JDK1.8 HotSpot虚拟机逃逸分析
逃逸分析是JIT编译器的用来优化代码的一种手段,下面粘贴一下官方的Hot Spot说明。
链接打不开的话可能要扶个梯子往上爬。
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/technotes/guides/vm/performance-enhancements-7.html
Escape analysis is a technique by which the Java Hotspot Server Compiler can analyze the scope of a new object’s uses and decide whether to allocate it on the Java heap.
Escape analysis is supported and enabled by default in Java SE 6u23 and later.
The Java Hotspot Server Compiler implements the flow-insensitive escape analysis algorithm described in:
[Choi99] Jong-Deok Choi, Manish Gupta, Mauricio Seffano,
Vugranam C. Sreedhar, Sam Midkiff,
“Escape Analysis for Java”, Procedings of ACM SIGPLAN
OOPSLA Conference, November 1, 1999
Based on escape analysis, an object’s escape state might be one of the following:
-
GlobalEscape – An object escapes the method and thread. For example, an object stored in a static field, or, stored in a field of an escaped object, or, returned as the result of the current method.
-
ArgEscape – An object passed as an argument or referenced by an argument but does not globally escape during a call. This state is determined by analyzing the bytecode of called method.
-
NoEscape – A scalar replaceable object, meaning its allocation could be removed from generated code.
After escape analysis, the server compiler eliminates scalar replaceable object allocations and associated locks from generated code. The server compiler also eliminates locks for all non-globally escaping objects. It does not replace a heap allocation with a stack allocation for non-globally escaping objects.
Some scenarios for escape analysis are described next.
The server compiler might eliminate certain object allocations. Consider the example where a method makes a defensive copy of an object and returns the copy to the caller.
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String personName, int personAge) {
name = personName;
age = personAge;
}
public Person(Person p) { this(p.getName(), p.getAge()); }
public int getName() { return name; }
public int getAge() { return age; }
}
public class Employee {
private Person person;
// makes a defensive copy to protect against modifications by callerpublic Person getPerson() { return new Person(person) };public void printEmployeeDetail(Employee emp) {Person person = emp.getPerson();// this caller does not modify the object, so defensive copy was unnecessarySystem.out.println ("Employee's name: " + person.getName() + "; age: " + person.getAge()); }
}
The method makes a copy to prevent modification of the original object by the caller. If the compiler determines that the getPerson method is being invoked in a loop, it will inline that method. In addition, through escape analysis, if the compiler determines that the original object is never modified, it might optimize and eliminate the call to make a copy.
The server compiler might eliminate synchronization blocks (lock elision) if it determines that an object is thread local. For example, methods of classes such as StringBuffer and Vector are synchronized because they can be accessed by different threads. However, in most scenarios, they are used in a thread local manner. In cases where the usage is thread local, the compiler might optimize and remove the synchronization blocks.
简单总结下
JVM热点编译器在编译期间会对代码进行逃逸分析,逃逸分析在JDK 6u23之后默认开启,经过逃逸分析后,如果判定为逃逸失败,那么这个对象就是可被标量替换的,会替换成标量(也就是java中的基本数据类型)即将对象拆解,从而实现不在堆上分配对象。
接着,这段话很重要:
After escape analysis, the server compiler eliminates scalar replaceable object allocations and associated locks from generated code. The server compiler also eliminates locks for all non-globally escaping objects. It does not replace a heap allocation with a stack allocation for non-globally escaping objects.
【小学三年级的翻译水平】
经过了逃逸分析,如果对象逃逸失败,编译器会将相关的锁消除,并消除可被标量替换的对象(对象拆解)。编译器也同样会将非全局逃逸的对象锁消除。但是非全局逃逸对象的栈上分配并不能取代对象在堆上分配。
个人理解:
经过逃逸分析后,对于没能成功逃逸的对象,会进行锁消除或者栈上分配,但是这里的栈上分配不是真正意义上的栈上分配,不像堆那样开辟空间、初始化… 这里的栈上分配是用标量替换的方式实现的,也就是说,HotSpot中的对象还是全部分配在堆空间!!!
实验测试
使用visualVM记得不要用debug模式,不然看不出效果!!!
代码
public class StackAllocation {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {allc();}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("共耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒");Thread.currentThread().join();}public static void allc() {User user = new User();}static class User {}
}
开启逃逸分析,关闭标量替换
-Xms256m -Xmx256m -XX:+DoEscapeAnalysis -XX:-EliminateAllocations -XX:+PrintGCDetails
发生了GC,耗时较长,对象分配在堆空间中
开启逃逸分析,开启标量替换
-Xms256m -Xmx256m -XX:+DoEscapeAnalysis -XX:+EliminateAllocations -XX:+PrintGCDetails
未发生了GC,耗时较短,对象少部分分配在堆中(这里不是很理解为什么不是0,可能一部分对象没用到JIT编译器吧,所以少量分配到堆中)
关闭逃逸分析,开启标量替换
-Xms256m -Xmx256m -XX:-DoEscapeAnalysis -XX:+EliminateAllocations -XX:+PrintGCDetails
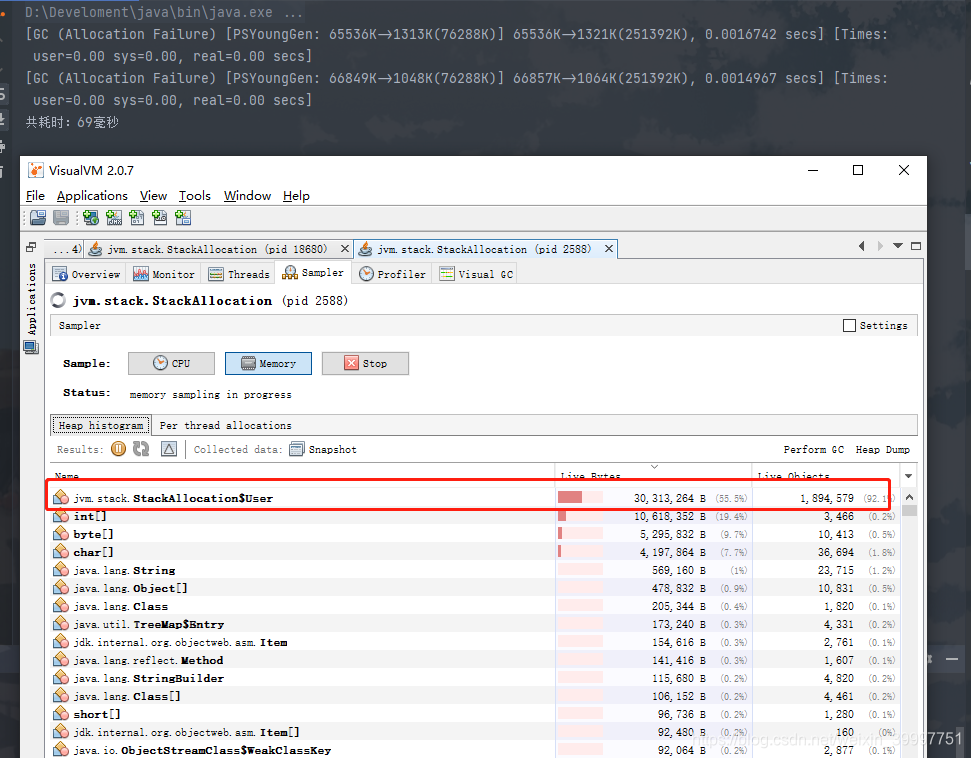
发生了GC,耗时较长,对象分配在堆空间中
总结
逃逸分析是JIT编译器代码分析的过程,分析后可能做栈上分配、锁消除、标量替换的优化,逃逸分析是后三者前提条件。
HotSpot虚拟机的栈上分配不是真正意义上的在栈上分配对象,只是借用标量替换来实现栈上分配。
所以HotSpot的对象都是分配在堆上,这句话是没错的。
| 逃逸分析 | 标量替换 | 效果 |
|---|---|---|
| 开启 | 关闭 | 发生GC,对象分配在堆中 |
| 开启 | 开启 | 未发生GC,对象随栈帧弹栈而消亡 |
| 关闭 | 开启 | 发生GC,对象分配在堆中 |
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!

