数据结构进阶篇,二叉树构造专题
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
「题目:」
给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历, inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
「示例:」
输入: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7],输出: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]。
「解题思路:」
由于二叉树是递归定义的,所以只需要寻找根节点、左子树以及右子树之间的关系,即可构造出二叉树。
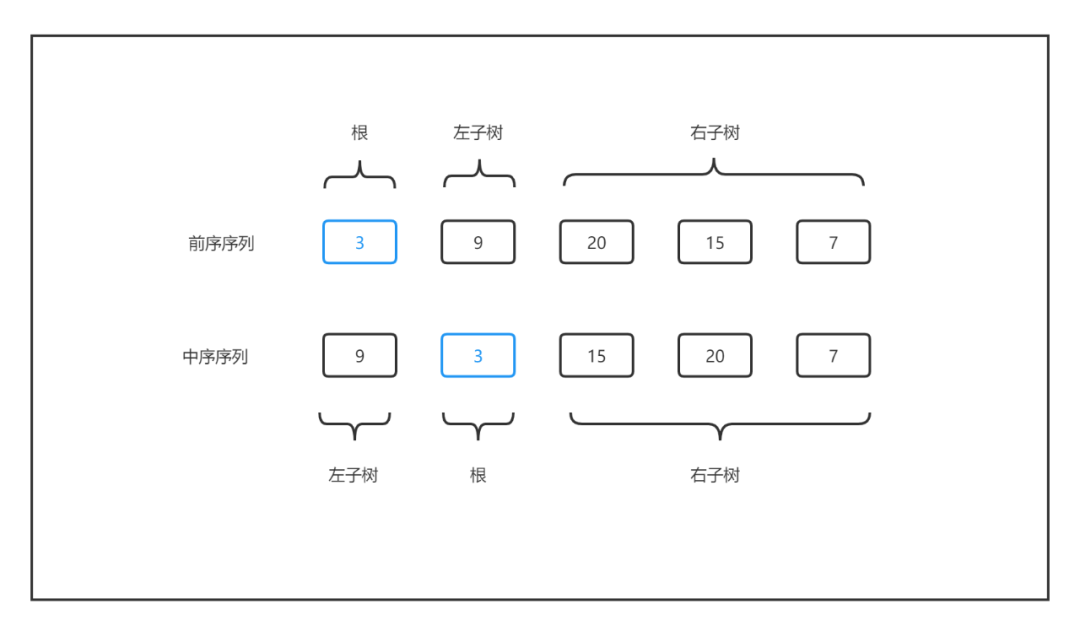
参照上述图解,通过前序序列可以轻松地找到当前子树的根节点,然后通过中序序列依据该根节点分割其左右子树,所以这里有一个重要的隐藏条件就是二叉树中的元素值不能重复!
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n)。
const buildTree = (preorder, inorder) => {// 递归中止条件if (preorder.length === 0) {return null;}const rootElement = preorder[0];const root = new TreeNode(rootElement);const rootElementIndex = inorder.indexOf(rootElement);root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(1, rootElementIndex + 1), inorder.slice(0, rootElementIndex));root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(rootElementIndex + 1), inorder.slice(rootElementIndex + 1));return root;
}针对上述解法中的 indexOf 耗时,可以通过空间换时间的技巧来优化。
利用哈希表将中序序列中各个根节点的映射关系提前保存好,但是这样会面临一个新的问题?就是不能再对 inorder 进行 slice,这样会导致映射关系发生变化。这里就需要转化为利用下标来维护两个序列的区间。
而计算下标其中一个重要的点就是计算出左右子树的长度,这个仍然是利用前序序列和中序序列的特性来解决。
另一个值得注意的点就是递归条件的变化。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n)。
const buildTree = (preorder, inorder) => {const record = new Map();for (let i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {record.set(inorder[i], i);}const _buildTree = (start1, end1, start2, end2) => {// 递归中止条件if (start1 > end1) {return null;}const element = preorder[start1];const root = new TreeNode(element);const index = record.get(element);const rightTreeLength = end2 - index;const leftTreeLength = end1 - start1 - rightTreeLength;root.left = _buildTree(start1 + 1, start1 + 1 + leftTreeLength - 1, index - leftTreeLength, index - 1);root.right = _buildTree(start1 + leftTreeLength + 1, end1, index + 1, end2);return root;}return _buildTree(0, preorder.length - 1, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
「题目:」
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这棵 二叉树 。
「示例:」
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3],输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]。
「解题思路:」
本道题的后序序列发挥着与前道题中的前序序列一样的作用,也是在后序序列中寻找根节点的位置,然后再根据根节点的位置,在中序序列中分割出左右子树。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n)。
const buildTree = (inorder, postorder) => {if (inorder.length === 0) {return null;}const el = postorder.pop();const root = new TreeNode(el);const index = inorder.indexOf(el);root.left = buildTree(inorder.slice(0, index), postorder.slice(0, index));root.right = buildTree(inorder.slice(index + 1), postorder.slice(index));return root;
}至于优化解法,有兴趣的同学可以参考前道题的思路。
889. 根据前序和后序遍历构造二叉树
「题目:」
给定两个整数数组,preorder 和 postorder ,其中 preorder 是一个具有 无重复 值的二叉树的前序遍历,postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,重构并返回二叉树。
如果存在多个答案,您可以返回其中 任何 一个。
「示例:」
输入:preorder = [1,2,4,5,3,6,7], postorder = [4,5,2,6,7,3,1],输出:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]。
「解题思路:」
前序序列和后序序列都可以很容易地定位到根节点,但是两个序列同时出现的时候,无法直接分割出左右子树。
根据前序序列的特性,其序列的第一个元素是当前二叉树的根节点,那么其第二个元素就是左子树的根节点,根据该节点又可以在后序序列中分割出左右子树。
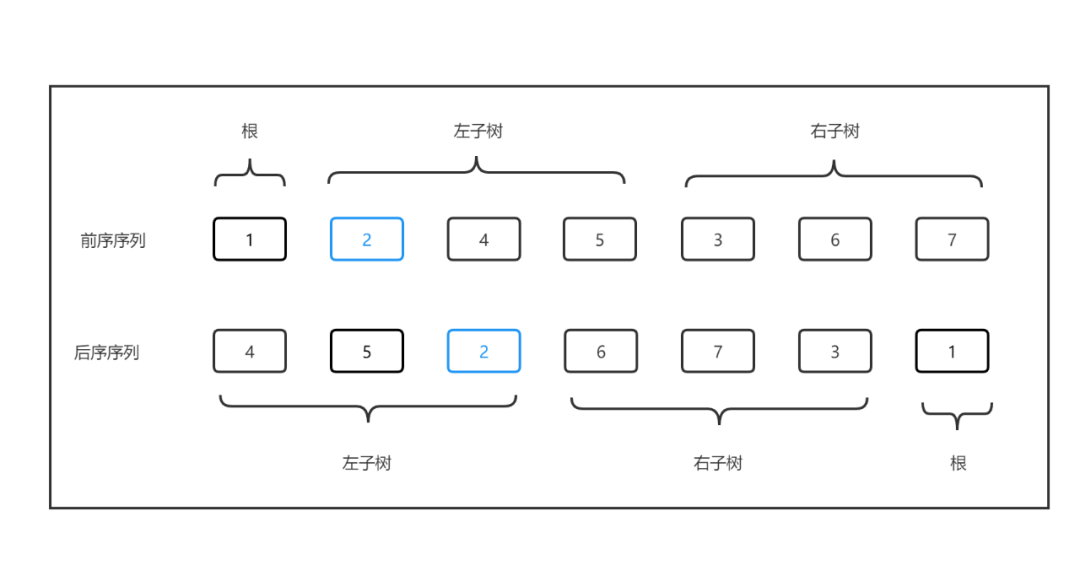
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n)。
const constructFromPrePost = (pre, post) => {if (pre.length === 0) {return null}// 拿出根节点const rootValue = pre.shift()post.pop()const root = new TreeNode(rootValue)if (pre.length > 0) {// 左子树的根节点const l = pre[0]const lIndex = post.indexOf(l)root.left = constructFromPrePost(pre.slice(0, lIndex + 1), post.slice(0, lIndex + 1))root.right = constructFromPrePost(pre.slice(lIndex + 1), post.slice(lIndex + 1))}return root
}1008. 前序遍历构造二叉搜索树
「题型:」
给定一个整数数组,它表示BST(即 二叉搜索树 )的 先序遍历 ,构造树并返回其根。
保证 对于给定的测试用例,总是有可能找到具有给定需求的二叉搜索树。
「示例:」
输入:preorder = [8,5,1,7,10,12],输出:[8,5,10,1,7,null,12]。
「第一种解题思路:」
由于 BST 的中序序列是一个升序序列,那么可以通过对前序序列排序得到其中序序列,从而将本题转化为【105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树】。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n)。
const bstFromPreorder = (preorder) => {const inorder = preorder.map(item => item).sort((a, b) => a - b);return buildTree(preorder, inorder);
}const buildTree = (preorder, inorder) => {if (preorder.length === 0) {return null;}const rootValue = preorder.shift();const root = new TreeNode(rootValue);const index = inorder.indexOf(rootValue);root.left = buildTree(preorder.slice(0, index), inorder.slice(0, index));root.right = buildTree(preorder.slice(index), inorder.slice(index + 1));return root;
}「第二种解题思路:」
利用 BST 的根元素严格大于其左子树的所有节点的特性,从而分割出左右子树。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n)。
const bstFromPreorder = preorder => {// 终止条件if (!preorder.length) {return null}const root = new TreeNode(preorder[0])// 寻找左右子树的分割点let index = 0const max = preorder.lengthfor (let i = 0; i < max; i++) {if (preorder[0] >= preorder[i]) {index = icontinue}break}root.left = bstFromPreorder(preorder.slice(1, index + 1)) root.right = bstFromPreorder(preorder.slice(index + 1))return root
}写在最后
「感谢您能耐心地读到这里,如果本文对您有帮助,欢迎点赞、分享、或者关注下方的公众号哟。」
相关链接:
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-postorder-traversal/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-search-tree-from-preorder-traversal/

本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!