COW和SSO
GCC 4.x.x string的实现是 COW (写时复制)
GCC 5.x.x string的实现是 SSO (短字符串优先)
验证COW的存在
在g++ 4.
std::string s1 = "hello,world";std::string s2(s1);printf("s1'addr = %p, str = %s, s2'addr = %p,str = %s\n", s1.c_str(), s1.c_str(), s2.c_str(), s2.c_str());s2[0] = 'H';printf("s1'addr = %p, str = %s, s2'addr = %p,str = %s\n", s1.c_str(), s1.c_str(), s2.c_str(), s2.c_str());
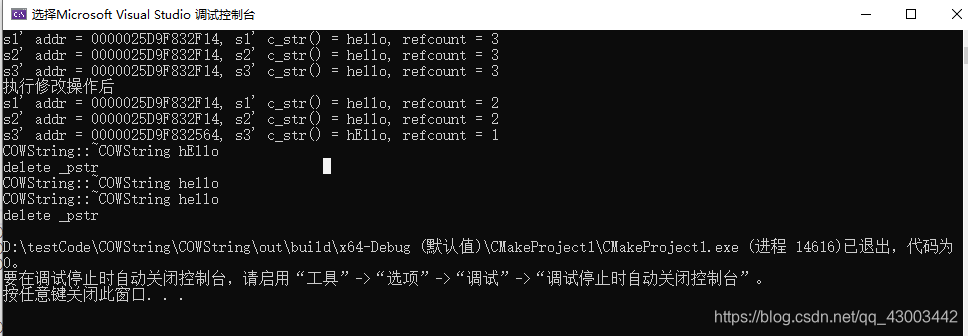
该例子可以看到,s2复制s1的时候进行的是浅拷贝,两者指向同一块空间,当s2发生修改时,s2会重新申请空间。
验证SSO的存在
在g++ 5.4.0
std::string s1 = "hello,world";printf("s1'size = %d\n", sizeof(s1)); // 可以看到string不再是一个指针std::string s3 = "1234567891111111"; // 可以看到超过15个字符s3就在堆上了printf("s1'size = %p\n", s3.c_str());std::string s2(s1);printf("s1'addr = %p, str = %s, s2'addr = %p,str = %s\n", s1.c_str(), s1.c_str(), s2.c_str(), s2.c_str());std::string s4(s3); // 可以看到SSO没用引用计数,每次都是重新申请空间printf("s3'addr = %p, str = %s, s4'addr = %p,str = %s\n", s3.c_str(), s3.c_str(), s4.c_str(), s4.c_str());
如果想让SSO提升,在大于15字符后采用引用计数,可以看看FaceBook开源库中string的实现 https://github.com/facebook/folly.git
一个简单的写时复制实现
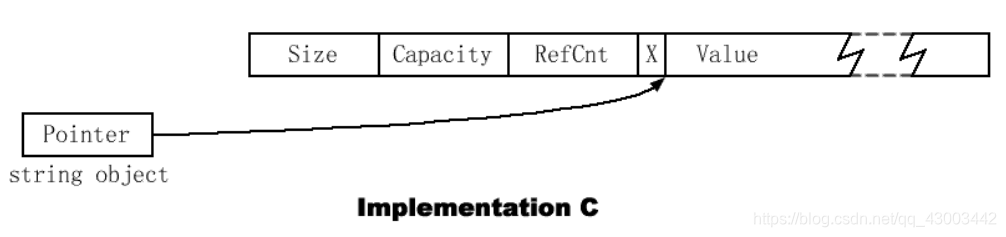
实现思路:
上图来自《Effective STL》条款15,本例只实现RefCnt和Value,Size Capactity暂时不管。
①class COWString中定义一个char的成员,char的前四个字节存放引用计数,后面存放实际的字符串。
②当发生复制构造和赋值操作时,执行浅拷贝,引用计数加1,有对象析构时引用计数减1,只有当引用计数为0时才释放空间
③当对象发生修改时,重载operator[],进行深拷贝
#include 执行结果如图:
思考:
引用计数为什么要与char*放一起,不能单独定义一个成员变量存储?
①引用计数作为成员变量如:
class COWString{char* _pstr;int _refCnt;
}
这样不行,每个对象的引用计数相互独立了,无法同步增减。
②引用计数作为静态成员变量如:
class COWString{char* _pstr;static int _refCnt;
}
这样不行,静态成员变量为整个类共有,会造成不是指向同一个字符串的对象的引用计数也一致了。
③通过保存引用计数的指针:
class COWString{char* _pstr;int* _refCnt;
}
这样可行,不过要申请两次内存,因此将两个成员合并就是本例的实现。
④通过对象成员:
class String{friend class COWString;char* _pstr;int _refCnt;
}
class COWString{String* _string;;
}
可行。
区分读写操作的写时复制实现
上面的例子有个问题,就是只访问下标的元素,没有发生修改时,也会去重新开辟空间,如:const char c = s1[0];
实现思路:
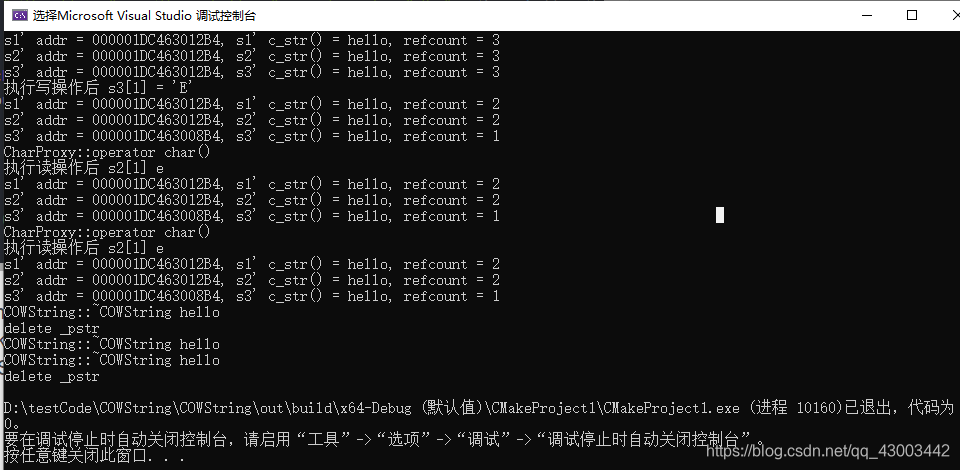
①写操作:s1[0] = ‘H’; 先调用COWString::operator[idx]返回char,然后调用char的operator=修改变量
读操作:const char c = s1[0]; 仅仅调用COWString::operator[idx]返回char
因此区分读还是写操作就在于是否调用了char类型对象的operator=对operator[idx]重新赋值,COWString::operator[idx]返回的是一个char,由于char是内置类型,不能重载,因此我们考虑将COWString::operator[idx]返回一个自定义对象,然后重载自定义对象的operator=,这样写操作就实现了
②由于COWString::operator[idx]返回一个自定义对象,例const char c = s1[0]返回的自定义对象不能直接赋值给char类型变量,因此需要类型转换函数来解决。
#include 执行结果如图:
参考资料:https://www.cnblogs.com/cthon/p/9181979.html
http://www.kohn.com.cn/wordpress/?p=245
《Effective STL》
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!