r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.RLock()defer r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.RUnlock()return r.lastSyncResourceVersion
}func (r *Reflector) setLastSyncResourceVersion(v string) {r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.Lock()defer r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.Unlock()r.lastSyncResourceVersion = v
}// relistResourceVersion determines the resource version the reflector should list or relist from.
// Returns either the lastSyncResourceVersion so that this reflector will relist with a resource
// versions no older than has already been observed in relist results or watch events, or, if the last relist resulted
// in an HTTP 410 (Gone) status code, returns "" so that the relist will use the latest resource version available in
// etcd via a quorum read.
func (r *Reflector) relistResourceVersion() string {r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.RLock()defer r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.RUnlock()if r.isLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable {// Since this reflector makes paginated list requests, and all paginated list requests skip the watch cache// if the lastSyncResourceVersion is unavailable, we set ResourceVersion="" and list again to re-establish reflector// to the latest available ResourceVersion, using a consistent read from etcd.return ""}if r.lastSyncResourceVersion == "" {// For performance reasons, initial list performed by reflector uses "0" as resource version to allow it to// be served from the watch cache if it is enabled.return "0"}return r.lastSyncResourceVersion
}// setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable sets if the last list or watch request with lastSyncResourceVersion returned
// "expired" or "too large resource version" error.
func (r *Reflector) setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(isUnavailable bool) {r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.Lock()defer r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.Unlock()r.isLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable = isUnavailable
}func isExpiredError(err error) bool {// In Kubernetes 1.17 and earlier, the api server returns both apierrors.StatusReasonExpired and// apierrors.StatusReasonGone for HTTP 410 (Gone) status code responses. In 1.18 the kube server is more consistent// and always returns apierrors.StatusReasonExpired. For backward compatibility we can only remove the apierrors.IsGone// check when we fully drop support for Kubernetes 1.17 servers from reflectors.return apierrors.IsResourceExpired(err) || apierrors.IsGone(err)
}func isTooLargeResourceVersionError(err error) bool {if apierrors.HasStatusCause(err, metav1.CauseTypeResourceVersionTooLarge) {return true}// In Kubernetes 1.17.0-1.18.5, the api server doesn't set the error status cause to// metav1.CauseTypeResourceVersionTooLarge to indicate that the requested minimum resource// version is larger than the largest currently available resource version. To ensure backward// compatibility with these server versions we also need to detect the error based on the content// of the error message field.if !apierrors.IsTimeout(err) {return false}apierr, ok := err.(apierrors.APIStatus)if !ok || apierr == nil || apierr.Status().Details == nil {return false}for _, cause := range apierr.Status().Details.Causes {// Matches the message returned by api server 1.17.0-1.18.5 for this error conditionif cause.Message == "Too large resource version" {return true}}return false
}
list watch主要分三步:
- 获得所有对象list并调用DeltaFIFO.Replace(syncWith)用list替代Replace之前的元素,并获得了最新的ResourceVersion.
- 启动一个异步goroutine每隔r.resyncPeriod时间调用DeltaFIFO的Resync.
- 根据当前最新的ResourceVersion生成一个watch, 开始一直监控后面的变化.
流程图如下
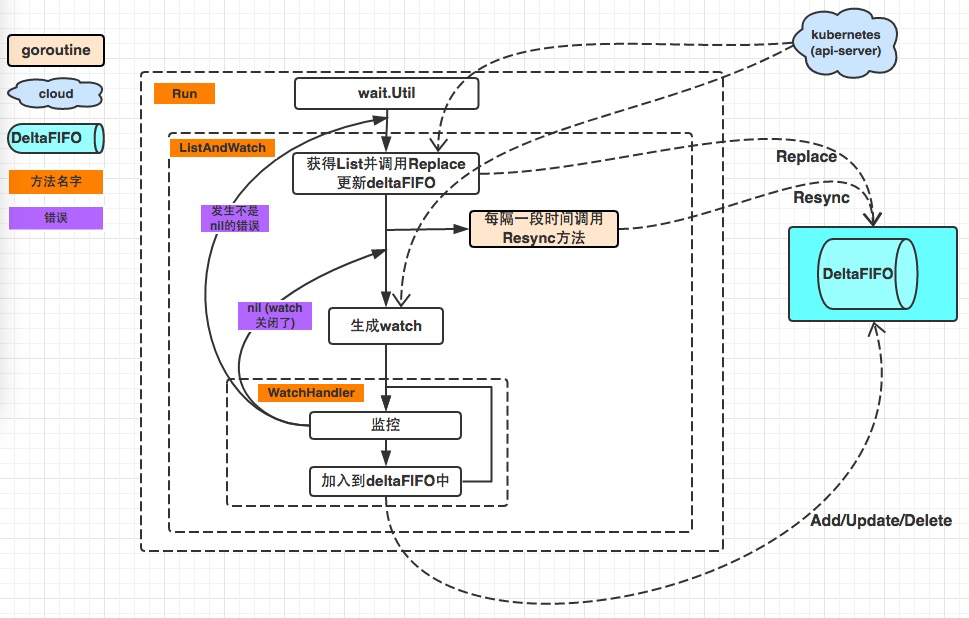
controller
原理
controller中run函数的目的
1 通过reflector的listwatch一直在往DeltaFIFO中存数据
2 从DeltaFIFO中出队并且给自定义用户逻辑c.config.Process处理.
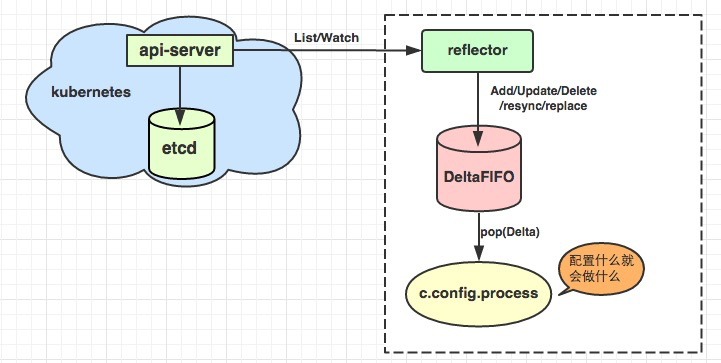
源码
// Config contains all the settings for one of these low-level controllers.
type Config struct {// The queue for your objects - has to be a DeltaFIFO due to// assumptions in the implementation. Your Process() function// should accept the output of this Queue's Pop() method.// delta queue一级缓存Queue// Something that can list and watch your objects.// reflector的listwatch接口ListerWatcher// Something that can process a popped Deltas.// delta queue的pop的出事件的处理函数Process ProcessFunc// ObjectType is an example object of the type this controller is// expected to handle. Only the type needs to be right, except// that when that is `unstructured.Unstructured` the object's// `"apiVersion"` and `"kind"` must also be right.ObjectType runtime.Object// FullResyncPeriod is the period at which ShouldResync is considered.// reflector中同步二级缓存到一级缓存的时间间隔FullResyncPeriod time.Duration// ShouldResync is periodically used by the reflector to determine// whether to Resync the Queue. If ShouldResync is `nil` or// returns true, it means the reflector should proceed with the// resync.ShouldResync ShouldResyncFunc// If true, when Process() returns an error, re-enqueue the object.// TODO: add interface to let you inject a delay/backoff or drop// the object completely if desired. Pass the object in// question to this interface as a parameter. This is probably moot// now that this functionality appears at a higher level.RetryOnError bool// Called whenever the ListAndWatch drops the connection with an error.WatchErrorHandler WatchErrorHandler
}// ShouldResyncFunc is a type of function that indicates if a reflector should perform a
// resync or not. It can be used by a shared informer to support multiple event handlers with custom
// resync periods.
type ShouldResyncFunc func() bool// ProcessFunc processes a single object.
type ProcessFunc func(obj interface{}) error// `*controller` implements Controller
type controller struct {config Configreflector *ReflectorreflectorMutex sync.RWMutexclock clock.Clock
}// Controller is a low-level controller that is parameterized by a
// Config and used in sharedIndexInformer.
type Controller interface {// Run does two things. One is to construct and run a Reflector// to pump objects/notifications from the Config's ListerWatcher// to the Config's Queue and possibly invoke the occasional Resync// on that Queue. The other is to repeatedly Pop from the Queue// and process with the Config's ProcessFunc. Both of these// continue until `stopCh` is closed.Run(stopCh <-chan struct{})// HasSynced delegates to the Config's QueueHasSynced() bool// LastSyncResourceVersion delegates to the Reflector when there// is one, otherwise returns the empty stringLastSyncResourceVersion() string
}// New makes a new Controller from the given Config.
func New(c *Config) Controller {ctlr := &controller{config: *c,clock: &clock.RealClock{},}return ctlr
}// Run begins processing items, and will continue until a value is sent down stopCh or it is closed.
// It's an error to call Run more than once.
// Run blocks; call via go.
// 启动逻辑 1 reflector listwatch到delta queue 2 从delta queue弹出事件处理
func (c *controller) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()go func() {<-stopChc.config.Queue.Close()}()r := NewReflector(c.config.ListerWatcher,c.config.ObjectType,c.config.Queue,c.config.FullResyncPeriod,)r.ShouldResync = c.config.ShouldResyncr.clock = c.clockif c.config.WatchErrorHandler != nil {r.watchErrorHandler = c.config.WatchErrorHandler}c.reflectorMutex.Lock()c.reflector = rc.reflectorMutex.Unlock()var wg wait.Groupwg.StartWithChannel(stopCh, r.Run)wait.Until(c.processLoop, time.Second, stopCh)wg.Wait()
}// Returns true once this controller has completed an initial resource listing
func (c *controller) HasSynced() bool {return c.config.Queue.HasSynced()
}func (c *controller) LastSyncResourceVersion() string {c.reflectorMutex.RLock()defer c.reflectorMutex.RUnlock()if c.reflector == nil {return ""}return c.reflector.LastSyncResourceVersion()
}// processLoop drains the work queue.
// TODO: Consider doing the processing in parallel. This will require a little thought
// to make sure that we don't end up processing the same object multiple times
// concurrently.
//
// TODO: Plumb through the stopCh here (and down to the queue) so that this can
// actually exit when the controller is stopped. Or just give up on this stuff
// ever being stoppable. Converting this whole package to use Context would
// also be helpful.
func (c *controller) processLoop() {for {obj, err := c.config.Queue.Pop(PopProcessFunc(c.config.Process))if err != nil {if err == ErrFIFOClosed {return}if c.config.RetryOnError {// This is the safe way to re-enqueue.c.config.Queue.AddIfNotPresent(obj)}}}
}// ResourceEventHandler can handle notifications for events that
// happen to a resource. The events are informational only, so you
// can't return an error. The handlers MUST NOT modify the objects
// received; this concerns not only the top level of structure but all
// the data structures reachable from it.
// * OnAdd is called when an object is added.
// * OnUpdate is called when an object is modified. Note that oldObj is the
// last known state of the object-- it is possible that several changes
// were combined together, so you can't use this to see every single
// change. OnUpdate is also called when a re-list happens, and it will
// get called even if nothing changed. This is useful for periodically
// evaluating or syncing something.
// * OnDelete will get the final state of the item if it is known, otherwise
// it will get an object of type DeletedFinalStateUnknown. This can
// happen if the watch is closed and misses the delete event and we don't
// notice the deletion until the subsequent re-list.
// 增删改事件的处理器接口
type ResourceEventHandler interface {OnAdd(obj interface{})OnUpdate(oldObj, newObj interface{})OnDelete(obj interface{})
}// ResourceEventHandlerFuncs is an adaptor to let you easily specify as many or
// as few of the notification functions as you want while still implementing
// ResourceEventHandler. This adapter does not remove the prohibition against
// modifying the objects.
type ResourceEventHandlerFuncs struct {AddFunc func(obj interface{})UpdateFunc func(oldObj, newObj interface{})DeleteFunc func(obj interface{})
}// OnAdd calls AddFunc if it's not nil.
func (r ResourceEventHandlerFuncs) OnAdd(obj interface{}) {if r.AddFunc != nil {r.AddFunc(obj)}
}// OnUpdate calls UpdateFunc if it's not nil.
func (r ResourceEventHandlerFuncs) OnUpdate(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {if r.UpdateFunc != nil {r.UpdateFunc(oldObj, newObj)}
}// OnDelete calls DeleteFunc if it's not nil.
func (r ResourceEventHandlerFuncs) OnDelete(obj interface{}) {if r.DeleteFunc != nil {r.DeleteFunc(obj)}
}// FilteringResourceEventHandler applies the provided filter to all events coming
// in, ensuring the appropriate nested handler method is invoked. An object
// that starts passing the filter after an update is considered an add, and an
// object that stops passing the filter after an update is considered a delete.
// Like the handlers, the filter MUST NOT modify the objects it is given.
type FilteringResourceEventHandler struct {FilterFunc func(obj interface{}) boolHandler ResourceEventHandler
}// OnAdd calls the nested handler only if the filter succeeds
func (r FilteringResourceEventHandler) OnAdd(obj interface{}) {if !r.FilterFunc(obj) {return}r.Handler.OnAdd(obj)
}// OnUpdate ensures the proper handler is called depending on whether the filter matches
func (r FilteringResourceEventHandler) OnUpdate(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {newer := r.FilterFunc(newObj)older := r.FilterFunc(oldObj)switch {case newer && older:r.Handler.OnUpdate(oldObj, newObj)case newer && !older:r.Handler.OnAdd(newObj)case !newer && older:r.Handler.OnDelete(oldObj)default:// do nothing}
}// OnDelete calls the nested handler only if the filter succeeds
func (r FilteringResourceEventHandler) OnDelete(obj interface{}) {if !r.FilterFunc(obj) {return}r.Handler.OnDelete(obj)
}// DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc checks for
// DeletedFinalStateUnknown objects before calling
// MetaNamespaceKeyFunc.
func DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj interface{}) (string, error) {if d, ok := obj.(DeletedFinalStateUnknown); ok {return d.Key, nil}return MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj)
}// NewInformer returns a Store and a controller for populating the store
// while also providing event notifications. You should only used the returned
// Store for Get/List operations; Add/Modify/Deletes will cause the event
// notifications to be faulty.
//
// Parameters:
// * lw is list and watch functions for the source of the resource you want to
// be informed of.
// * objType is an object of the type that you expect to receive.
// * resyncPeriod: if non-zero, will re-list this often (you will get OnUpdate
// calls, even if nothing changed). Otherwise, re-list will be delayed as
// long as possible (until the upstream source closes the watch or times out,
// or you stop the controller).
// * h is the object you want notifications sent to.
// informer 1 二级本地缓存没有索引
func NewInformer(lw ListerWatcher,objType runtime.Object,resyncPeriod time.Duration,h ResourceEventHandler,
) (Store, Controller) {// This will hold the client state, as we know it.clientState := NewStore(DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc)return clientState, newInformer(lw, objType, resyncPeriod, h, clientState)
}// NewIndexerInformer returns a Indexer and a controller for populating the index
// while also providing event notifications. You should only used the returned
// Index for Get/List operations; Add/Modify/Deletes will cause the event
// notifications to be faulty.
//
// Parameters:
// * lw is list and watch functions for the source of the resource you want to
// be informed of.
// * objType is an object of the type that you expect to receive.
// * resyncPeriod: if non-zero, will re-list this often (you will get OnUpdate
// calls, even if nothing changed). Otherwise, re-list will be delayed as
// long as possible (until the upstream source closes the watch or times out,
// or you stop the controller).
// * h is the object you want notifications sent to.
// * indexers is the indexer for the received object type.
// informer 2 二级本地缓存有索引
func NewIndexerInformer(lw ListerWatcher,objType runtime.Object,resyncPeriod time.Duration,h ResourceEventHandler,indexers Indexers,
) (Indexer, Controller) {// This will hold the client state, as we know it.clientState := NewIndexer(DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc, indexers)return clientState, newInformer(lw, objType, resyncPeriod, h, clientState)
}// newInformer returns a controller for populating the store while also
// providing event notifications.
//
// Parameters
// * lw is list and watch functions for the source of the resource you want to
// be informed of.
// * objType is an object of the type that you expect to receive.
// * resyncPeriod: if non-zero, will re-list this often (you will get OnUpdate
// calls, even if nothing changed). Otherwise, re-list will be delayed as
// long as possible (until the upstream source closes the watch or times out,
// or you stop the controller).
// * h is the object you want notifications sent to.
// * clientState is the store you want to populate
// <<<<< newInformer 单个自定义事件处理listener
// <<<<< sharedIndexInformer 可以添加多个自定义事件处理listeners
// staging/src/k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/shared_informer.go
func newInformer(lw ListerWatcher,objType runtime.Object,resyncPeriod time.Duration,h ResourceEventHandler,clientState Store,
) Controller {// This will hold incoming changes. Note how we pass clientState in as a// KeyLister, that way resync operations will result in the correct set// of update/delete deltas.// 一级缓存DeltaFIFO 其中装配了二级缓存indexerfifo := NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{KnownObjects: clientState,EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,})cfg := &Config{Queue: fifo,ListerWatcher: lw,ObjectType: objType,FullResyncPeriod: resyncPeriod,RetryOnError: false,// 从一级缓存Delta queue中弹出事件的处理函数// 二级本地缓存中没有就添加 有就更新 删除事件就删除// 同时会触发自定义事件处理逻辑 ResourceEventHandlerProcess: func(obj interface{}) error {// from oldest to newestfor _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {switch d.Type {case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:if old, exists, err := clientState.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {if err := clientState.Update(d.Object); err != nil {return err}h.OnUpdate(old, d.Object)} else {if err := clientState.Add(d.Object); err != nil {return err}h.OnAdd(d.Object)}case Deleted:if err := clientState.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {return err}h.OnDelete(d.Object)}}return nil},}return New(cfg)
}
sharedinformer
自定义处理handle通过注册监听发布的模式实现,具体的事件的处理通过增删改的接口实现。
引用:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/5cd7f7666797
https://www.jianshu.com/p/12d2912d5ac3
原理
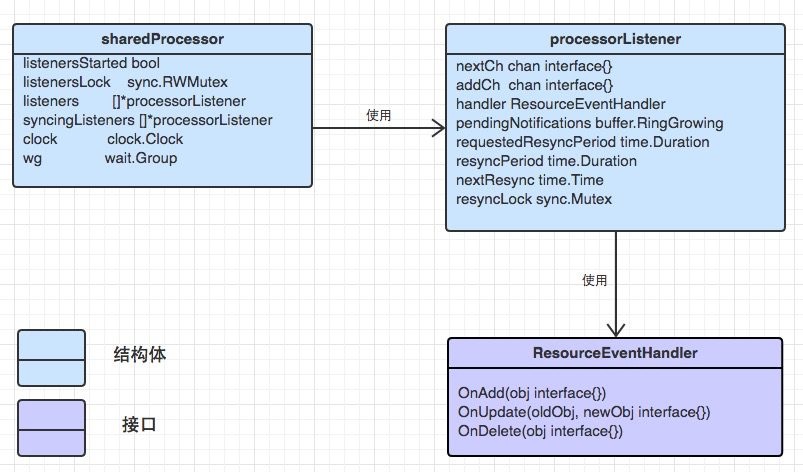
ResourceEventHandler
// client-go/tools/cache/controller.go
type ResourceEventHandler interface {OnAdd(obj interface{})OnUpdate(oldObj, newObj interface{})OnDelete(obj interface{})
}
用户可以在这里定义自己的逻辑.
processorListener
add pop run
pop和run属于消费者, 消费从add方法中过来的notification, 但是为了防止处理速度(调用handler)跟不上生产速度, 设置了一个缓冲区pendingNotifications, 把从add中过来的notification先加入到pendingNotifications, 然后从pendingNotifications读取一个notification后, 将notification通过nextCh这个channel来进而传递给消费者run,用户定义的自定义处理器会处理。
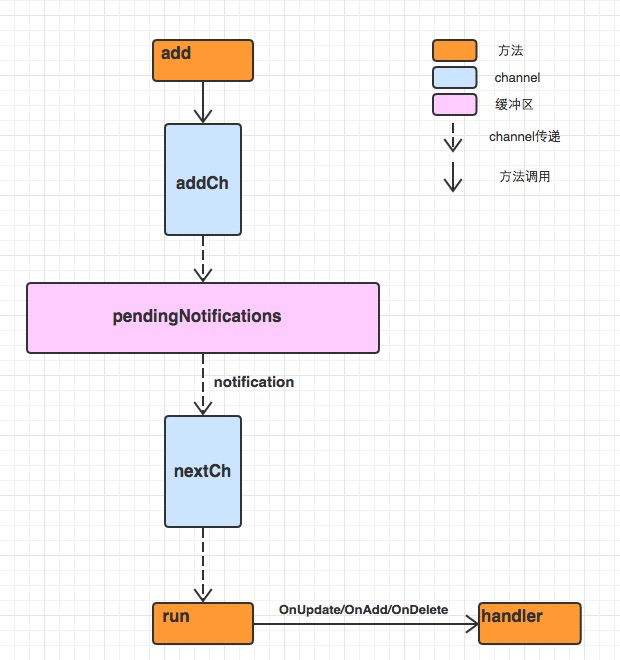
func (p *processorListener) add(notification interface{}) {p.addCh <- notification
}func (p *processorListener) pop() {defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()defer close(p.nextCh) // Tell .run() to stopvar nextCh chan<- interface{}var notification interface{}for {select {case nextCh <- notification:// Notification dispatchedvar ok boolnotification, ok = p.pendingNotifications.ReadOne()if !ok { // Nothing to popnextCh = nil // Disable this select case}case notificationToAdd, ok := <-p.addCh:if !ok {return}if notification == nil { // No notification to pop (and pendingNotifications is empty)// Optimize the case - skip adding to pendingNotificationsnotification = notificationToAddnextCh = p.nextCh} else { // There is already a notification waiting to be dispatchedp.pendingNotifications.WriteOne(notificationToAdd)}}}
}func (p *processorListener) run() {// this call blocks until the channel is closed. When a panic happens during the notification// we will catch it, **the offending item will be skipped!**, and after a short delay (one second)// the next notification will be attempted. This is usually better than the alternative of never// delivering again.stopCh := make(chan struct{})wait.Until(func() {for next := range p.nextCh {switch notification := next.(type) {case updateNotification:p.handler.OnUpdate(notification.oldObj, notification.newObj)case addNotification:p.handler.OnAdd(notification.newObj)case deleteNotification:p.handler.OnDelete(notification.oldObj)default:utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unrecognized notification: %T", next))}}// the only way to get here is if the p.nextCh is empty and closedclose(stopCh)}, 1*time.Second, stopCh)
}
sharedProcessor
这里sharedProcessor就是管理着所有的processorListener的集合。从delta拿到一个消息, 然后可以分发给所有的listeners。
func (p *sharedProcessor) run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {func() {p.listenersLock.RLock()defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()// 以goroutine的方式启动所有的listeners监听for _, listener := range p.listeners {// 消费消息p.wg.Start(listener.run)// 从缓冲区拿出消息p.wg.Start(listener.pop)}p.listenersStarted = true}()<-stopChp.listenersLock.RLock()defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()for _, listener := range p.listeners {close(listener.addCh) // Tell .pop() to stop. .pop() will tell .run() to stop}p.wg.Wait() // Wait for all .pop() and .run() to stop
}
sharedinformer
Run
1 启动了一些listeners来监听.
2 controller.Run 见上。 haredIndexInformer中配置了controller.config.process = HandleDeltas ,HandleDeltas从DeltaFIFO的pop方法中得到了Delta, 做了两件事情:1 根据Add/Update/Delete类型操作本地存储Indexer. 2 将当前obj构造成notification类型分发给所有的listeners, 然后每个listener都会调用用户的ResouceEventHandler进行处理.
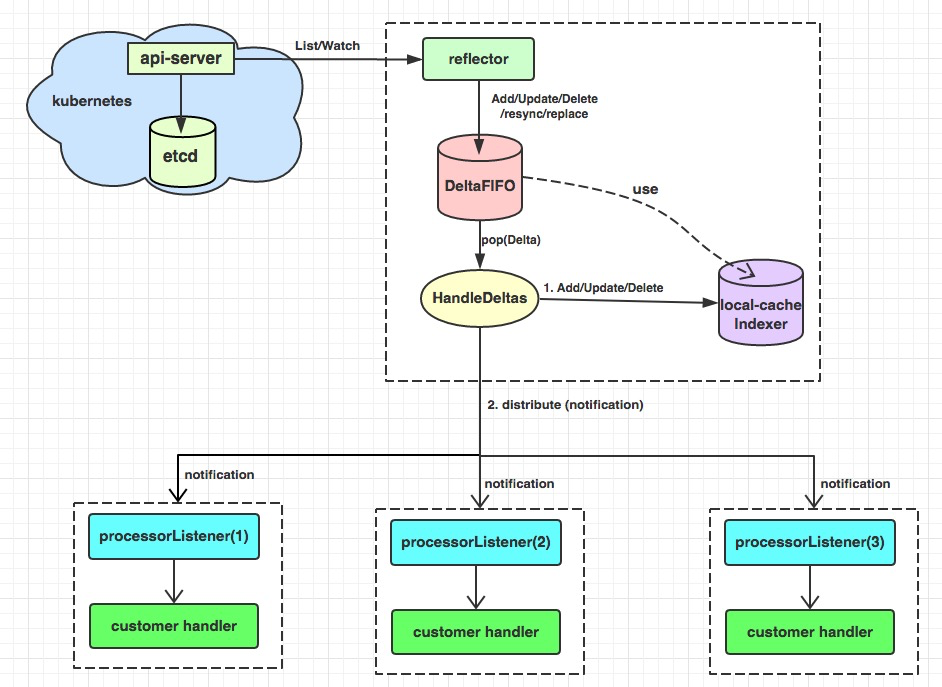
源码
type SharedInformer interface {// AddEventHandler adds an event handler to the shared informer using the shared informer's resync// period. Events to a single handler are delivered sequentially, but there is no coordination// between different handlers.AddEventHandler(handler ResourceEventHandler)// AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod adds an event handler to the// shared informer with the requested resync period; zero means// this handler does not care about resyncs. The resync operation// consists of delivering to the handler an update notification// for every object in the informer's local cache; it does not add// any interactions with the authoritative storage. Some// informers do no resyncs at all, not even for handlers added// with a non-zero resyncPeriod. For an informer that does// resyncs, and for each handler that requests resyncs, that// informer develops a nominal resync period that is no shorter// than the requested period but may be longer. The actual time// between any two resyncs may be longer than the nominal period// because the implementation takes time to do work and there may// be competing load and scheduling noise.AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(handler ResourceEventHandler, resyncPeriod time.Duration)// GetStore returns the informer's local cache as a Store.GetStore() Store// GetController is deprecated, it does nothing usefulGetController() Controller// Run starts and runs the shared informer, returning after it stops.// The informer will be stopped when stopCh is closed.Run(stopCh <-chan struct{})// HasSynced returns true if the shared informer's store has been// informed by at least one full LIST of the authoritative state// of the informer's object collection. This is unrelated to "resync".HasSynced() bool// LastSyncResourceVersion is the resource version observed when last synced with the underlying// store. The value returned is not synchronized with access to the underlying store and is not// thread-safe.LastSyncResourceVersion() string// The WatchErrorHandler is called whenever ListAndWatch drops the// connection with an error. After calling this handler, the informer// will backoff and retry.//// The default implementation looks at the error type and tries to log// the error message at an appropriate level.//// There's only one handler, so if you call this multiple times, last one// wins; calling after the informer has been started returns an error.//// The handler is intended for visibility, not to e.g. pause the consumers.// The handler should return quickly - any expensive processing should be// offloaded.SetWatchErrorHandler(handler WatchErrorHandler) error
}// SharedIndexInformer provides add and get Indexers ability based on SharedInformer.
type SharedIndexInformer interface {SharedInformer// AddIndexers add indexers to the informer before it starts.AddIndexers(indexers Indexers) errorGetIndexer() Indexer
}// NewSharedInformer creates a new instance for the listwatcher.
func NewSharedInformer(lw ListerWatcher, exampleObject runtime.Object, defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod time.Duration) SharedInformer {return NewSharedIndexInformer(lw, exampleObject, defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod, Indexers{})
}// NewSharedIndexInformer creates a new instance for the listwatcher.
// The created informer will not do resyncs if the given
// defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod is zero. Otherwise: for each
// handler that with a non-zero requested resync period, whether added
// before or after the informer starts, the nominal resync period is
// the requested resync period rounded up to a multiple of the
// informer's resync checking period. Such an informer's resync
// checking period is established when the informer starts running,
// and is the maximum of (a) the minimum of the resync periods
// requested before the informer starts and the
// defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod given here and (b) the constant
// `minimumResyncPeriod` defined in this file.
// 默认用户层调用的函数
func NewSharedIndexInformer(lw ListerWatcher, exampleObject runtime.Object, defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers Indexers) SharedIndexInformer {realClock := &clock.RealClock{}sharedIndexInformer := &sharedIndexInformer{processor: &sharedProcessor{clock: realClock},indexer: NewIndexer(DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc, indexers),listerWatcher: lw,objectType: exampleObject,resyncCheckPeriod: defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod,defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod: defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod,cacheMutationDetector: NewCacheMutationDetector(fmt.Sprintf("%T", exampleObject)),clock: realClock,}return sharedIndexInformer
}// InformerSynced is a function that can be used to determine if an informer has synced. This is useful for determining if caches have synced.
type InformerSynced func() boolconst (// syncedPollPeriod controls how often you look at the status of your sync funcssyncedPollPeriod = 100 * time.Millisecond// initialBufferSize is the initial number of event notifications that can be buffered.initialBufferSize = 1024
)// WaitForNamedCacheSync is a wrapper around WaitForCacheSync that generates log messages
// indicating that the caller identified by name is waiting for syncs, followed by
// either a successful or failed sync.
func WaitForNamedCacheSync(controllerName string, stopCh <-chan struct{}, cacheSyncs ...InformerSynced) bool {klog.Infof("Waiting for caches to sync for %s", controllerName)if !WaitForCacheSync(stopCh, cacheSyncs...) {utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to sync caches for %s", controllerName))return false}klog.Infof("Caches are synced for %s ", controllerName)return true
}// WaitForCacheSync waits for caches to populate. It returns true if it was successful, false
// if the controller should shutdown
// callers should prefer WaitForNamedCacheSync()
// 等待资源同步到本地缓存完成
//该方法是等待所有已经启动的informers完成同步. 因为不等到同步完成的时候, 本地缓存中是没有数据的, 如果直接就运行逻辑代码, 有些调用list方法就会获取不到, 因为服务器端是有数据的, 所以就会产生一定的偏差, 因此一般都是等到服务器端数据同步到本地缓存完了才开始运行用户自己的逻辑.
func WaitForCacheSync(stopCh <-chan struct{}, cacheSyncs ...InformerSynced) bool {err := wait.PollImmediateUntil(syncedPollPeriod,func() (bool, error) {for _, syncFunc := range cacheSyncs {if !syncFunc() {return false, nil}}return true, nil},stopCh)if err != nil {klog.V(2).Infof("stop requested")return false}klog.V(4).Infof("caches populated")return true
}// `*sharedIndexInformer` implements SharedIndexInformer and has three
// main components. One is an indexed local cache, `indexer Indexer`.
// The second main component is a Controller that pulls
// objects/notifications using the ListerWatcher and pushes them into
// a DeltaFIFO --- whose knownObjects is the informer's local cache
// --- while concurrently Popping Deltas values from that fifo and
// processing them with `sharedIndexInformer::HandleDeltas`. Each
// invocation of HandleDeltas, which is done with the fifo's lock
// held, processes each Delta in turn. For each Delta this both
// updates the local cache and stuffs the relevant notification into
// the sharedProcessor. The third main component is that
// sharedProcessor, which is responsible for relaying those
// notifications to each of the informer's clients.
type sharedIndexInformer struct {indexer Indexercontroller Controllerprocessor *sharedProcessorcacheMutationDetector MutationDetectorlisterWatcher ListerWatcher// objectType is an example object of the type this informer is// expected to handle. Only the type needs to be right, except// that when that is `unstructured.Unstructured` the object's// `"apiVersion"` and `"kind"` must also be right.objectType runtime.Object// resyncCheckPeriod is how often we want the reflector's resync timer to fire so it can call// shouldResync to check if any of our listeners need a resync.// 在reflector中每隔resyncCheckPeriod时间会调用shouldResync方法来判断是否有任何一个listener需要resync操作resyncCheckPeriod time.Duration// defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod is the default resync period for any handlers added via// AddEventHandler (i.e. they don't specify one and just want to use the shared informer's default// value).defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod time.Duration// clock allows for testabilityclock clock.Clockstarted, stopped boolstartedLock sync.Mutex// blockDeltas gives a way to stop all event distribution so that a late event handler// can safely join the shared informer.blockDeltas sync.Mutex// Called whenever the ListAndWatch drops the connection with an error.watchErrorHandler WatchErrorHandler
}type updateNotification struct {oldObj interface{}newObj interface{}
}type addNotification struct {newObj interface{}
}type deleteNotification struct {oldObj interface{}
}func (s *sharedIndexInformer) SetWatchErrorHandler(handler WatchErrorHandler) error {s.startedLock.Lock()defer s.startedLock.Unlock()if s.started {return fmt.Errorf("informer has already started")}s.watchErrorHandler = handlerreturn nil
}func (s *sharedIndexInformer) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()// 生成一个DeltaFIFO 并且knowObjects是s.indexer 也就是本地缓存fifo := NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{KnownObjects: s.indexer,EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,})cfg := &Config{Queue: fifo,ListerWatcher: s.listerWatcher,ObjectType: s.objectType,FullResyncPeriod: s.resyncCheckPeriod,RetryOnError: false,// 对应的是sharedProcessor的shouldResync 会去计算所有的listeners是否有谁到了resync的时间ShouldResync: s.processor.shouldResync,// 出DeltaFIFO队列的时候 调用用户自定义的处理逻辑 在这里是HandleDeltasProcess: s.HandleDeltas,WatchErrorHandler: s.watchErrorHandler,}func() {s.startedLock.Lock()defer s.startedLock.Unlock()s.controller = New(cfg)s.controller.(*controller).clock = s.clocks.started = true}()// Separate stop channel because Processor should be stopped strictly after controllerprocessorStopCh := make(chan struct{})var wg wait.Groupdefer wg.Wait() // Wait for Processor to stopdefer close(processorStopCh) // Tell Processor to stopwg.StartWithChannel(processorStopCh, s.cacheMutationDetector.Run)// 启动所有的listeners进行监听 等待事件的消费wg.StartWithChannel(processorStopCh, s.processor.run)defer func() {s.startedLock.Lock()defer s.startedLock.Unlock()s.stopped = true // Don't want any new listeners}()s.controller.Run(stopCh)
}func (s *sharedIndexInformer) HasSynced() bool {s.startedLock.Lock()defer s.startedLock.Unlock()if s.controller == nil {return false}return s.controller.HasSynced()
}func (s *sharedIndexInformer) LastSyncResourceVersion() string {s.startedLock.Lock()defer s.startedLock.Unlock()if s.controller == nil {return ""}return s.controller.LastSyncResourceVersion()
}func (s *sharedIndexInformer) GetStore() Store {return s.indexer
}func (s *sharedIndexInformer) GetIndexer() Indexer {return s.indexer
}func (s *sharedIndexInformer) AddIndexers(indexers Indexers) error {s.startedLock.Lock()defer s.startedLock.Unlock()if s.started {return fmt.Errorf("informer has already started")}return s.indexer.AddIndexers(indexers)
}func (s *sharedIndexInformer) GetController() Controller {return &dummyController{informer: s}
}func (s *sharedIndexInformer) AddEventHandler(handler ResourceEventHandler) {s.AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(handler, s.defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod)
}func determineResyncPeriod(desired, check time.Duration) time.Duration {if desired == 0 {return desired}if check == 0 {klog.Warningf("The specified resyncPeriod %v is invalid because this shared informer doesn't support resyncing", desired)return 0}if desired < check {klog.Warningf("The specified resyncPeriod %v is being increased to the minimum resyncCheckPeriod %v", desired, check)return check}return desired
}const minimumResyncPeriod = 1 * time.Secondfunc (s *sharedIndexInformer) AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(handler ResourceEventHandler, resyncPeriod time.Duration) {s.startedLock.Lock()defer s.startedLock.Unlock()if s.stopped {klog.V(2).Infof("Handler %v was not added to shared informer because it has stopped already", handler)return}if resyncPeriod > 0 {if resyncPeriod < minimumResyncPeriod {klog.Warningf("resyncPeriod %d is too small. Changing it to the minimum allowed value of %d", resyncPeriod, minimumResyncPeriod)resyncPeriod = minimumResyncPeriod}if resyncPeriod < s.resyncCheckPeriod {if s.started {klog.Warningf("resyncPeriod %d is smaller than resyncCheckPeriod %d and the informer has already started. Changing it to %d", resyncPeriod, s.resyncCheckPeriod, s.resyncCheckPeriod)resyncPeriod = s.resyncCheckPeriod} else {// if the event handler's resyncPeriod is smaller than the current resyncCheckPeriod, update// resyncCheckPeriod to match resyncPeriod and adjust the resync periods of all the listeners// accordinglys.resyncCheckPeriod = resyncPeriods.processor.resyncCheckPeriodChanged(resyncPeriod)}}}listener := newProcessListener(handler, resyncPeriod, determineResyncPeriod(resyncPeriod, s.resyncCheckPeriod), s.clock.Now(), initialBufferSize)if !s.started {s.processor.addListener(listener)return}// in order to safely join, we have to// 1. stop sending add/update/delete notifications// 2. do a list against the store// 3. send synthetic "Add" events to the new handler// 4. unblocks.blockDeltas.Lock()defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()s.processor.addListener(listener)for _, item := range s.indexer.List() {listener.add(addNotification{newObj: item})}
}// 从deltaqueue弹出的消息的处理 1 同步到二级本地缓存 2 入队到用户自定义处理的队列中
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) HandleDeltas(obj interface{}) error {s.blockDeltas.Lock()defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()// from oldest to newestfor _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {switch d.Type {case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:s.cacheMutationDetector.AddObject(d.Object)if old, exists, err := s.indexer.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {// 更新本地缓存if err := s.indexer.Update(d.Object); err != nil {return err}isSync := falseswitch {case d.Type == Sync:// Sync events are only propagated to listeners that requested resyncisSync = truecase d.Type == Replaced:if accessor, err := meta.Accessor(d.Object); err == nil {if oldAccessor, err := meta.Accessor(old); err == nil {// Replaced events that didn't change resourceVersion are treated as resync events// and only propagated to listeners that requested resyncisSync = accessor.GetResourceVersion() == oldAccessor.GetResourceVersion()}}}// 根据isSync分发给对应的listenerss.processor.distribute(updateNotification{oldObj: old, newObj: d.Object}, isSync)} else {// 增加到本地缓存if err := s.indexer.Add(d.Object); err != nil {return err}s.processor.distribute(addNotification{newObj: d.Object}, false)}case Deleted:// 从本地缓存中删除if err := s.indexer.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {return err}// 分发给所有的listenerss.processor.distribute(deleteNotification{oldObj: d.Object}, false)}}return nil
}// sharedProcessor has a collection of processorListener and can
// distribute a notification object to its listeners. There are two
// kinds of distribute operations. The sync distributions go to a
// subset of the listeners that (a) is recomputed in the occasional
// calls to shouldResync and (b) every listener is initially put in.
// The non-sync distributions go to every listener.
// 自定义handle的发布订阅模式处理
type sharedProcessor struct {listenersStarted boollistenersLock sync.RWMutexlisteners []*processorListenersyncingListeners []*processorListenerclock clock.Clockwg wait.Group
}func (p *sharedProcessor) addListener(listener *processorListener) {p.listenersLock.Lock()defer p.listenersLock.Unlock()p.addListenerLocked(listener)if p.listenersStarted {p.wg.Start(listener.run)p.wg.Start(listener.pop)}
}func (p *sharedProcessor) addListenerLocked(listener *processorListener) {p.listeners = append(p.listeners, listener)p.syncingListeners = append(p.syncingListeners, listener)
}func (p *sharedProcessor) distribute(obj interface{}, sync bool) {p.listenersLock.RLock()defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()if sync {for _, listener := range p.syncingListeners {listener.add(obj)}} else {for _, listener := range p.listeners {listener.add(obj)}}
}func (p *sharedProcessor) run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {func() {p.listenersLock.RLock()defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()for _, listener := range p.listeners {p.wg.Start(listener.run)p.wg.Start(listener.pop)}p.listenersStarted = true}()<-stopChp.listenersLock.RLock()defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()for _, listener := range p.listeners {close(listener.addCh) // Tell .pop() to stop. .pop() will tell .run() to stop}p.wg.Wait() // Wait for all .pop() and .run() to stop
}// shouldResync queries every listener to determine if any of them need a resync, based on each
// listener's resyncPeriod.
func (p *sharedProcessor) shouldResync() bool {p.listenersLock.Lock()defer p.listenersLock.Unlock()p.syncingListeners = []*processorListener{}resyncNeeded := falsenow := p.clock.Now()for _, listener := range p.listeners {// need to loop through all the listeners to see if they need to resync so we can prepare any// listeners that are going to be resyncing.if listener.shouldResync(now) {resyncNeeded = truep.syncingListeners = append(p.syncingListeners, listener)listener.determineNextResync(now)}}return resyncNeeded
}func (p *sharedProcessor) resyncCheckPeriodChanged(resyncCheckPeriod time.Duration) {p.listenersLock.RLock()defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()for _, listener := range p.listeners {resyncPeriod := determineResyncPeriod(listener.requestedResyncPeriod, resyncCheckPeriod)listener.setResyncPeriod(resyncPeriod)}
}// processorListener relays notifications from a sharedProcessor to
// one ResourceEventHandler --- using two goroutines, two unbuffered
// channels, and an unbounded ring buffer. The `add(notification)`
// function sends the given notification to `addCh`. One goroutine
// runs `pop()`, which pumps notifications from `addCh` to `nextCh`
// using storage in the ring buffer while `nextCh` is not keeping up.
// Another goroutine runs `run()`, which receives notifications from
// `nextCh` and synchronously invokes the appropriate handler method.
//
// processorListener also keeps track of the adjusted requested resync
// period of the listener.
type processorListener struct {nextCh chan interface{}addCh chan interface{}// 一个自定义处理数据的handlerhandler ResourceEventHandler// pendingNotifications is an unbounded ring buffer that holds all notifications not yet distributed.// There is one per listener, but a failing/stalled listener will have infinite pendingNotifications// added until we OOM.// TODO: This is no worse than before, since reflectors were backed by unbounded DeltaFIFOs, but// we should try to do something better.// 一个环形的buffer 存着那些还没有被分发的notifications。防止消费速度跟不上生产速度,缓冲区pendingNotifications buffer.RingGrowing// requestedResyncPeriod is how frequently the listener wants a// full resync from the shared informer, but modified by two// adjustments. One is imposing a lower bound,// `minimumResyncPeriod`. The other is another lower bound, the// sharedProcessor's `resyncCheckPeriod`, that is imposed (a) only// in AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod invocations made after the// sharedProcessor starts and (b) only if the informer does// resyncs at all.requestedResyncPeriod time.Duration// resyncPeriod is the threshold that will be used in the logic// for this listener. This value differs from// requestedResyncPeriod only when the sharedIndexInformer does// not do resyncs, in which case the value here is zero. The// actual time between resyncs depends on when the// sharedProcessor's `shouldResync` function is invoked and when// the sharedIndexInformer processes `Sync` type Delta objects.resyncPeriod time.Duration// nextResync is the earliest time the listener should get a full resyncnextResync time.Time// resyncLock guards access to resyncPeriod and nextResyncresyncLock sync.Mutex
}func newProcessListener(handler ResourceEventHandler, requestedResyncPeriod, resyncPeriod time.Duration, now time.Time, bufferSize int) *processorListener {ret := &processorListener{nextCh: make(chan interface{}),addCh: make(chan interface{}),handler: handler,pendingNotifications: *buffer.NewRingGrowing(bufferSize),requestedResyncPeriod: requestedResyncPeriod,resyncPeriod: resyncPeriod,}ret.determineNextResync(now)return ret
}// 生产消息
func (p *processorListener) add(notification interface{}) {p.addCh <- notification
}// 从缓冲区读取消息到p.nextCh中; 写入消息到缓存区
func (p *processorListener) pop() {defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()defer close(p.nextCh) // Tell .run() to stopvar nextCh chan<- interface{}var notification interface{}for {select {case nextCh <- notification:// Notification dispatchedvar ok boolnotification, ok = p.pendingNotifications.ReadOne()if !ok { // Nothing to popnextCh = nil // Disable this select case}case notificationToAdd, ok := <-p.addCh:if !ok {return}if notification == nil { // No notification to pop (and pendingNotifications is empty)// Optimize the case - skip adding to pendingNotificationsnotification = notificationToAdd// 引用p.nextChnextCh = p.nextCh} else { // There is already a notification waiting to be dispatchedp.pendingNotifications.WriteOne(notificationToAdd)}}}
}// 消费消息
func (p *processorListener) run() {// this call blocks until the channel is closed. When a panic happens during the notification// we will catch it, **the offending item will be skipped!**, and after a short delay (one second)// the next notification will be attempted. This is usually better than the alternative of never// delivering again.stopCh := make(chan struct{})wait.Until(func() {for next := range p.nextCh {switch notification := next.(type) {case updateNotification:p.handler.OnUpdate(notification.oldObj, notification.newObj)case addNotification:p.handler.OnAdd(notification.newObj)case deleteNotification:p.handler.OnDelete(notification.oldObj)default:utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unrecognized notification: %T", next))}}// the only way to get here is if the p.nextCh is empty and closedclose(stopCh)}, 1*time.Second, stopCh)
}// shouldResync deterimines if the listener needs a resync. If the listener's resyncPeriod is 0,
// this always returns false.
func (p *processorListener) shouldResync(now time.Time) bool {p.resyncLock.Lock()defer p.resyncLock.Unlock()if p.resyncPeriod == 0 {return false}return now.After(p.nextResync) || now.Equal(p.nextResync)
}func (p *processorListener) determineNextResync(now time.Time) {p.resyncLock.Lock()defer p.resyncLock.Unlock()p.nextResync = now.Add(p.resyncPeriod)
}func (p *processorListener) setResyncPeriod(resyncPeriod time.Duration) {p.resyncLock.Lock()defer p.resyncLock.Unlock()p.resyncPeriod = resyncPeriod
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!