nerf三维重建
Nerf(Neural Radiance Fields)是一种用于三维重建和图像合成的机器学习技术。它基于深度学习,使用神经网络来预测场景中每个点的颜色和密度,从而生成高质量的三维重建结果。
Nerf 通过训练神经网络从不同角度的图像中学习场景的表面和光照特征,然后使用学习到的信息来生成新的视角的图像。与传统的三维重建方法不同,Nerf 不需要对场景进行显式的几何建模,也不需要使用多张图像进行立体匹配。相反,它使用单张图像和相机参数来训练神经网络,从而生成高质量的三维重建结果。
Nerf 技术已经被广泛应用于虚拟现实、增强现实和电影等领域,可以生成逼真的三维场景和高质量的图像。同时,它也是当前计算机视觉和深度学习领域的研究热点之一,引起了广泛的关注和研究。
train-nerf.py
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from tqdm import tqdm
import cv2
import os
import json
import argparse
import imageio# 主要知识点
# 1. 位置编码,Positional Encoding
# - 对于输入的x、y、z坐标,因为是连续的无法进行区分,因此采用ff特征,即傅立叶特征进行编码
# - 编码为cos、sin不同频率的叠加,使得连续值可以具有足够的区分性
# 2. 视图独立性,View Dependent
# - 输入不仅仅是光线采样点的x、y、z坐标,加上了视图依赖,即x、y、z、theta、pi,5d输入,此时多了射线所在视图
# 3. 分层采样,Hierarchical sampling
# - 将渲染分为两级,由于第一级别的模型是均匀采样,而实际会有很多无效的采样(即对颜色没有贡献的区域会占比太多),在模型
# 中看来,就是某些点的梯度为0,对模型训练没有贡献
# - 因此采用两级模型,model、fine,model模型使用均匀采样,推断后得到weights的分布,通过对weights分布进行重采样,使得采样点
# 更加集中在更重要的区域,今儿使得参与训练的点大都是有效的点。所以model作为一级推理,fine则推理重采样后的点
#
# x. 拓展,对于射线的方向和原点的理解,需要具有基本的3d变换知识,建议看GAMES101的前5章补充知识
# PSNR是峰值信噪比,表示重建的逼真程度
# 这三个环节有了,效果就会非常逼真,但是某些细节上还是存在不足。另外训练时间非常关键class BlenderProvider:def __init__(self, root, transforms_file, half_resolution=True):self.meta = json.load(open(os.path.join(root, transforms_file), "r"))self.root = rootself.frames = self.meta["frames"]self.images = []self.poses = []self.camera_angle_x = self.meta["camera_angle_x"]for frame in self.frames:image_file = os.path.join(self.root, frame["file_path"] + ".png")image = imageio.imread(image_file)if half_resolution:image = cv2.resize(image, dsize=None, fx=0.5, fy=0.5, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)self.images.append(image)self.poses.append(frame["transform_matrix"])self.poses = np.stack(self.poses)self.images = (np.stack(self.images) / 255.0).astype(np.float32)self.width = self.images.shape[2]self.height = self.images.shape[1]self.focal = 0.5 * self.width / np.tan(0.5 * self.camera_angle_x)alpha = self.images[..., [3]]rgb = self.images[..., :3]self.images = rgb * alpha + (1 - alpha)class NeRFDataset:def __init__(self, provider, batch_size=1024, device="cpu"):self.images = provider.imagesself.poses = provider.posesself.focal = provider.focalself.width = provider.widthself.height = provider.heightself.batch_size = batch_sizeself.num_image = len(self.images)self.precrop_iters = 500self.precrop_frac = 0.5self.niter = 0self.device = deviceself.initialize()def initialize(self):warange = torch.arange(self.width, dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device)harange = torch.arange(self.height, dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device)y, x = torch.meshgrid(harange, warange)self.transformed_x = (x - self.width * 0.5) / self.focalself.transformed_y = (y - self.height * 0.5) / self.focal# pre center cropself.precrop_index = torch.arange(self.width * self.height).view(self.height, self.width)dH = int(self.height // 2 * self.precrop_frac)dW = int(self.width // 2 * self.precrop_frac)self.precrop_index = self.precrop_index[self.height // 2 - dH:self.height // 2 + dH, self.width // 2 - dW:self.width // 2 + dW].reshape(-1)poses = torch.FloatTensor(self.poses, device=self.device)all_ray_dirs, all_ray_origins = [], []for i in range(len(self.images)):ray_dirs, ray_origins = self.make_rays(self.transformed_x, self.transformed_y, poses[i])all_ray_dirs.append(ray_dirs)all_ray_origins.append(ray_origins)self.all_ray_dirs = torch.stack(all_ray_dirs, dim=0)self.all_ray_origins = torch.stack(all_ray_origins, dim=0)self.images = torch.FloatTensor(self.images, device=self.device).view(self.num_image, -1, 3)def __getitem__(self, index):self.niter += 1ray_dirs = self.all_ray_dirs[index]ray_oris = self.all_ray_origins[index]img_pixels = self.images[index]if self.niter < self.precrop_iters:ray_dirs = ray_dirs[self.precrop_index]ray_oris = ray_oris[self.precrop_index]img_pixels = img_pixels[self.precrop_index]nrays = self.batch_sizeselect_inds = np.random.choice(ray_dirs.shape[0], size=[nrays], replace=False)ray_dirs = ray_dirs[select_inds]ray_oris = ray_oris[select_inds]img_pixels = img_pixels[select_inds]# dirs是指:direction# ori是指: originreturn ray_dirs, ray_oris, img_pixelsdef __len__(self):return self.num_imagedef make_rays(self, x, y, pose):# 100, 100, 3# 坐标系在-y,-z方向上directions = torch.stack([x, -y, -torch.ones_like(x)], dim=-1)camera_matrix = pose[:3, :3]# 10000 x 3ray_dirs = directions.reshape(-1, 3) @ camera_matrix.Tray_origin = pose[:3, 3].view(1, 3).repeat(len(ray_dirs), 1)return ray_dirs, ray_origindef get_test_item(self, index=0):ray_dirs = self.all_ray_dirs[index]ray_oris = self.all_ray_origins[index]img_pixels = self.images[index]for i in range(0, len(ray_dirs), self.batch_size):yield ray_dirs[i:i+self.batch_size], ray_oris[i:i+self.batch_size], img_pixels[i:i+self.batch_size]def get_rotate_360_rays(self):def trans_t(t):return np.array([[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0],[0,0,1,t],[0,0,0,1],], dtype=np.float32)def rot_phi(phi):return np.array([[1,0,0,0],[0,np.cos(phi),-np.sin(phi),0],[0,np.sin(phi), np.cos(phi),0],[0,0,0,1],], dtype=np.float32)def rot_theta(th) : return np.array([[np.cos(th),0,-np.sin(th),0],[0,1,0,0],[np.sin(th),0, np.cos(th),0],[0,0,0,1],], dtype=np.float32)def pose_spherical(theta, phi, radius):c2w = trans_t(radius)c2w = rot_phi(phi/180.*np.pi) @ c2wc2w = rot_theta(theta/180.*np.pi) @ c2wc2w = np.array([[-1,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,1]]) @ c2wreturn c2wfor th in np.linspace(-180., 180., 41, endpoint=False):pose = torch.FloatTensor(pose_spherical(th, -30., 4.), device=self.device)def genfunc():ray_dirs, ray_origins = self.make_rays(self.transformed_x, self.transformed_y, pose)for i in range(0, len(ray_dirs), 1024):yield ray_dirs[i:i+1024], ray_origins[i:i+1024]yield genfunc# Hierarchical sampling (section 5.2)
def sample_pdf(bins, weights, N_samples, det=False):# Get pdfdevice = weights.deviceweights = weights + 1e-5 # prevent nanspdf = weights / torch.sum(weights, -1, keepdim=True)cdf = torch.cumsum(pdf, -1)cdf = torch.cat([torch.zeros_like(cdf[...,:1]), cdf], -1) # (batch, len(bins))# Take uniform samplesif det:u = torch.linspace(0., 1., steps=N_samples, device=device)u = u.expand(list(cdf.shape[:-1]) + [N_samples])else:u = torch.rand(list(cdf.shape[:-1]) + [N_samples])# Invert CDFu = u.contiguous()inds = torch.searchsorted(cdf, u, right=True)below = torch.max(torch.zeros_like(inds-1), inds-1)above = torch.min((cdf.shape[-1]-1) * torch.ones_like(inds), inds)inds_g = torch.stack([below, above], -1) # (batch, N_samples, 2)# cdf_g = tf.gather(cdf, inds_g, axis=-1, batch_dims=len(inds_g.shape)-2)# bins_g = tf.gather(bins, inds_g, axis=-1, batch_dims=len(inds_g.shape)-2)matched_shape = [inds_g.shape[0], inds_g.shape[1], cdf.shape[-1]]cdf_g = torch.gather(cdf.unsqueeze(1).expand(matched_shape), 2, inds_g)bins_g = torch.gather(bins.unsqueeze(1).expand(matched_shape), 2, inds_g)denom = (cdf_g[...,1]-cdf_g[...,0])denom = torch.where(denom<1e-5, torch.ones_like(denom), denom)t = (u-cdf_g[...,0])/denomsamples = bins_g[...,0] + t * (bins_g[...,1]-bins_g[...,0])return samplesdef sample_rays(ray_directions, ray_origins, sample_z_vals):nrays = len(ray_origins)sample_z_vals = sample_z_vals.repeat(nrays, 1)# a.shape = (3, 3, 4, 5) a[..., 4]rays = ray_origins[:, None, :] + ray_directions[:, None, :] * sample_z_vals[..., None]return rays, sample_z_valsdef sample_viewdirs(ray_directions):return ray_directions / torch.norm(ray_directions, dim=-1, keepdim=True)def predict_to_rgb(sigma, rgb, z_vals, raydirs, white_background=False):device = sigma.devicedelta_prefix = z_vals[..., 1:] - z_vals[..., :-1]delta_addition = torch.full((z_vals.size(0), 1), 1e10, device=device)delta = torch.cat([delta_prefix, delta_addition], dim=-1)delta = delta * torch.norm(raydirs[..., None, :], dim=-1)alpha = 1.0 - torch.exp(-sigma * delta)exp_term = 1.0 - alphaepsilon = 1e-10exp_addition = torch.ones(exp_term.size(0), 1, device=device)exp_term = torch.cat([exp_addition, exp_term + epsilon], dim=-1)transmittance = torch.cumprod(exp_term, axis=-1)[..., :-1]weights = alpha * transmittancergb = torch.sum(weights[..., None] * rgb, dim=-2)depth = torch.sum(weights * z_vals, dim=-1)acc_map = torch.sum(weights, -1)if white_background:rgb = rgb + (1.0 - acc_map[..., None])return rgb, depth, acc_map, weightsdef render_rays(model, fine, raydirs, rayoris, sample_z_vals, importance=0, white_background=False):rays, z_vals = sample_rays(raydirs, rayoris, sample_z_vals)view_dirs = sample_viewdirs(raydirs)sigma, rgb = model(rays, view_dirs)sigma = sigma.squeeze(dim=-1)rgb1, depth1, acc_map1, weights1 = predict_to_rgb(sigma, rgb, z_vals, raydirs, white_background)# 使用weights1进行重采样z_vals_mid = .5 * (z_vals[...,1:] + z_vals[...,:-1])z_samples = sample_pdf(z_vals_mid, weights1[...,1:-1], importance, det=True)z_samples = z_samples.detach()z_vals, _ = torch.sort(torch.cat([z_vals, z_samples], -1), -1)rays = rayoris[...,None,:] + raydirs[...,None,:] * z_vals[...,:,None] # [N_rays, N_samples + N_importance, 3]sigma, rgb = fine(rays, view_dirs)sigma = sigma.squeeze(dim=-1)# 第二次重采样的预测才是最终结果,这是论文中,分层采样环节(Hierarchical sampling)rgb2, depth2, acc_map2, weights2 = predict_to_rgb(sigma, rgb, z_vals, raydirs, white_background)return rgb1, rgb2# 无视图独立性的head
class NoViewDirHead(nn.Module):def __init__(self, ninput, noutput):super().__init__()self.head = nn.Linear(ninput, noutput)def forward(self, x, view_dirs):x = self.head(x)rgb = x[..., :3].sigmoid()sigma = x[..., 3].relu()return sigma, rgb# 视图独立性的head
class ViewDenepdentHead(nn.Module):def __init__(self, ninput, nview):super().__init__()self.feature = nn.Linear(ninput, ninput)self.view_fc = nn.Linear(ninput + nview, ninput // 2)self.alpha = nn.Linear(ninput, 1)self.rgb = nn.Linear(ninput // 2, 3)def forward(self, x, view_dirs):feature = self.feature(x)sigma = self.alpha(x).relu()feature = torch.cat([feature, view_dirs], dim=-1)feature = self.view_fc(feature).relu()rgb = self.rgb(feature).sigmoid()return sigma, rgb# 位置编码实现
class Embedder(nn.Module):def __init__(self, positional_encoding_dim):super().__init__()self.positional_encoding_dim = positional_encoding_dimdef forward(self, x):positions = [x]for i in range(self.positional_encoding_dim):for fn in [torch.sin, torch.cos]:positions.append(fn((2.0 ** i) * x))return torch.cat(positions, dim=-1)# 基本模型结构
class NeRF(nn.Module):def __init__(self, x_pedim=10, nwidth=256, ndepth=8, view_pedim=4):super().__init__()xdim = (x_pedim * 2 + 1) * 3layers = []layers_in = [nwidth] * ndepthlayers_in[0] = xdimlayers_in[5] = nwidth + xdim# 模型中特定层[5]会存在concatfor i in range(ndepth):layers.append(nn.Linear(layers_in[i], nwidth))if view_pedim > 0:view_dim = (view_pedim * 2 + 1) * 3self.view_embed = Embedder(view_pedim)self.head = ViewDenepdentHead(nwidth, view_dim)else:self.head = NoViewDirHead(nwidth, 4)self.xembed = Embedder(x_pedim)self.layers = nn.Sequential(*layers)def forward(self, x, view_dirs):xshape = x.shapex = self.xembed(x)if self.view_embed is not None:view_dirs = view_dirs[:, None].expand(xshape)view_dirs = self.view_embed(view_dirs)raw_x = xfor i, layer in enumerate(self.layers):x = torch.relu(layer(x))if i == 4:x = torch.cat([x, raw_x], axis=-1)return self.head(x, view_dirs)def train():pbar = tqdm(range(1, maxiters))for global_step in pbar:idx = np.random.randint(0, len(trainset))raydirs, rayoris, imagepixels = trainset[idx]rgb1, rgb2 = render_rays(model, fine, raydirs, rayoris, sample_z_vals, importance, white_background)loss1 = ((rgb1 - imagepixels)**2).mean()loss2 = ((rgb2 - imagepixels)**2).mean()psnr = -10. * torch.log(loss2.detach()) / np.log(10.)loss = loss1 + loss2optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward()optimizer.step()pbar.set_description(f"{global_step} / {maxiters}, Loss: {loss.item():.6f}, PSNR: {psnr.item():.6f}")decay_rate = 0.1new_lrate = lrate * (decay_rate ** (global_step / lrate_decay))for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:param_group['lr'] = new_lrateif global_step % 5000 == 0 or global_step == 500:imgpath = f"imgs/{global_step:02d}.png"pthpath = f"ckpt/{global_step:02d}.pth"model.eval()with torch.no_grad():rgbs, imgpixels = [], []for raydirs, rayoris, imagepixels in trainset.get_test_item():rgb1, rgb2 = render_rays(model, fine, raydirs, rayoris, sample_z_vals, importance, white_background)rgbs.append(rgb2)imgpixels.append(imagepixels)rgb = torch.cat(rgbs, dim=0)imgpixels = torch.cat(imgpixels, dim=0)loss = ((rgb - imgpixels)**2).mean()psnr = -10. * torch.log(loss) / np.log(10.)print(f"Save image {imgpath}, Loss: {loss.item():.6f}, PSNR: {psnr.item():.6f}")model.train()temp_image = (rgb.view(height, width, 3).cpu().numpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8)cv2.imwrite(imgpath, temp_image[..., ::-1])torch.save([model.state_dict(), fine.state_dict()], pthpath)def make_video360():mstate, fstate = torch.load(args.ckpt, map_location="cpu")model.load_state_dict(mstate)fine.load_state_dict(fstate)model.eval()fine.eval()imagelist = []for i, gfn in tqdm(enumerate(trainset.get_rotate_360_rays()), desc="Rendering"):with torch.no_grad():rgbs = []for raydirs, rayoris in gfn():rgb1, rgb2 = render_rays(model, fine, raydirs, rayoris, sample_z_vals, importance, white_background)rgbs.append(rgb2)rgb = torch.cat(rgbs, dim=0)rgb = (rgb.view(height, width, 3).cpu().numpy() * 255).astype(np.uint8)file = f"rotate360/{i:03d}.png"print(f"Rendering to {file}")cv2.imwrite(file, rgb[..., ::-1])imagelist.append(rgb)video_file = f"videos/rotate360.mp4"print(f"Write imagelist to video file {video_file}")imageio.mimwrite(video_file, imagelist, fps=30, quality=10)if __name__ == "__main__":parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()parser.add_argument("--datadir", type=str, default='data/nerf_synthetic/lego', help='input data directory')parser.add_argument("--make-video360", action="store_true", help="make 360 rotation video")parser.add_argument("--half-resolution", action="store_true", help="use half resolution")parser.add_argument("--ckpt", default="300000.pth", type=str, help="model file used to make 360 rotation video")args = parser.parse_args()device = "cpu"maxiters = 100000 + 1batch_size = 1024lrate_decay = 500 * 1000lrate = 5e-4importance = 128num_samples = 64 # 每个光线的采样数量positional_encoding_dim = 10 # 位置编码维度view_encoding_dim = 4 # View Dependent对应的位置编码维度white_background = True # 图片背景是白色的half_resolution = args.half_resolution # 只进行一半分辨率的重建(400x400),False表示(800x800)分辨率sample_z_vals = torch.linspace(2.0, 6.0, num_samples, device=device).view(1, num_samples)model = NeRF(x_pedim = positional_encoding_dim,view_pedim = view_encoding_dim).to(device)params = list(model.parameters())# 使用model产生的权重进行重采样,然后再推理,所以这个才是效果更好的模型fine = NeRF(x_pedim = positional_encoding_dim,view_pedim = view_encoding_dim).to(device)params.extend(list(fine.parameters()))optimizer = optim.Adam(params, lrate)os.makedirs("imgs", exist_ok=True)os.makedirs("rotate360", exist_ok=True)os.makedirs("videos", exist_ok=True)os.makedirs("ckpt", exist_ok=True)print(model)provider = BlenderProvider("data/nerf_synthetic/lego", "transforms_train.json", half_resolution)trainset = NeRFDataset(provider, batch_size, device)width = trainset.widthheight = trainset.heightif args.make_video360:make_video360()else:train()print("Program done.")
- 500.png
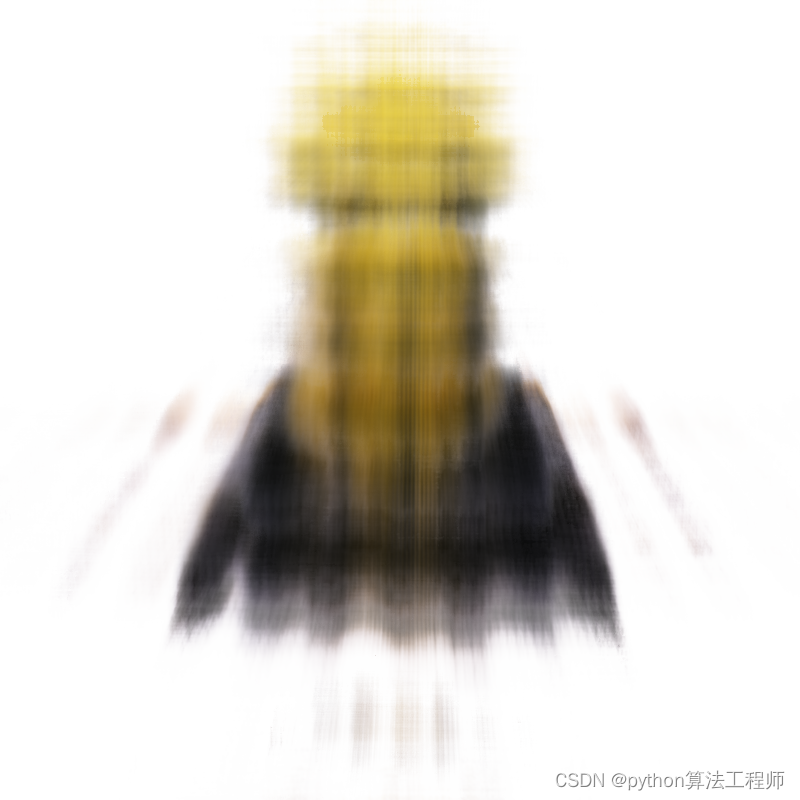

- 1000.png
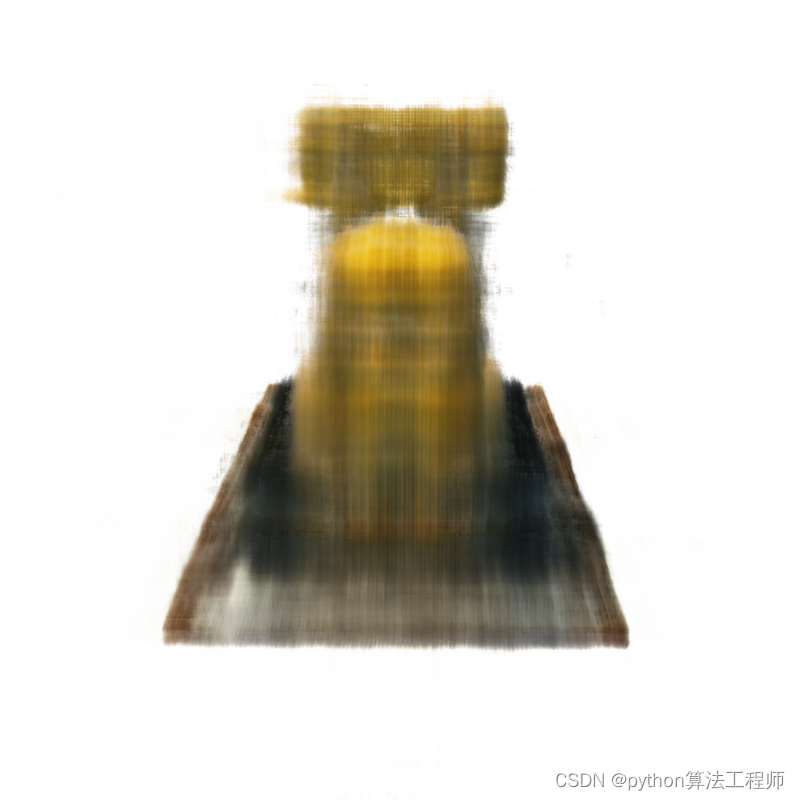
- 1500.png
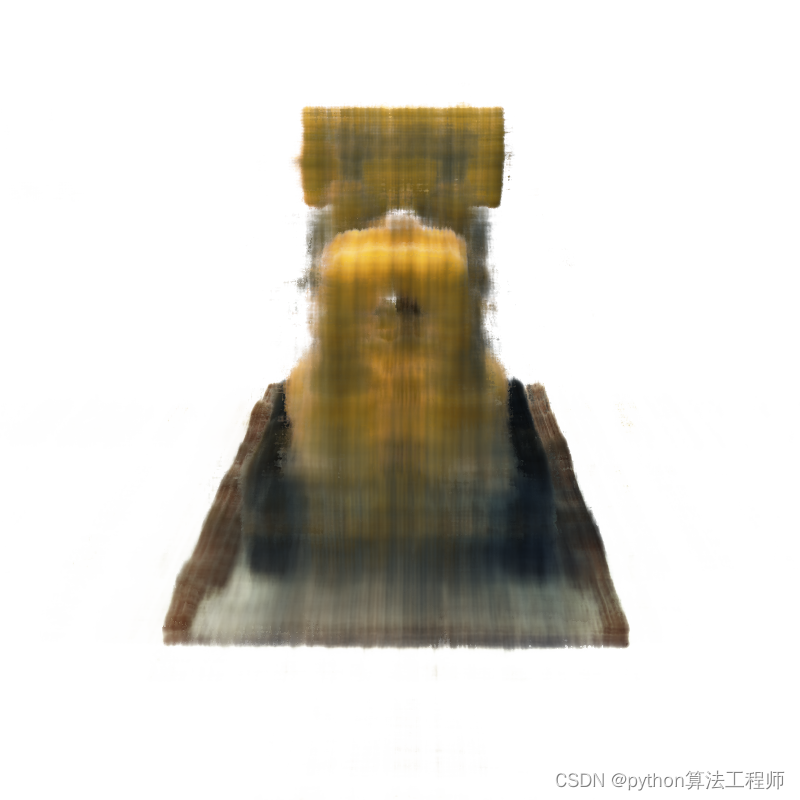
- 5000.png
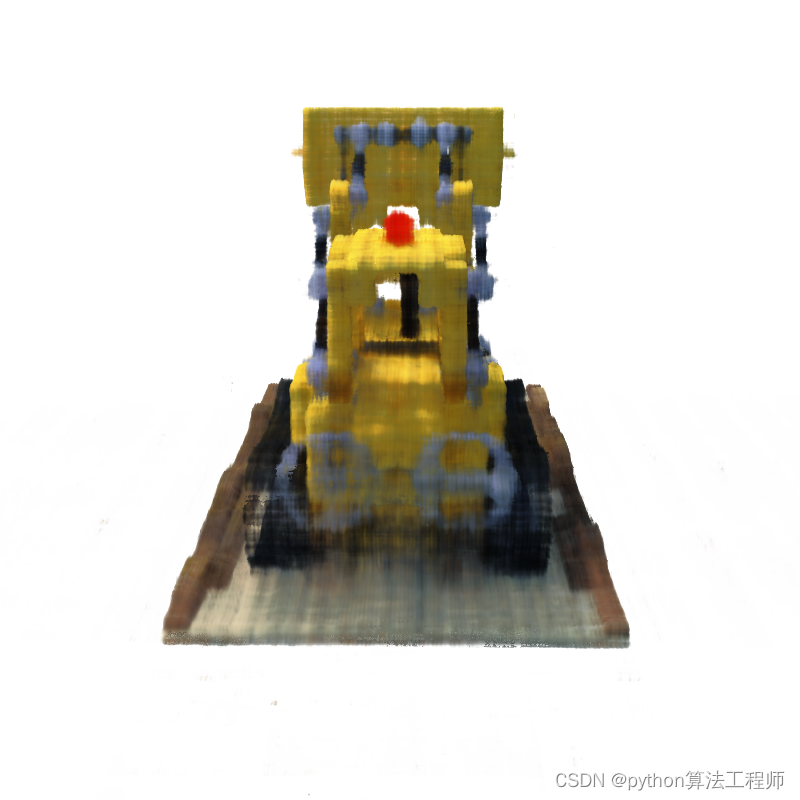 10000.png
10000.png
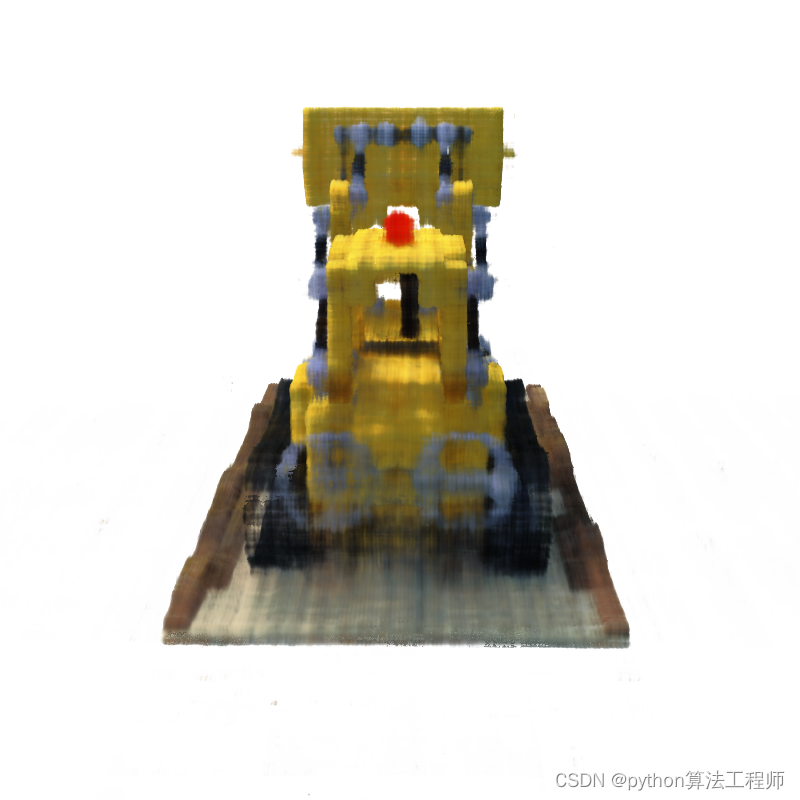

15000.png
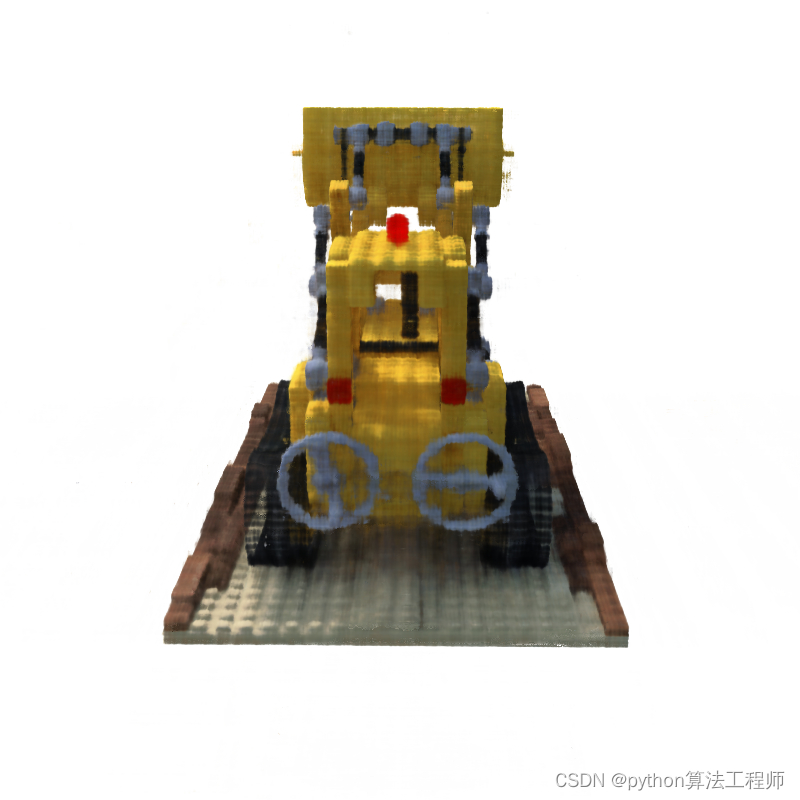

- 20000.png

- 50000.png

- 300000.png

本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!