Linux下的进程通信:匿名管道(模拟实现一个父进程与多个子进程间的通信)
1.进程间通信的目的
a.数据传输
b.资源共享
c.消息通知
d.进程控制
2.匿名管道的实现原理
我们都知道进程是存在内存中的,那么我们要实现进程通信的前提是必须在内存中找到一块共享区域。这块区域不属于父子进程中的任意一个。这片公共区域就可以称之为父子进程通信的管道。
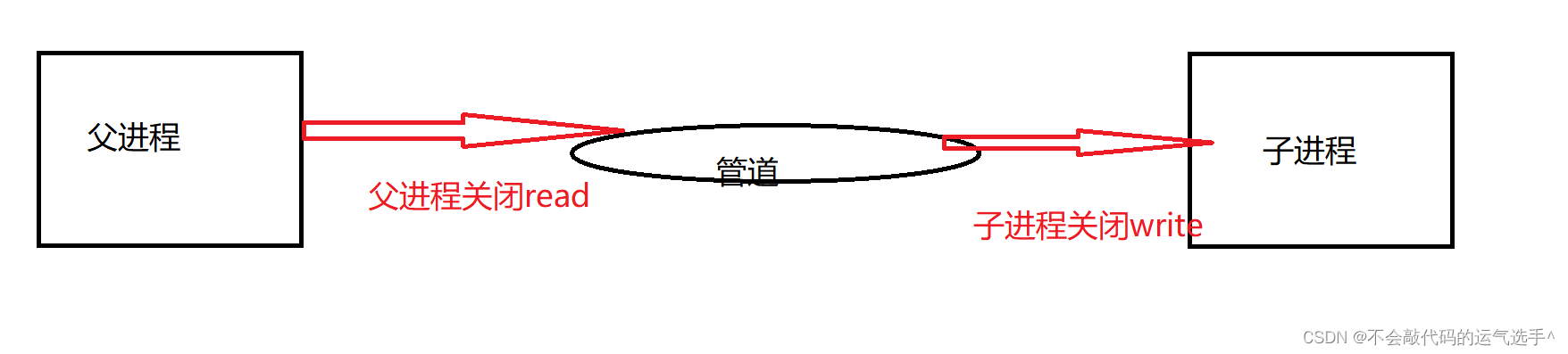
管道就和文件的使用方法差不多,我们只需要留下需要对它操作部分的权限。这样就可以实现父进程发送数据到管道,子进程从管道读出数据。
但是,要注意匿名管道这种通信是半双工的,只能从一边传入另一边,不可以俩边一起读或者一起写。
3.pipe函数
int arr[2]={0};
int ret=pipe(arr);
这个函数可以用来开辟一个管道。我们只需要传入一个大小为2的数组进去,返回值为0表示创建成功。arr[0]就是代表以read的方式打开管道的文件描述符fd,arr[1]就是表示以write的方式打开管道的文件描述符fd。
4.来实现一个简单的单父进程与多个子进程间的通信
a.task.h文件
#pragma once2 3 #include 4 #include 5 #include 6 #include 7 #include 8 #include 9 10 using namespace std;11 12 typedef function func; //打包下面的任务13 vector callbacks; 14 unordered_map mp; //用下标与任务对应起来15 16 void readWysql()17 {18 cout<<"sub process ["< b. test.cpp文件
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "Task.hpp"#define PROCESS_NUM 5using namespace std;int waitCommand(int waitFd, bool &quit) //如果对方不发,我们就阻塞
{uint32_t command = 0;ssize_t s = read(waitFd, &command, sizeof(command));if (s == 0){quit = true;return -1;}assert(s == sizeof(uint32_t));return command;
}void sendAndWakeup(pid_t who, int fd, uint32_t command)
{write(fd, &command, sizeof(command));cout << "main process: call process " << who << " execute " << desc[command] << " through " << fd << endl;
}int main()
{// 代码中关于fd的处理,有一个小问题,不影响我们使用,但是你能找到吗??load();// pid: pipefdvector> slots;// 先创建多个进程for (int i = 0; i < PROCESS_NUM; i++){// 创建管道int pipefd[2] = {0};int n = pipe(pipefd);assert(n == 0);(void)n;pid_t id = fork();assert(id != -1);// 子进程我们让他进行读取if (id == 0){// 关闭写端close(pipefd[1]);// childwhile (true){// pipefd[0]// 等命令bool quit = false;int command = waitCommand(pipefd[0], quit); //如果对方不发,我们就阻塞if (quit)break;// 执行对应的命令if (command >= 0 && command < handlerSize()){callbacks[command]();}else{cout << "非法command: " << command << endl;}}exit(1);}// father,进行写入,关闭读端close(pipefd[0]); // pipefd[1]slots.push_back(pair(id, pipefd[1]));}// 父进程派发任务srand((unsigned long)time(nullptr) ^ getpid() ^ 23323123123L); // 让数据源更随机while (true){// 选择一个任务, 如果任务是从网络里面来的?int command = rand() % handlerSize();// 选择一个进程 ,采用随机数的方式,选择进程来完成任务,随机数方式的负载均衡int choice = rand() % slots.size();// 把任务给指定的进程sendAndWakeup(slots[choice].first, slots[choice].second, command);sleep(1);//手输入任务的方式(菜单)// int select;// int command;// cout << "############################################" << endl;// cout << "# 1. show funcitons 2.send command #" << endl;// cout << "############################################" << endl;// cout << "Please Select> ";// cin >> select;// if (select == 1)// showHandler();// else if (select == 2)// {// cout << "Enter Your Command> ";// // 选择任务// cin >> command;// // 选择进程// int choice = rand() % slots.size();// // 把任务给指定的进程// sendAndWakeup(slots[choice].first, slots[choice].second, command);// }// else// {// }}// 关闭fd, 所有的子进程都会退出for (const auto &slot : slots){close(slot.second);}// 回收所有的子进程信息for (const auto &slot : slots){waitpid(slot.first, nullptr, 0);}
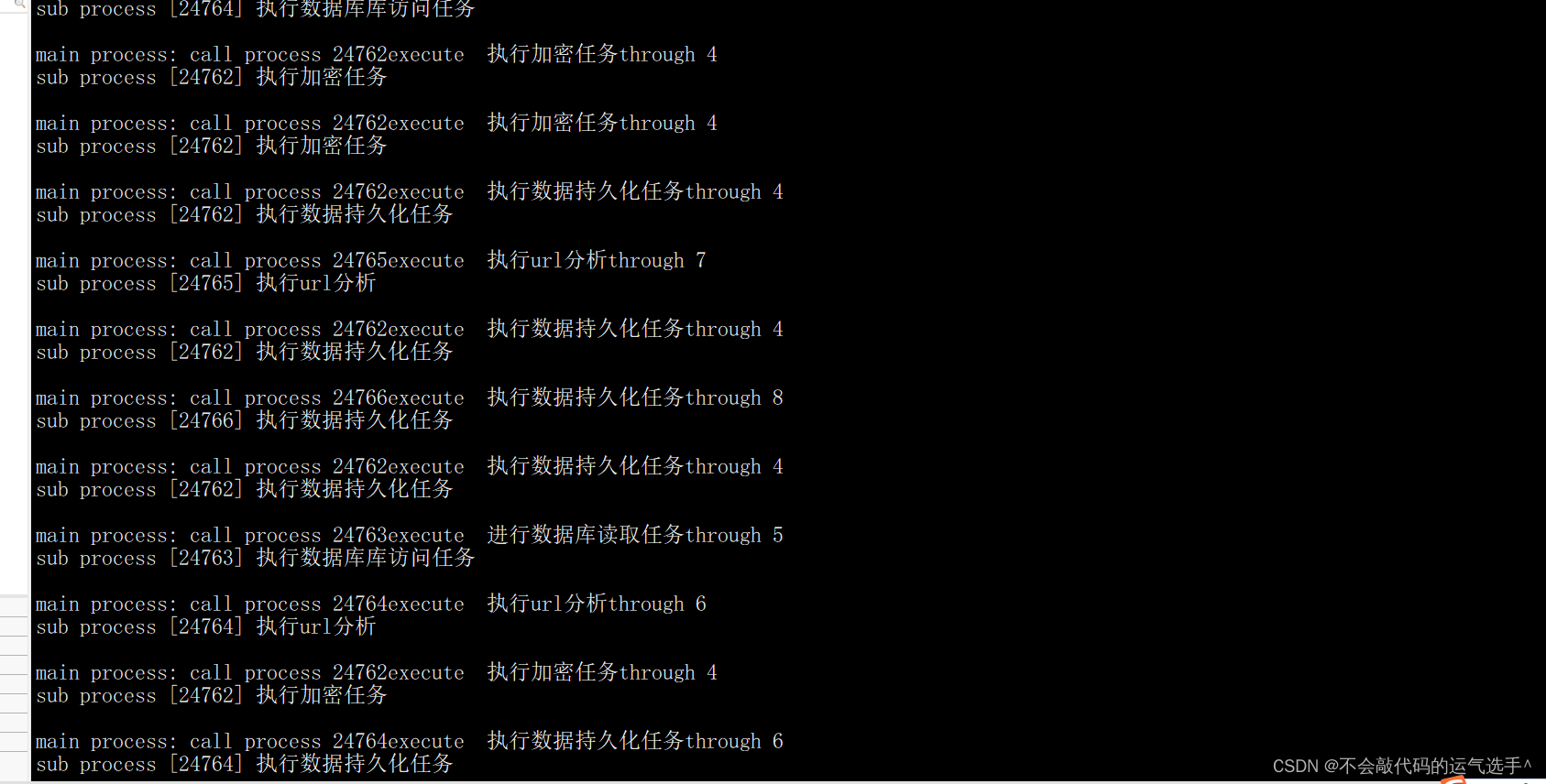
} 最后来看看结果吧(采用的是随机数的方式)
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!