1167839 流
流
流是一组有序的数据序列,根据操作的类型,可分为输入流和输出流两种。IO(Input/Output,输入/输出)流提供了一条通道程序,可以使用这条通道把源中的字节序列送到目的地。
- 输入输出流
- InputStream
- OutputStream
- Reader
- Writer
- 读取和写入文件的几种方式
- Zip流
输入输出流
- 输入流有:InputStream(字节输入流)、Reader(字符输入流)。
- 输出流有:OutputStream(字节输出流)、Writer(字符输出流)。
他们的基本结构如下:
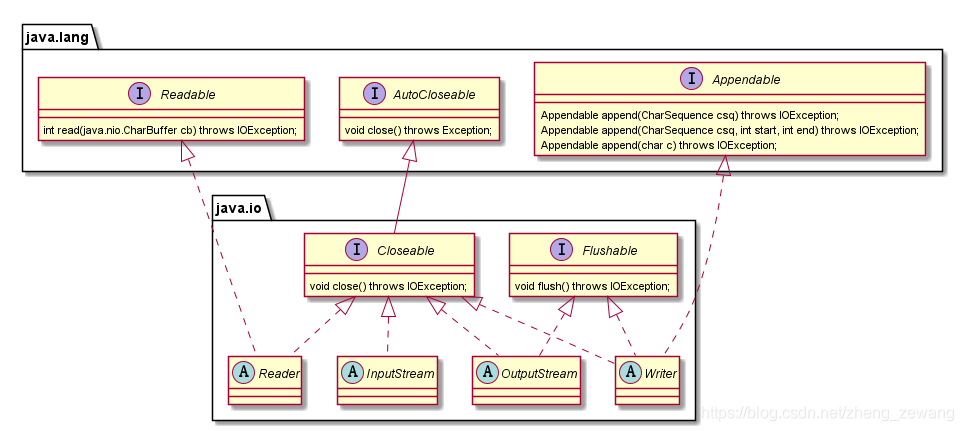
输入输出流根据分类包括:
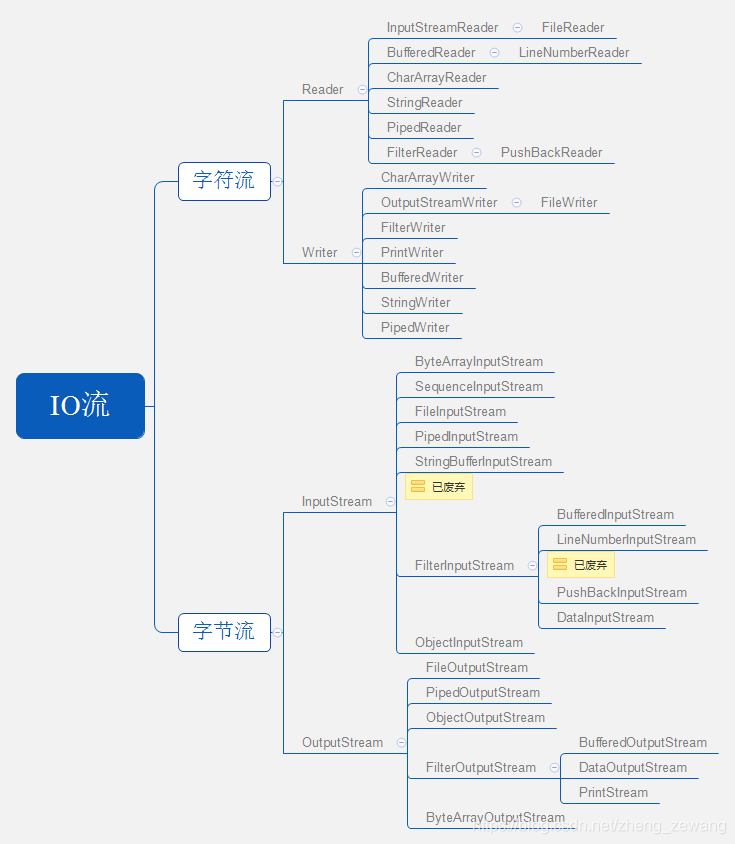
- Reader
- InputStreamReader:处理字节流的字符输入流
- FileReader:文件输入流
- BufferedReader:缓冲字符输入流
- LineNumberReader:可操作行号的缓冲字符输入流
- CharArrayReader:用于char的缓冲字符流
- StringReader:字符串输入流
- PipedReader:管道输入流
- FilterReader:字符过滤输入流
- PushBackReader:推回输入流
- InputStreamReader:处理字节流的字符输入流
- Writer
- CharArrayWriter:用于char的缓冲输出流
- OutputStreamWriter:处理字节流的字符输出流
- FileWriter:文件输出流
- FilterWriter:字符过滤输出流
- PrintWriter:打印输出流
- BufferedWriter:缓冲字符输出流
- StringWriter:字符串输出流
- PipedWriter:管道输出流
- InputStream
- ByteArrayInputStream:字节数组输入流
- SequenceInputStream:合并输入流
- FileInputStream:文件输入流
- PipedInputStream:管道输入流
- StringBufferInputStream:字符输入流(已废弃)
- FilterInputStream:字节过滤输入流
- BufferedInputStream:缓冲字节输入流
- LineNumberInputStream:可操作行号的缓冲字节输入流(已废弃)
- PushBackInputStream:推回输入流
- DataInputStream:数据输入流
- ObjectInputStream:对象输入流
- OutputStream
- ByteArrayOutputStream:字节数组输出流
- FileOutputStream:文件输出流
- PipedOutputStream:管道输出流
- FilterOutputStream:过滤器字节输出流
- BufferedOutputStream:缓冲输出流
- DataOutputStream:数据输出流
- PrintStream:打印输出流
- ObjectOutputStream:对象输出流
InputStream
InputStream类是字节输入流的抽象类,是所有字节输入流的父类。
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| public abstract int read() | 从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节,返回0~255范围的int字节值。 可以将返回值理解为无符号的byte值 |
| public int read(byte b[]) | 从输入流中读入一定长度的字节,返回字节数 |
| public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) | 从指定位置读取指定长度的字节,返回字节数。 off不是指跳过字节流开始读,而是指读到b[]数组中开始的位置 如果len超过最大可读字节数,则抛出异常 |
| public long skip(long n) | 跳过输入流上的n个字节,返回实际跳过的字节数 |
| public int available() | 得到输入流中有多少字节。有时并不是准确,比如网络操作 |
| public void close() | 关闭输入流 |
| public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) | 在输入流的当前位置放置一个标记。readlimit表示允许读取的字节数 超过这个字节数可能会导致reset失败 |
| public synchronized void reset() | 将输入指针返回标记处 |
| public boolean markSupported() | 如果当前流支持mark()/reset()操作就返回true |
注:并不是所有的InputStream子类都支持这些方法。
ByteArrayInputStream
字节数组输入流。
构造方法:
public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[]) {}
public ByteArrayInputStream(byte buf[], int offset, int length) {}
- 第一个构造方法根据字节数组构造一个字节输入流,offset=0,length=buf.length
- 第二个构造方法指定标记位置为offset,以及可读取的长度为length(实际长度是offset+length与字节数组长度的最小值,Math.min(offset + length, buf.length))
继承方法:
- close()方法没有任何效果
- mark(int readlimit)方法,标记会生效,但是参数readlimit没有任何效果
示例:
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/4/7.*/
public class ByteArrayInputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = null;byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{-128, -1, 0, 127});// read方法System.out.println(byteArrayInputStream.read()); // 可以使用强制类型转换为byteSystem.out.println(byteArrayInputStream.read());System.out.println(byteArrayInputStream.read());System.out.println(byteArrayInputStream.read());System.out.println();//read(byteArrayInputStream);//byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{-128, -1, 0, 127});byte[] bytes = new byte[byteArrayInputStream.available()];System.out.println(byteArrayInputStream.read(bytes, 1, 2));System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));System.out.println();// skipbyteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{-128, -1, 0, 127});byteArrayInputStream.skip(1);read(byteArrayInputStream);// mark resetbyteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{-128, -1, 0, 127});System.out.println(byteArrayInputStream.markSupported());byteArrayInputStream.mark(0); // 参数不会生效,随便填byteArrayInputStream.skip(1);byteArrayInputStream.reset();read(byteArrayInputStream);//byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{-128, -1, 0, 127});byteArrayInputStream.close();read(byteArrayInputStream);}private static void read(ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream) throws IOException {byte[] bytes = new byte[byteArrayInputStream.available()];System.out.println(byteArrayInputStream.read(bytes));System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));System.out.println();}}
运行输出:
128
255
0
127-1
[]2
[0, -128, -1, 0]3
[-1, 0, 127]true
4
[-128, -1, 0, 127]4
[-128, -1, 0, 127]SequenceInputStream
SequenceInputStream是将多个流合并,其内部实现用的是
java.util.Enumeration
构造方法:
public SequenceInputStream(Enumeration<? extends InputStream> e) {}
public SequenceInputStream(InputStream s1, InputStream s2)
- 无论是何种构造方法,最终都会将其存在SequenceInputStream中定义的一个Enumeration属性中
继承方法:
- 不支持mark与reset方法,即
markSupported()返回false - read()方法将按顺序读取每个流的字节
- available()只返回当前流(Enumeration取出的当前元素)的字节数
- read(byte b[])与read(byte b[], int off, int len)默认读取当前流的数据。如果当前流没有数据,则读取下个流的数据
- available()方法与read(byte b[])结合只能读取到当前流数据(循环调用)。因为当前流数据读取完毕后,available()方法返回0
- 流只能读一次。
- 支持skip方法。
- 支持close方法。
综上:实际使用中,建议使用read()方法while循环的形式读取。
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/4/7.* * 合并输入流*/
public class SequenceInputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream1 = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{5, 6, 7});ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream2 = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{9, 10, 11});SequenceInputStream sequenceInputStream = new SequenceInputStream(byteArrayInputStream1, byteArrayInputStream2);read2(sequenceInputStream);byteArrayInputStream1.reset();byteArrayInputStream2.reset();sequenceInputStream = new SequenceInputStream(byteArrayInputStream1, byteArrayInputStream2);System.out.println(sequenceInputStream.markSupported());read(sequenceInputStream);read(sequenceInputStream);byteArrayInputStream1.reset();byteArrayInputStream2.reset();sequenceInputStream = new SequenceInputStream(byteArrayInputStream1, byteArrayInputStream2);sequenceInputStream.close();read2(sequenceInputStream); // 关闭后读取不到任何数据}private static void read(SequenceInputStream sequenceInputStream) throws IOException {byte[] bytes = new byte[sequenceInputStream.available()]; // 第二次读取时available返回0System.out.println(sequenceInputStream.read(bytes));System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));System.out.println();}private static void read2(SequenceInputStream sequenceInputStream) throws IOException {int t = sequenceInputStream.read();while (t != -1) {System.out.println((byte) t);t = sequenceInputStream.read();}System.out.println();}}
运行输出:
5
6
7
9
10
11false
3
[5, 6, 7]0
[]FileInputStream
文件字节输入流
构造方法:
public FileInputStream(String name) {} // 参数为文件路径
public FileInputStream(File file) {}
public FileInputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) {} // FileDescriptor是文件描述符
继承方法:
- 不支持mark与reset方法,即markSupported()返回false
- 流只能读取一次
- 支持skip和close方法
用法同其他InputStream类似,示例省略
新增方法:
- public final FileDescriptor getFD() throws IOException {} // 获取文件描述符,可用于创建文件输出流
- public FileChannel getChannel() {} // 获取文件通道。通道能够用于读或写
PipedInputStream&PipedOutputStream
管道流。PipedInputStream与PipedOutputStream结合使用
PipedInputStream构造方法:
public PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src) {}
public PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src, int pipeSize) {}
public PipedInputStream() {}
public PipedInputStream(int pipeSize) {}
PipedOutputStream构造方法:
public PipedOutputStream(PipedInputStream snk) {}
public PipedOutputStream() {}
PipedInputStream继承方法:
- 不支持mark与reset方法,即markSupported()返回false
- 流只能读取一次
- 支持skip和close方法
PipedOutputStream继承方法:
- 支持flush和close方法
如构造方法所示,PipedInputStream与PipedOutputStream可通过构造方法连接。如果不通过构造方法,也可以通过下列方法进行连接。
public void connect(PipedOutputStream src) {} // PipedInputStream
public synchronized void connect(PipedInputStream snk) {} // PipedOutputStream
实际上,构造方法也是通过调用connect方法进行连接。一个PipedInputStream或PipedOutputStream对象只能连接一次,多次连接会报Already connected异常。
PipedInputStream与PipedOutputStream的主要方法都是synchronized的,即线程安全的。它们的交互流程如下:
- PipedInputStream读取数据,判断是否存在连接,如果没有连接抛出异常。
- 存在连接,判断连接的PipedOutputStream是否有输出线程,如果没有,等待。
- 如果存在输出线程,判断线程是否已死,如果已死且数据已全部输入,则抛出异常,提示输出线程已死。
- 如果输出线程已死,但仍有待输入数据,则可继续输入。
- 如果输出线程未死,但无数据,等待。
由上可看出,以下情况容易造成死锁:
- 同一个线程内输出输入。
- 输出线程一直占据资源,且未有输出数据。
以下情况会造成死锁:
public static void lock1() throws IOException {PipedInputStream pipedInputStream = new PipedInputStream();PipedOutputStream pipedOutputStream = new PipedOutputStream();pipedInputStream.connect(pipedOutputStream);pipedInputStream.read(); // 会一直等待有数据输出到pipedOutputStream
}public static void lock2() throws IOException {PipedInputStream pipedInputStream = new PipedInputStream();PipedOutputStream pipedOutputStream = new PipedOutputStream();pipedInputStream.connect(pipedOutputStream);new Thread(() -> {try {pipedOutputStream.write(2);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}).start();System.out.println(pipedInputStream.read());System.out.println("开始第二次读入数据");System.out.println(pipedInputStream.read());System.out.println("程序走不到这里");
}
推荐的使用方式:
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/4/7.*/
public class PipedInputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {test();}private static void test() throws IOException {PipedInputStream pipedInputStream = new PipedInputStream();PipedOutputStream pipedOutputStream = new PipedOutputStream();pipedInputStream.connect(pipedOutputStream);new Thread(() -> {while (true) {try {System.out.println("读取到数据:" + (byte) pipedInputStream.read());} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println("读取数据结束"); // 当输出线程关闭,抛出异常break;}}}).start();new Thread(() -> {int i = '0';while (i <= '9') {try {pipedOutputStream.write(i++);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}).start();}}
StringBufferInputStream(已废弃)
这是一个已废弃的类,主要是对字符串进行字节流读取
构造方法:
public StringBufferInputStream(String s) {} // 看到构造方法大概就明白什么意思了
继承方法:
- 不支持mark与reset方法,即markSupported()返回false
- 支付skip方法
- 不支持close方法
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/4/9.*/
public class StringBufferInputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {StringBufferInputStream stringBufferInputStream = new StringBufferInputStream("abc");read(stringBufferInputStream); // 依次输出abc}public static void read(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {int i = inputStream.read();while (i != -1) {System.out.println((char)i);i = inputStream.read();}}}
FilterInputStream
FilterInputStream是对InputStream做了一层包装,其内部包含了一个InputStream。FilterInputStream提供的构造方法是protected修饰的:
protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) {this.in = in;
}
其常见的子类有:
- BufferedInputStream
- LineNumberInputStream(已废弃)
- PushBackInputStream
- DataInputStream
BufferedInputStream
字节缓冲流
构造方法
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {}
第一个构造方法是传入一个InputStream,第二个构造方法则是指定了大小。(注意,这里指定的大小是内存缓冲的大小,第一个构造方法默认大小是8192)
继承方法:
- 支持所有的父类方法
- 对于方法
mark(int readlimit)的参数readlimit也是支持的。也就是readlimit表示此后允许读取的字节数,超过这个字节数可能会导致reset失败。
这里我们着重讲解一下readlimit。
BufferedInputStream,顾名思义,是一个包装了InputStream的缓冲流。它的size可能比被包装流小很多,这也就是缓冲的意义。BufferedInputStream可以不用将被包装流中数据全部取出,而是动态的将其加载到缓冲中。简单地说:
- BufferedInputStream从被包装流中读取size字节数据
- 当这些数据被读完时,BufferedInputStream刷新数据,重新从被包装流中读取size字节数据。
看到这里,大概就有个疑问了。假设size=10(被包装流的数据远大于10),在pos=1的时候调用了mark方法,接下来一直读数据,直到将缓冲流中的数据刷新。此时再调用reset方法,就该是得不到期望的结果了。因为此前mark的地方数据已经被刷新了。
实际上:缓冲数据被刷新后,再调用reset方法是会抛出异常的。
那么readlimit有什么作用呢?
它的作用就是支持扩容,当readlimit被指定为20时,即表示读取了20个字节后,mark才可能失效。也就是读取了20个字节之内是不会失效了,是仍然支持reset方法。
而前面说了,读取了10字节就会失效了,那又是怎么回事?
原来,当指定了readlimit,那么read方法就会自动扩容,将size根据readlimit值进行扩大,从而支持mark的readlimit参数。直到读取超过了readlimit字节,才会将标记废弃掉。
看到这里,想必也明白了前面说的可能会导致reset失败的可能是什么含义了。明显的,如果将readlimit设置为5,即使读取超过了readlimit,但是因为没有达到刷新的限制,所以reset还是有效的。
上面部分的讲解可以参考BufferedInputStream源码中
fill()方法。
看一个例子:
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/4/9.*/
public class FilterInputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'}));System.out.println((char) bufferedInputStream.read());bufferedInputStream.mark(3);int i = 0;while (i++ < 4) { // 读取已超过readlimitSystem.out.println(bufferedInputStream.read());}bufferedInputStream.reset();}
}
因为缓冲流默认大小8192,所以即使读取超出了readlimit,也不会导致reset失效。
而如果将缓冲流的大小改为2,则调用reset方法时就会抛出异常了。
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'}),2);
LineNumberInputStream(已废弃)
这是一个已废弃的类,主要是增加了读取行号的功能。
构造方法
public LineNumberInputStream(InputStream in) {}
这个类在包装了字节流的基础上提供了获取行号的功能。而行号则是由换行符决定的。
继承方法:
- 基本上取决于被包装类。
新增方法:
- public int getLineNumber():获取当前行号
- public void setLineNumber(int lineNumber):设置当前行号
换行用\r或\r\n表示
PushBackInputStream
回退流支持将读取的字节重新放回流中。也可以放入其他任意字节数据。
构造方法:
public PushbackInputStream(InputStream in) {} // size = 1
public PushbackInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {}
size是指可支持的回退的流的长度。
继承方法:
- 不支持mark与reset方法,即markSupported()返回false。意味着流只能读取一次。
- 支持skip方法和close方法
新增方法:
- public void unread(int b) throws IOException {} //
- public void unread(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {} //
- public void unread(byte[] b) throws IOException {} //
回退流有什么作用呢?可能我们有这种场景,读取流的数据,当读到某个字节时,停止读取,但该字节依然需要被保留在流中。
public class PushBackInputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {PushbackInputStream pushbackInputStream = new PushbackInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'}));//int read = pushbackInputStream.read();while (read != 'h') {read = pushbackInputStream.read();}pushbackInputStream.unread(read);read(pushbackInputStream);}private static void read(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {int read = inputStream.read();while (read != -1) {System.out.print((char) read);read = inputStream.read();}}}
运行输出:
hello
DataInputStream
DataInputStream对字节流进行了一层包装,以便其能够读取基本Java数据类型。
构造方法:
public DataInputStream(InputStream in) {} //
继承方法:
- 所有继承方法的实现均取决于被包装流
新增方法:
- public final void readFully(byte b[]) throws IOException {} // 读满缓冲区b,读不满则等待。没有数据可读了且没满抛出异常
- public final void readFully(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {} //
- public final int skipBytes(int n) throws IOException {} // 和skip的区别在于skip只尝试一次,有可能跳过的数并不是n,而skipBytes尽量保证为跳过的数为n,除非真的没有了
- public final boolean readBoolean() throws IOException {} // 读取一个字节,如果是0(无符号),则返回true,否则为false
- public final byte readByte() throws IOException {} // 读取一个字节,并返回byte类型(-128~127)
- public final int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException {} // 读取一个字节,返回无符号数值(0~255)
- public final short readShort() throws IOException {} // 读取两个字节,并返回short类型(-32768~32767)
- public final int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException {} // 读取两个字节,并返回无符号数值(0~65535)
- public final char readChar() throws IOException {} // 读取两个字节,并返回一个char类型
- public final int readInt() throws IOException {} // 读取4个字节,并返回int类型
- public final long readLong() throws IOException {} // 读取8个字节,并返回long类型
- public final float readFloat() throws IOException {} // 读取4个字节,并返回short类型
- public final double readDouble() throws IOException {} // 读取8个字节,并返回double类型
- public final String readLine() throws IOException {} // 已废弃。读取一行,直到换行符
- public final String readUTF() throws IOException {} // 以UTF-8形式读取数据
- public final static String readUTF(DataInput in) throws IOException {} //
Byte&UnsignedByte:
byte在java中用一个字节存储,同样一个字节也可以存储一个字符。但是只能存储0~255范围内的字符。
以字符a为例,在ASCII编码中为:97,转换成二进制为:01100001。如果这个二进制表示的是一个byte,那它对应的数值为:97。
看着好像没什么问题。看一个例子
public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println((byte)(char) 127);System.out.println((byte)(char) 128);
}
运行输出:
127
-128
这是因为:
- java存储字符的方法仅存储字符对应编码的二进制数据。1个字节能表达的范围为0~255
- java存储数值型的方式则是带有符号位的补码方式。1个字节表达的范围为-128~127
以128号为字符为例,其对应的二进制:10000000。而通过补码的解析规则,该二进制对应的byte数值为:-128。
很显然,得到这种结果,会对开发人员使用流产生一种很不好的体验。这也是为什么流的read方法返回的是int,而不是byte的原因。因为int为4个字节,对于上述的二进制,补齐4字节为:00000000 00000000 00000000 10000000。该二进制对应的数值为:128。
这不正是UnsignedByte?
同理,UnsignedShort亦是如此。
利用UnsignedShort证明java内存采用的编码方式为UTF-16
public static void main(String[] args) {int i = '郑'; // 不要使用0~255之间的字符测试String a = "郑";byte[] bytes = a.getBytes("UTF-16");DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));dataInputStream.readChar(); // 去掉前面的标识位System.out.println(dataInputStream.readUnsignedShort() == i); // true
}
如上例,如果使用UTF-16之外的任何编码都得不到结果true。
readUTF:使用UTF-8编码读取字符数。但需要注意的是,流的前两个字节(UnsignedShort)表示需要读取数的长度。
public static void main(String[] args) {byte[] bytes = new byte[]{0, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c'}; // 前两位标识待读取的长度 UnsignedShortDataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));System.out.println(dataInputStream.available());System.out.println(dataInputStream.readUTF());//bytes = new byte[]{0, (byte) "郑泽旺".getBytes().length};byte[] bytes_utf = "郑泽旺".getBytes();int length1 = bytes.length;int length2 = bytes_utf.length;bytes = Arrays.copyOf(bytes, length1 + length2);System.arraycopy(bytes_utf, 0, bytes, length1, length2);dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));System.out.println(dataInputStream.available());System.out.println(dataInputStream.readUTF());
}
运行输出:
5
abc
11
郑泽旺
如果没有前面两个字节标识长度怎么办?很简单,可以利用上面讲到的回退流:
public static void main(String[] args) {DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream("郑泽旺".getBytes()));//PushbackInputStream pushbackInputStream = new PushbackInputStream(dataInputStream,2);pushbackInputStream.unread(dataInputStream.available());pushbackInputStream.unread(0);//DataInputStream dataInputStream_utf = new DataInputStream(pushbackInputStream);System.out.println(dataInputStream_utf.readUTF());
}
ObjectInputStream
ObjectInputStream用于对象的序列化操作。一般用ObjectOutputStream同时使用。
构造方法:
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) throws IOException {} //
继承方法:
- 不支持mark与reset方法,即markSupported()返回false
- 支持skip和close方法
新增方法:
- public final Object readObject() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {} // 读取对象。
- public Object readUnshared() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {} // 读取“非共享”对象。?
- public void defaultReadObject() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {} // ?
- public ObjectInputStream.GetField readFields() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {} // ?
- public void registerValidation(ObjectInputValidation obj, int prio) throws NotActiveException, InvalidObjectException {} // ?
- public boolean readBoolean() throws IOException {} // 读取bool型数据。(包括包装类)
- public byte readByte() throws IOException {} // 读取byte型数据。(包括包装类)
- public int readUnsignedByte() throws IOException {} // 读取无符号byte型数据。(包括包装类)
- public char readChar() throws IOException {} // 读取字符型数据。(包括包装类)
- public short readShort() throws IOException {} // 读取Short型数据。(包括包装类)
- public int readUnsignedShort() throws IOException {} // 读取无符号Short型数据。(包括包装类)
- public int readInt() throws IOException {} // 读取int型数据。(包括包装类)
- public long readLong() throws IOException {} // 读取long型数据。(包括包装类)
- public float readFloat() throws IOException {} // 读取float型数据。(包括包装类)
- public double readDouble() throws IOException {} // 读取double型数据。(包括包装类)
- public void readFully(byte[] buf) throws IOException {} // 读满缓冲区b,读不满则等待。没有数据可读了且没满抛出异常
- public void readFully(byte[] buf, int off, int len) throws IOException {} //
- public int skipBytes(int len) throws IOException {} // 和skip的区别在于skip只尝试一次,有可能跳过的数并不是n,而skipBytes尽量保证为跳过的数为n,除非真的没有了
- public String readLine() throws IOException {} // 已废弃
- public String readUTF() throws IOException {} // ?
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/4/24.*/
public class User implements Serializable {private String a;public String getA() {return a;}public void setA(String a) {this.a = a;}
}
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/4/23.*/
public class ObjectInputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {PipedOutputStream pipedOutputStream = new PipedOutputStream();PipedInputStream pipedInputStream = new PipedInputStream(pipedOutputStream);//ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(pipedOutputStream);ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(pipedInputStream);//User user = new User();user.setA("test");objectOutputStream.writeObject(user); // 这种通过管道流的方式只适合对象。其他的基本类型必须在写完后关流。//user = (User) objectInputStream.readObject();System.out.println(user.getA());}
}
OutputStream
OutputStream类是字节输出流的抽象类,是所有字节输出流的父类。
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| public abstract void write(int b) | 写入一个字节,传入值0~255范围。 超过这个范围的会被忽略(即只读取低八位字节) |
| public void write(byte b[]) | 向输出流写入一定长度的字节 |
| public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) | 向输出流写入一定长度的字节 |
| public void flush() | 刷新,即将缓冲区的数据写入到实际目标。默认什么都不做 |
| public void close() | 关闭输出流 |
不是所有的子类都支持flush和close
ByteArrayOutputStream
字节数组输出流
构造方法:
public ByteArrayOutputStream() {} //
public ByteArrayOutputStream(int size) {} //
继承方法:
- 没有重写flush方法,该方法不做任何事
- 不支持close方法
新增方法:
- public synchronized void writeTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {} // 将数据写入到指定的输出流
- public synchronized void reset() {} // 重置输出流,类似于清空数据。但实际是将下标变为0
- public synchronized byte toByteArray()[] {} // 得到输出流的数据
- public synchronized int size() {} // 输出流的长度
- public synchronized String toString() {} // 将字节转为String
- public synchronized String toString(String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {} // 指定编码的toString
- public synchronized String toString(int hibyte) {} // 废弃的方法
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/4/25.*/
public class ByteArrayOutputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 默认size=32byteArrayOutputStream.write('a');byteArrayOutputStream.write(new byte[]{'b','c'});byteArrayOutputStream.write(new byte[]{'d','e','f','g'},1,2);byteArrayOutputStream.flush(); // 什么都不做byteArrayOutputStream.close(); // 什么都不做System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString());System.out.println(Arrays.toString(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()));byteArrayOutputStream.reset();byteArrayOutputStream.write('a');System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString());}}
运行输出:
abcef
[97, 98, 99, 101, 102]
a
FileOutputStream
文件字节输出流
构造方法:
public FileOutputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException {} //
public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) throws FileNotFoundException {} // 为true表示从文件末尾写入
public FileOutputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {} //
public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) throws FileNotFoundException {} //
public FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor fdObj) {} // FileDescriptor是文件描述符
继承方法:
- 没有重写flush方法,该方法不做任何事
- 支持close方法
新增方法:
- public final FileDescriptor getFD() throws IOException {} // 获取文件描述符
- public FileChannel getChannel() {} // 获取文件通道
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/9.*/
public class FileOutputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\test\\test.txt");fileOutputStream.write('a');fileOutputStream.flush(); // 啥都不做FileDescriptor fileDescriptor = fileOutputStream.getFD(); // 获取文件描述符FileChannel fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel(); // 通过文件输出流打开的只能写,不能读ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);buf.put((byte) 'b');buf.flip();fileChannel.write(buf);FileOutputStream fileOutputStream2 = new FileOutputStream(fileDescriptor); // 不需要boolean参数,因为它与上一个就是一个流fileOutputStream2.write('c');//fileOutputStream.close(); // 关闭后文件描述符和文件通道都会关闭}}
执行代码后,会在文件test.txt中插入abc字符。
PipedOutputStream
见 PipedInputStream&PipedOutputStream
FilterOutputStream
FilterOutputStream是对OutputStream做了一层包装,其内部包含了一个OutputStream。FilterOutputStream提供的构造方法是需要保证OutpuStream:
public FilterOutputStream(OutputStream out) {this.out = out;
}
其常见的子类有:
- BufferedOutputStream
- DataOutputStream
- PrintStream
BufferedOutputStream
字节缓冲流
构造方法:
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) {} //
public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) {} //
继承方法:
- write方法默认写入缓存中,将缓存满了之后会写入到被包装流中
- flush方法会将缓冲中的数据写入到被包装流中,然后再调用被包装流的flush方法。
- close方法先flush,再调用被包装流的close方法
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/10.*/
public class BufferedOutputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 默认size=32BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream,4);//bufferedOutputStream.write(new byte[]{'a','b','c'});System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString());bufferedOutputStream.flush();System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString());}}
运行输出:
abc
DataOutputStream
DataOutputStream对字节流进行了一层包装,以便其能够读取基本java数据类型。
构造方法:
public DataOutputStream(OutputStream out) {} //
继承方法:
- wirte方法调用被包装流的write方法。并在DataOutputStream标记+1。
- flush方法调用被包装流的flush方法。
- close方法先flush,再调用被包装流的close方法
新增方法:
- public final void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOException {} // 表示输出一个boolean数据
- public final void writeByte(int v) throws IOException {} // 输出byte
- public final void writeShort(int v) throws IOException {} // 输出short
- public final void writeChar(int v) throws IOException {} // 输出char
- public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOException {} // 输出int
- public final void writeLong(long v) throws IOException {} // 输出long
- public final void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException {} // 输出float
- public final void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException {} // 输出double
- public final void writeBytes(String s) throws IOException {} // 输出String(这方法仅适合输出字符串每个字符均占一个字节的情况)
- public final void writeChars(String s) throws IOException {} // 输出String(注意,输出是以java内存使用的编码输出的,即Unicode)
- public final void writeUTF(String str) throws IOException {} // 以UTF-8格式输出数据
- public final int size() {} // 输出数据的长度
下面的例子讨论下writeChars和writeUTF的区别
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/19.*/
public class DataOutputStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 默认size=32DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);//dataOutputStream.writeChars("郑泽旺");dataOutputStream.flush();System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString());System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString("Unicode"));//byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 默认size=32dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);dataOutputStream.writeUTF("郑泽旺");dataOutputStream.flush();System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString());System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString("Unicode"));}}
PrintStream
打印输出流
构造方法:
public PrintStream(OutputStream out) {} //
public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush) {} // 自动flush
public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {} //
public PrintStream(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException {} //
public PrintStream(String fileName, String csn) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {} //
public PrintStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {} //
public PrintStream(File file, String csn) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {} //
继承方法:
- 支持flush方法,调用被包装流的flush方法
- 支持close方法
新增方法:
- public boolean checkError() {} // 判断是否有错误
- public void print(boolean b) {} // 打印bool
- public void print(char c) {}
- public void print(int i) {}
- public void print(long l) {}
- public void print(float f) {}
- public void print(double d) {}
- public void print(char s[]) {}
- public void print(String s) {}
- public void print(Object obj) {}
- public void println() {}
- public void println(boolean x) {}
- public void println(char x) {}
- public void println(int x) {}
- public void println(long x) {}
- public void println(float x) {}
- public void println(double x) {}
- public void println(char x[]) {}
- public void println(String x) {}
- public void println(Object x) {}
- public PrintStream printf(String format, Object … args) {}
- public PrintStream printf(Locale l, String format, Object … args) {}
- public PrintStream format(String format, Object … args) {}
- public PrintStream format(Locale l, String format, Object … args) {}
- public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq) {}
- public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) {}
- public PrintStream append(char c) {}
ObjectOutputStream
对象输出流
构造方法:
protected ObjectOutputStream() throws IOException, SecurityException {} // protected
public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) throws IOException {} //
继承方法:
- 支持flush方法和close,但依赖于被包装流的实现
新增方法:
- public void useProtocolVersion(int version) throws IOException {} // 指定写入流时要使用的流协议版本
- public final void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException {} // 输出一个对象
- public void writeUnshared(Object obj) throws IOException {} // 输出非共享对象?
- public void defaultWriteObject() throws IOException {} // ?
- public ObjectOutputStream.PutField putFields() throws IOException {} // ?
- public void writeFields() throws IOException {} //
- public void reset() throws IOException {}
- …
其他剩余不介绍了,一般也用不上
Reader
Reader类是字符输入流的抽象类,是所有字符输入流的父类。
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| public int read(java.nio.CharBuffer target) | 尝试将字符读入指定的字符缓冲区 |
| public int read() | 读取单个字符。 |
| public int read(char cbuf[]) | 将字符读取数组中 |
| abstract public int read(char cbuf[], int off, int len) | 将字符读入到数组中 |
| public long skip(long n) | 跳过指定长度 |
| public boolean ready() | 是否准备好 |
| public boolean markSupported() | 是否支持标记。默认不支持 |
| public void mark(int readAheadLimit) | 标记。默认抛异常 |
| public void reset() | 重置。默认抛异常 |
| abstract public void close() | 关闭流 |
markSupported、mark、reset、close方法是否支持由子类决定
InputStreamReader
处理字节流的字符输入流
构造方法:
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in) {} //
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {} //
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs) {} //
public InputStreamReader(InputStream in, CharsetDecoder dec) {} //
继承方法:
- 不支持markSupported、mark、reset等方法
- 支持重写了close方法
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/21.*/
public class InputStreamReaderTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{'a', 'b'});InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(byteArrayInputStream);//System.out.println(inputStreamReader.markSupported());//System.out.println(inputStreamReader.read());char[] chars = new char[1];inputStreamReader.read(chars);System.out.println(chars[0]);}}
运行输出:
false
97
b
FileReader
文件输入流,是InputStreamReader的子类。
构造方法:
public FileReader(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException {} //
public FileReader(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {} //
public FileReader(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {} //
继承方法:
- 同InputStreamReader一样
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/21.*/
public class FileReaderTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("D:\\test\\test.txt");System.out.println(fileReader.markSupported());System.out.println(fileReader.read());char[] chars = new char[1];fileReader.read(chars);System.out.println(chars[0]);}}
BufferedReader
缓冲字符输入流,增加了readLine方法,从而更好读取字符串
构造方法:
public BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) {} // sz为缓冲大小
public BufferedReader(Reader in) {} // 默认大小为8192
继承方法:
- 支持markSupported,即意味着支持mark、reset等方法
- 支持重写了close方法。
新增方法:
- public String readLine() throws IOException {} // 用于读取一行数据
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/21.*/
public class BufferedReaderTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'});InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(byteArrayInputStream);BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader, 3);System.out.println(bufferedReader.readLine());//
// mark(bufferedReader);//}}
运行输出
abcde
再来谈谈,mark(int readAheadLimit),同inputStream是一样的。
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/21.*/
public class BufferedReaderTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{'a', 'b','c', 'd', 'e'});InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(byteArrayInputStream);BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader,3);//System.out.println(bufferedReader.markSupported());bufferedReader.mark(2); // 如果将2改为大于等于4,则第二次reset也不会报错。System.out.println(bufferedReader.read());System.out.println(bufferedReader.read());System.out.println(bufferedReader.read());bufferedReader.reset(); // 不报错bufferedReader.mark(3);System.out.println(bufferedReader.read());System.out.println(bufferedReader.read());System.out.println(bufferedReader.read());System.out.println(bufferedReader.read());bufferedReader.reset(); // 报错//}}
如上,当第二次reset的时候会报错。但是第一mark时,将2改为4或4以上,则第二次也不会报错。因为第一次mark会触发扩容。
LineNumberReader
可操作行号的缓冲字符输入流,继承于BufferedReader,增加了读取行的功能
构造方法:
public LineNumberReader(Reader in) {} //
public LineNumberReader(Reader in, int sz) {} //
继承方法:
- 继承自BufferedReader,支持markSupported,即支持mark和reset方法
- 继承自BufferedReader,支持close方法。
新增方法:
- public String readLine() throws IOException {} // 读取一行,以换行符结尾
- public int getLineNumber() {} // 获取当前行
- public void setLineNumber(int lineNumber) {} // 设置当前行的行(并不是跳到指定行)
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/25.*/
public class LineNumberReaderTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{'a', 'b', '\n', 'c', 'd', '\n', 'e', 'f', '\n', 'g', 'h', '\n', 'i'});InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(byteArrayInputStream);LineNumberReader lineNumberReader = new LineNumberReader(inputStreamReader);//System.out.println(lineNumberReader.markSupported()); // trueSystem.out.println(lineNumberReader.getLineNumber()); // 0System.out.println(lineNumberReader.readLine()); // abSystem.out.println(lineNumberReader.getLineNumber()); // 1lineNumberReader.setLineNumber(3);System.out.println(lineNumberReader.getLineNumber()); // 3System.out.println(lineNumberReader.readLine()); // cdSystem.out.println(lineNumberReader.getLineNumber()); // 4}}
CharArrayReader
用于char的缓冲字符流
构造方法:
public CharArrayReader(char buf[]) {} //
public CharArrayReader(char buf[], int offset, int length) {} //
继承方法:
- 支持markSupported,即支持mark和reset方法。但mark方法的readAheadLimit参数被忽略
- 支持重写了close方法
StringReader
字符串输入流
构造方法:
public StringReader(String s) {} //
继承方法:
- 支持markSupported,即支持mark和reset方法。但mark方法的readAheadLimit参数被忽略,但不能小于0
- 支持重写了close方法
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/25.*/
public class StringReaderTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {StringReader stringReader = new StringReader("郑泽旺");System.out.println(stringReader.markSupported()); // trueSystem.out.println((char) stringReader.read()); // 郑stringReader.close();}}
PipedReader&PipedWriter
管道输入流。PipedReader与PipedWriter结合使用
PipedReader构造方法:
public PipedReader(PipedWriter src) throws IOException {} // 默认大小1024
public PipedReader(PipedWriter src, int pipeSize) throws IOException {} //
public PipedReader() {} //
public PipedReader(int pipeSize) {} //
PipedWriter构造方法:
public PipedWriter(PipedReader snk) throws IOException {}
public PipedWriter() {}
PipedReader继承方法:
- 不支持markSupported,即不支持mark和reset方法。
- 支持重写了close方法
PipedWriter继承方法:
- 实现了flush方法
- 实现了close方法
新增方法:
如构造方法所示,PipedReader与PipedWriter可通过构造方法连接。如果不通过构造方法,也可以通过下列方法进行连接。
public void connect(PipedWriter src) throws IOException {} // PipedReader
public synchronized void connect(PipedReader snk) throws IOException {} // PipedWriter
PipedReader与PipedWriter的主要方法都是synchronized线程安全的,它们交互流程如下:
- PipedReader读取数据,判断是否存在连接,如果没有拦截抛出异常。
- 存在连接,判断连接的PipedWriter是否存在输出线程,如果没有,等待。
- 如果存在输出线程,判断线程是否已死,如果已死其数据已全部输入,则抛出异常,提示输出线程已死。
- 如果线程已死,但仍有待输入数据,则可继续输入。
- 如果输出线程未死,但无数据,等待。
以下情况容易造成死锁:
- 同一个线程内输出输入
- 输出线程一直占有资源,且未有输出数据。
以下是造成阻塞的两个示例
private static void lock1() throws IOException {PipedWriter pipedWriter = new PipedWriter();PipedReader pipedReader = new PipedReader(pipedWriter);pipedReader.read(); // 一直等待
}private static void lock2() throws IOException {PipedWriter pipedWriter = new PipedWriter();PipedReader pipedReader = new PipedReader(pipedWriter);//new Thread(() -> {try {pipedWriter.write(97);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}).start();System.out.println(pipedReader.read());System.out.println("已读取一次数据");System.out.println(pipedReader.read()); // 一直等待System.out.println("已读取两次数据");
}
推荐的使用方法:
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class PipedReaderTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {PipedWriter pipedWriter = new PipedWriter();PipedReader pipedReader = new PipedReader(pipedWriter);new Thread(() -> {while (true) {try {System.out.print((char) pipedReader.read());} catch (IOException e) {// TODO 异常被吃掉了,为什么不提供一个方法判断连接是否关闭break;}}}).start();new Thread(() -> {String str = "为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗";for (char c : str.toCharArray()) {try {pipedWriter.write(c);Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}).start();}
}
FilterReader
字符过滤输入流
FilterReader是对Reader做了一层包装,其内部包含了一个Reader。FilterReader是一个抽象类,默认的构造方法是protected修饰的:
protected FilterReader(Reader in) {} //
常见的子类有:
- PushbackReader
PushBackReader
推回输入流
构造方法:
public PushbackReader(Reader in, int size) {} // 指可回退的数量
public PushbackReader(Reader in) {} // 默认大小为1
继承方法:
- 不支持markSupported方法,即不支持mark和reset方法
- 支持重写了close方法
新增方法:
- public void unread(int c) throws IOException {} // 回写一个字符
- public void unread(char cbuf[], int off, int len) throws IOException {} //
- public void unread(char cbuf[]) throws IOException {} //
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class PushbackReaderTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'});InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(byteArrayInputStream);PushbackReader pushbackReader = new PushbackReader(inputStreamReader, 3);//System.out.println(pushbackReader.markSupported());pushbackReader.unread(97);pushbackReader.unread(0xffff);pushbackReader.unread(0xffff + 1);System.out.println((char) pushbackReader.read());System.out.println((char) pushbackReader.read());System.out.println((char) pushbackReader.read());pushbackReader.unread(97);pushbackReader.close();}}
运行输出:
falsea
Writer
Reader类是字符输出流的抽象类,是所有字符输出流的父类。
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| public void write(int c) | 输出一个字符 |
| public void write(char cbuf[]) | 输出字符数组 |
| abstract public void write(char cbuf[], int off, int len) | 输出字符数组 |
| public void write(String str) | 输出字符串 |
| public void write(String str, int off, int len) | 输出字符串 |
| public Writer append(CharSequence csq) | 添加字符序列 |
| public Writer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) | 添加字符序列 |
| public Writer append(char c) | 添加字符 |
| abstract public void flush() | 刷新。一般用于将数据从缓冲中刷新到实际输出流中 |
| abstract public void close() | 关闭流 |
不是所有的子类都支持flush和close
CharArrayWriter
用于char的缓冲输出流
构造方法:
public CharArrayWriter() {} //
public CharArrayWriter(int initialSize) {} //
继承方法:
- flush方法什么都不做。
- close方法什么都不做。
新增方法:
- public void reset() {} // 重置
- public char toCharArray()[] {} // 输出字符数组
- public int size() {} //
- public String toString() {} //
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class CharArrayWriterTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {CharArrayWriter charArrayWriter = new CharArrayWriter();charArrayWriter.write("为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗");System.out.println(charArrayWriter.toString());}}
OutputStreamWriter
处理字节流的字符输出流
构造方法:
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {} //
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) {} //
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, Charset cs) {} //
public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, CharsetEncoder enc) {} //
继承方法:
- 实现了flush方法
- 实现了close方法
新增方法:
- public String getEncoding() {} // 获取编码方法
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class OutputStreamWriterTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(byteArrayOutputStream);outputStreamWriter.write("为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗");System.out.println(outputStreamWriter.getEncoding());System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString());outputStreamWriter.flush();System.out.println(byteArrayOutputStream.toString());outputStreamWriter.close();}}
FileWriter
文件输出流
构造方法:
public FileWriter(String fileName) throws IOException {}
public FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append) throws IOException {} // append指文本后继续输出
public FileWriter(File file) throws IOException {} //
public FileWriter(File file, boolean append) throws IOException {} //
public FileWriter(FileDescriptor fd) {} //
继承方法:
- 同OutputStreamWriter
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class FileWriterTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("D:\\test\\test.txt");fileWriter.write("为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗");fileWriter.flush(); // flush或close后,字符串才会被写入文本中fileWriter.close();}}
FilterWriter
字符过滤输出流
FilterWriter是对Writer做了一层包装,其内部包含了一个Writer。FilterWriter是一个抽象类,默认的构造方法是protected修饰的:
protected FilterWriter(Writer out) {} //
io包下面没有常用的子类
PrintWriter
打印输出流。打印输出流 包装了Writer或OutputStream,以打印的方式支持输出不同的数据类型
构造方法:
public PrintWriter (Writer out) {} //
public PrintWriter(Writer out, boolean autoFlush) {}
public PrintWriter(OutputStream out) {} //
public PrintWriter(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush) {}
public PrintWriter(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException {} //
public PrintWriter(String fileName, String csn) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {}
public PrintWriter(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {}
public PrintWriter(File file, String csn) throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException {}
继承方法:
- 实现了flush方法
- 实现了close方法
新增方法:
- public boolean checkError() {} //
- public void print(boolean b) {} // true or false
- public void print(char c) {} //
- public void print(int i) {} //
- public void print(long l) {} //
- public void print(float f) {}
- public void print(double d) {}
- public void print(char s[]) {}
- public void print(String s) {}
- public void print(Object obj) {} // obj.toString
- public void println() {} // 打印换行
- public void println(boolean x) {} // 先打印后换行
- public void println(char x) {}
- public void println(int x) {}
- public void println(long x) {}
- public void println(float x) {}
- public void println(double x) {}
- public void println(char x[]) {}
- public void println(String x) {}
- public void println(Object x) {} //
- public PrintWriter printf(String format, Object … args) {} //
- public PrintWriter printf(Locale l, String format, Object … args) {}
- public PrintWriter format(String format, Object … args) {}
- public PrintWriter format(Locale l, String format, Object … args) {}
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class PrintWriterTest {public static void main(String[] args) {CharArrayWriter charArrayWriter = new CharArrayWriter();PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(charArrayWriter);//printWriter.print("为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗");System.out.println(charArrayWriter.toString());}}
BufferedWriter
缓冲字符输出流
构造方法:
public BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz) {}
public BufferedWriter(Writer out) {} // 默认大小 8192
继承方法:
- 实现了flush方法
- 实现了close方法
新增方法:
- public void newLine() throws IOException {} // 增加换行
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class BufferedWriterTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {CharArrayWriter charArrayWriter = new CharArrayWriter();BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(charArrayWriter);//bufferedWriter.newLine();bufferedWriter.write("为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗");System.out.println(charArrayWriter.toString());bufferedWriter.flush();System.out.println(charArrayWriter.toString());bufferedWriter.close();}}
运行输出:
为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗
StringWriter
字符串输出流。其内部是使用StringBuffer实现的
构造方法:
public StringWriter(int initialSize) {} //
public StringWriter() {} // 默认大小16
继承方法:
- flush方法什么都不做。
- close方法什么都不做。
- 重写了Object的toString方法
新增方法:
- public StringBuffer getBuffer() {}
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class StringWriterTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {StringWriter stringWriter = new StringWriter();stringWriter.write("为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗");System.out.println(stringWriter.toString());System.out.println(stringWriter.getBuffer());stringWriter.flush();stringWriter.close();}}
PipedWriter
管道输出流。见 PipedReader&PipedWriter
读取和写入文件的几种方式
用FileInputStream读取。
因为FileInputStream是字节流,所以每次读的都是一个字节,实际用途可能不大。
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class WRFileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\test\\test.txt");byte[] bytes = new byte[fileInputStream.available()];fileInputStream.read(bytes);System.out.println(new String(bytes));}}
用BufferInputStream读取
使用BufferInputStream将FileInputStream包装一层。其本质FileInputStream没多大区别
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class WRFileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\test\\test.txt");BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(fileInputStream);byte[] bytes = new byte[bufferedInputStream.available()];bufferedInputStream.read(bytes);System.out.println(new String(bytes));}}
用FileReader读取
FileReader字符流,每次可读取一个字符。
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class WRFileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("D:\\test\\test.txt");int read = fileReader.read();while (read != -1) {System.out.print((char)read);read = fileReader.read();}System.out.println();}
}
用BufferedReader读取,推荐
使用BufferedReader包装FileReader读取文件。由于BufferedReader提供readLine方法,推荐。
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class WRFileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("D:\\test\\test.txt");BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);String s = bufferedReader.readLine();while (s != null) {System.out.println(s);s = bufferedReader.readLine();}}
}
用FileOutputStream写入
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class WRFileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String str = "为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗";FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\test\\test.txt");byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();fileOutputStream.write(bytes);fileOutputStream.close();}
}
用BufferedOutputStream、DataOutputStream、PrintStream写入
这三个均属于FilterOutputStream,其中DataOutputStream和PrintStream可以写入字符串,而BufferedOutputStream同FileOutputStream大同小异。
- BufferedOutputStream用法同FileOutputStream
- DataOutputStream在于需要小心的控制编码,实际上如果不在乎文件可读性,与DataInputStream配合实际,推荐这个
- PrintStream采用默认编码,推荐使用
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class WRFileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String str = "为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗";FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\test\\test.txt");PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(fileOutputStream); // 其他FilterOutputStream类似printStream.print(str);printStream.close();}
}
用FileWriter写入,推荐
直接使用FileWriter往文件写入数据。推荐使用
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class WRFileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String str = "为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗";FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("D:\\test\\test.txt");writer.write(str);writer.close();}
}
用PrintWriter、BufferedWriter等写入
BufferedWriter和BufferedWriter包装FileWriter,可直接往文件中写入数据。由于FileWriter可直接写入数据,故该方法没必要使用。
- BufferedWriter提供输出换行的功能,无序用户考虑不同系统换行兼容的问题
- PrintWriter提供各种格式化的方法,特殊情况可使用
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class WRFileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String str = "为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗";FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("D:\\test\\test.txt");BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(writer);bufferedWriter.write(str);bufferedWriter.close();}
}
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class WRFileTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String str = "为实现中华民族伟大复兴的中国梦不懈奋斗";FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("D:\\test\\test.txt");PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(writer);printWriter.format("%s",str);printWriter.close();}
}
Zip流
Zip流包括ZipInputStream和ZipOutputStream,分别用于解压和压缩文件。
ZipInputStream:
构造方法:
public ZipInputStream(InputStream in) {} //
public ZipInputStream(InputStream in, Charset charset) {} //
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| public ZipEntry getNextEntry() | 读取下一个ZipEntry,并将流内的位置移至该entry所指数据的开头 |
| public void closeEntry() | 关闭当前ZipEntry |
| public int available() | 判断是否已读完当前ZipEntry |
| public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 读取数据 |
| public long skip(long n) | 跳过当前ZipEntry指定的字节数 |
| public void close() | 关闭 |
ZipOutputStream:
构造方法:
public ZipOutputStream(OutputStream out) {}
public ZipOutputStream(OutputStream out, Charset charset) {}
| 方法 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| public void setComment(String comment) | 设置此Zip文件的注释文字 |
| public void setMethod(int method) | 使用的压缩方法? |
| public void setLevel(int level) | 压缩级别。共有0-9十个级别。从低到高,时间越长,空间越小。 |
| public void putNextEntry(ZipEntry e) | 开始一个新的ZipEntry,并将流内的位置移至此entry所指数据的开头 |
| public void closeEntry() | 关闭当前ZipEntry |
| public synchronized void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 输出数据到当前ZipEntry |
| public void finish() | 完成当前写入Zip输出流的内容,无须关闭它所配合的OutputStream |
| public void close() | 关闭流 |
用法示例:
/*** @author zhengzewang on 2019/5/26.*/
public class ZipTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String compressDir = "D:\\test\\compress";String decompressDir = "D:\\test\\decompress";String zipName = "D:\\test\\test.zip";compress(compressDir, zipName); // zip/rar/jar 等均支持decompress(decompressDir, zipName);//}private static void decompress(String dir, String zipName) throws IOException {File file = new File(zipName);FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);ZipInputStream zipInputStream = new ZipInputStream(fileInputStream);ZipEntry zipEntry = zipInputStream.getNextEntry();while (zipEntry != null) {String entryName = zipEntry.getName();File temp = new File(dir + File.separator + entryName);if (zipEntry.isDirectory() || entryName.endsWith("\\") || entryName.endsWith(File.separator)) {if (!temp.exists()) {temp.mkdirs();}} else {if (!temp.exists()) {temp.getParentFile().mkdirs();}FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(temp);int read = zipInputStream.read();while (read != -1) {fileOutputStream.write(read);read = zipInputStream.read();}fileOutputStream.close();zipInputStream.closeEntry();}zipEntry = zipInputStream.getNextEntry();}zipInputStream.close();}private static void compress(String dir, String zipName) throws IOException {File zip = new File(zipName);FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(zip);ZipOutputStream zipOutputStream = new ZipOutputStream(fileOutputStream);//zip(zipOutputStream, new File(dir), "", zip);zipOutputStream.close();}private static void zip(ZipOutputStream zipOutputStream, File file, String base, File zip) throws IOException {if (file.getPath().equals(zip.getPath())) {return;}if (file.isDirectory()) {File[] files = file.listFiles();base = (base == null || base.trim().isEmpty()) ? "" : base + File.separator;if (files.length == 0) {zipOutputStream.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(base));} else {for (File f : files) {base = (base == null || base.trim().isEmpty()) ? "" : base + File.separator;zip(zipOutputStream, f, base + f.getName(), zip);}}} else {zipOutputStream.putNextEntry(new ZipEntry(base));FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);int b = fileInputStream.read();while (b != -1) {zipOutputStream.write(b);b = fileInputStream.read();}fileInputStream.close();}}}
JarInputStream&JarOutputStream
TODO
参考文档
Java里的管道输入流 PipedInputStream与管道输出流 PipedOutputStream
thanks! 顶部 底部 ** --郑泽旺 ** 2019-04-06
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!