顺序表链表小结
一.顺序表
- 顺序表是基于数组实现的
- 顺序表上的数据在物理内存和逻辑结构上都是连续的
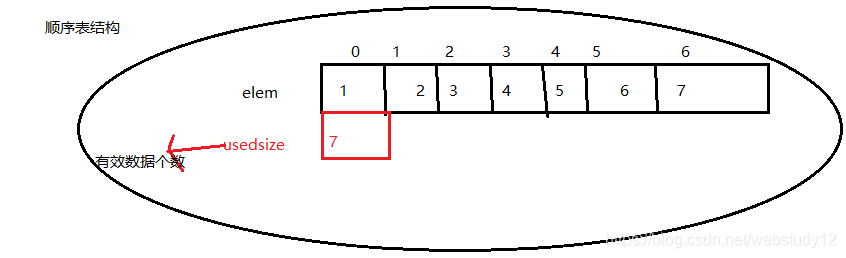
顺序表代码如下:
import java.util.Arrays;class MyArrayList {public int usedSize;//有效数据个数public int[] elem;public final int CAPACITY=10;//容量定为10public MyArrayList(){//构造方法,初始化成员属性this.usedSize=0;this.elem=new int[CAPACITY];}//判断是否为空private boolean isFull(){if (this.usedSize==this.elem.length){return true;}return false;}//判断是否未满private boolean isEmpty(){return this.usedSize==0;//为空返回true,不为空返回false}// 在 pos 位置新增元素public void add(int pos, int data) {if (isFull()){this.elem=Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,this.elem.length*2);}//1.判断POS是否合法if(pos<0||pos>this.usedSize){throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("pos位置不合法");//System.out.println("pos位置不合法");//return;}//2.挪数据for (int i=this.usedSize-1;i>=pos;i--){this.elem[i+1]=this.elem[i];}//3.插入数据this.elem[pos]=data;//4.usedSize++this.usedSize++;}// 判定是否包含某个元素public boolean contains(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize ; i++) {if (this.elem[i]==toFind){return true;}}return false;}// 查找某个元素对应的位置public int search(int toFind) {for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize ; i++) {if (this.elem[i]==toFind){return i;}}return -1;}// 获取 pos 位置的元素public int getPos(int pos) {if (pos<0||pos>this.usedSize){return -1;}return this.elem[pos];}// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
// public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
//
// }//删除第一次出现的关键字keypublic void remove(int toRemove) {//1.顺序表是否为空if (isEmpty()){System.out.println("为空");}//2查找toRemove下标.int index=search(toRemove);if (index==-1){System.out.println("没有你想删除的数字");return ;}//3.删除for (int i = index; i <this.usedSize-1 ; i++) {this.elem[i]=this.elem[i+1];}this.usedSize--;}// 获取顺序表长度public int size() {return this.usedSize;}// 清空顺序表public void clear() {this.usedSize=0;}// 打印顺序表public void display() {for (int i = 0; i <this.usedSize ; i++) {System.out.print(this.elem[i]+" ");}System.out.println();}
}
测试类如下:
package 顺序表和链表;public class TestMyArrayList {public static void main(String[] args) {MyArrayList myArrayList=new MyArrayList();myArrayList.add(0,1);myArrayList.add(0,2);myArrayList.add(0,3);myArrayList.add(0,4);myArrayList.add(0,5);myArrayList.display();myArrayList.contains(6);System.out.println(myArrayList.contains(6));}
}
二.链表
1.链表的分类:
单向,双向;带头,不带头;循环,非循环
2.链表特点:
· 链表在物理结构上不一定连续,但在逻辑结构上一定连续
·链表中的节点除第一个节点无直接前驱,最后一个节点无直接后继外,其余节点都有唯一的前驱和唯一的直接后继
三.实现链表:这里主要说无头单向链表和无头双向链表
1.单链表
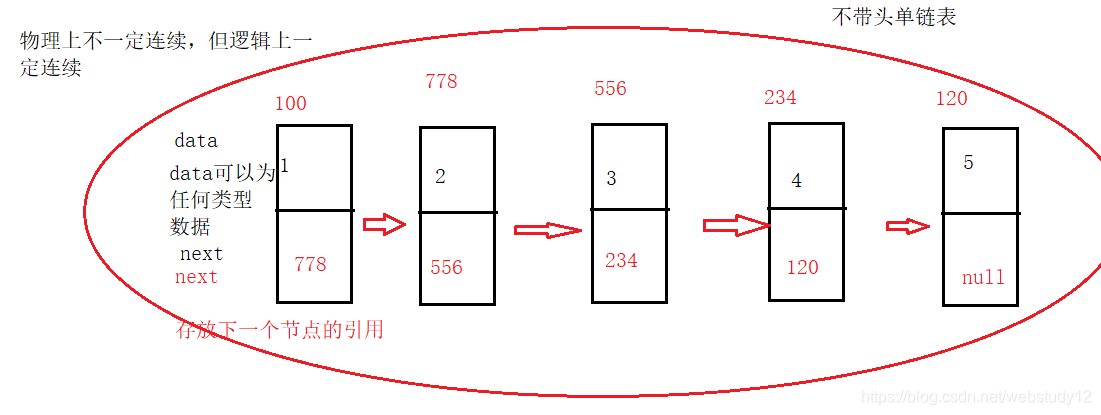
单链表的实现代码如下:
//节点类
class ListNode1 {public int data;public ListNode1 next;public ListNode1(int data) {this.data = data;this.next = null;}
}
//链表类
public class SingleList2 {public ListNode1 head;public SingleList2 (){this.head=null;}//头插法public void addFirst(int data){ListNode1 node=new ListNode1(data);//创建一个节点//首先判断链表是否为空,为空直接让head指向节点if (this.head==null){this.head=node;}else{node.next=this.head;this.head=node;}}//尾插法public void addLast(int data){ListNode1 node=new ListNode1(data);ListNode1 cur=this.head;if (this.head==null){this.head=node;}else {while (cur!=null){cur=cur.next;}cur.next=node;}}//找到index-1的位置private ListNode1 searchIndex(int index){ListNode1 cur=this.head;//cur->index-1while (index-1>0){cur=cur.next;index--;}return cur;}//任意位置插入public boolean addIndex(int index,int data){ListNode1 node= new ListNode1(3);if (index<0||index>getLength()){System.out.println("插入位置不合法");return false;}if (index==0){addFirst(data);return true;}else{ListNode1 cur=searchIndex(index);node.next=cur.next;cur.next=node;}return true;}//得到链表长度public int getLength(){ListNode1 cur=this.head ;int count=0;while(cur!=null){count++;cur=cur.next;}return count;}//反转链表public ListNode1 reverseList(){ListNode1 pre=null;ListNode1 newHead=null;ListNode1 cur=this.head;while(cur!=null){ListNode1 curNext=cur.next;if (curNext==null){newHead=cur;}cur.next=pre;pre=cur;cur=curNext;}return newHead;}//单链表的中间节点public ListNode1 middleNode() {//定义快慢指针ListNode1 fast=this.head;ListNode1 slow=this.head;while (fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;}return slow;}//找到倒数第k个节点public ListNode1 findKthToTail(int k){// k > getLength()if(k <= 0) {return null;}ListNode1 fast = this.head;ListNode1 slow = this.head;while (k-1>0) {if(fast != null) {fast = fast.next;k--;}else {System.out.println("没有这个节点");return null;}}while (fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}//显示链表public void display(){ListNode1 cur=this.head;while(cur!=null){System.out.print(cur.data+" ");cur=cur.next;}System.out.println();}public void display2(ListNode1 newHead){ListNode1 cur=newHead;while(cur!=null){System.out.print(cur.data+" ");cur=cur.next;}System.out.println();}
}测试类代码如下:
public class TestSingleList2 {public static void main(String []args){SingleList2 singleList2=new SingleList2();singleList2.addFirst(1);singleList2.addFirst(2);singleList2.addFirst(3);singleList2.addFirst(4);singleList2.addFirst(5);singleList2.addFirst(6);singleList2.addFirst(7);singleList2.addFirst(8);
// singleList2.display();
// ListNode1 node=singleList2.middleNode();
// System.out.println(node.data);
// ListNode1 head=singleList2.reverseList();
// singleList2.display2(head);ListNode1 node=singleList2.findKthToTail(5);System.out.println(node.data);int length=singleList2.getLength();System.out.println("单链表长度为: "+length);}
}头插法:
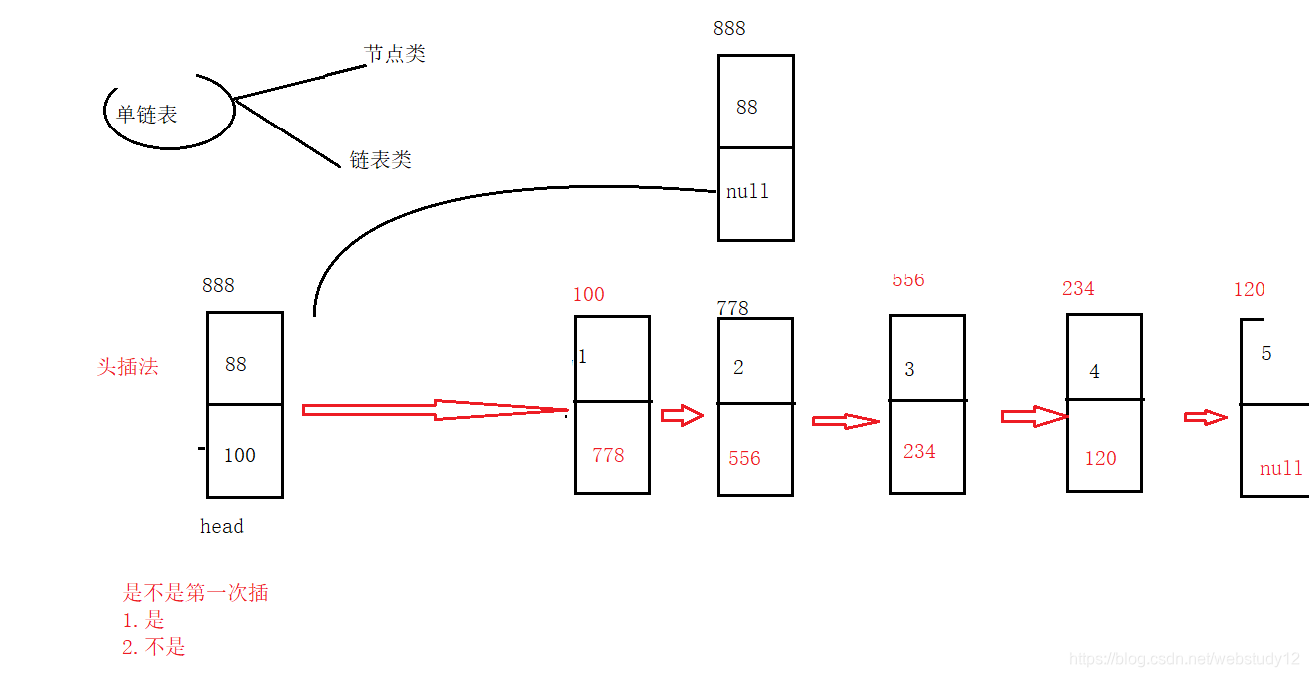
尾插法:
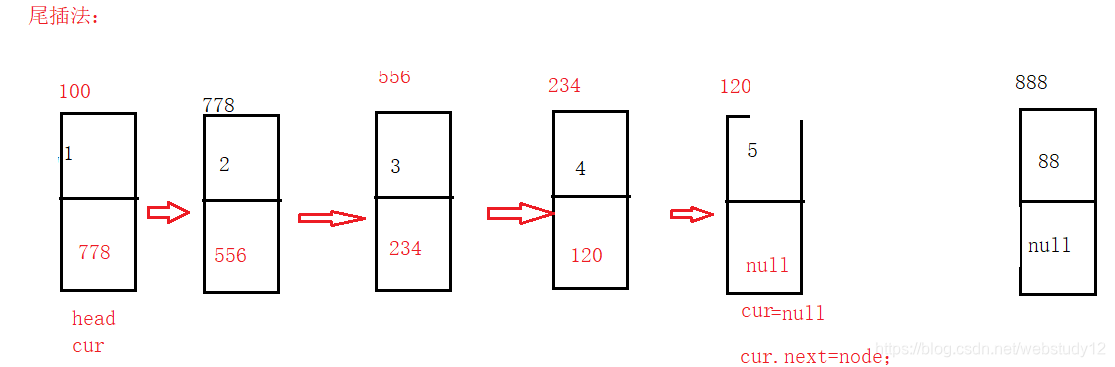
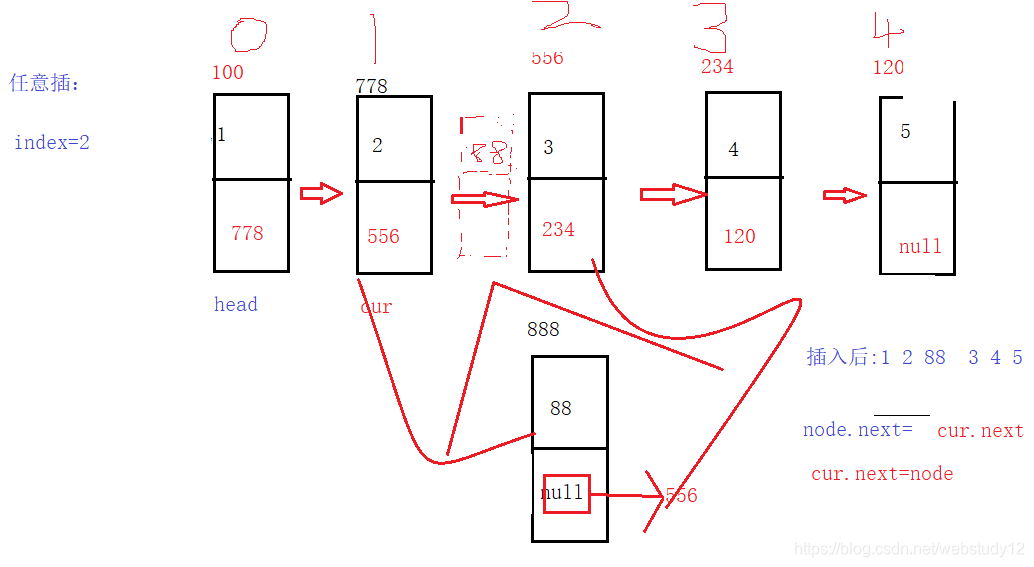
任意插:
反转链表:
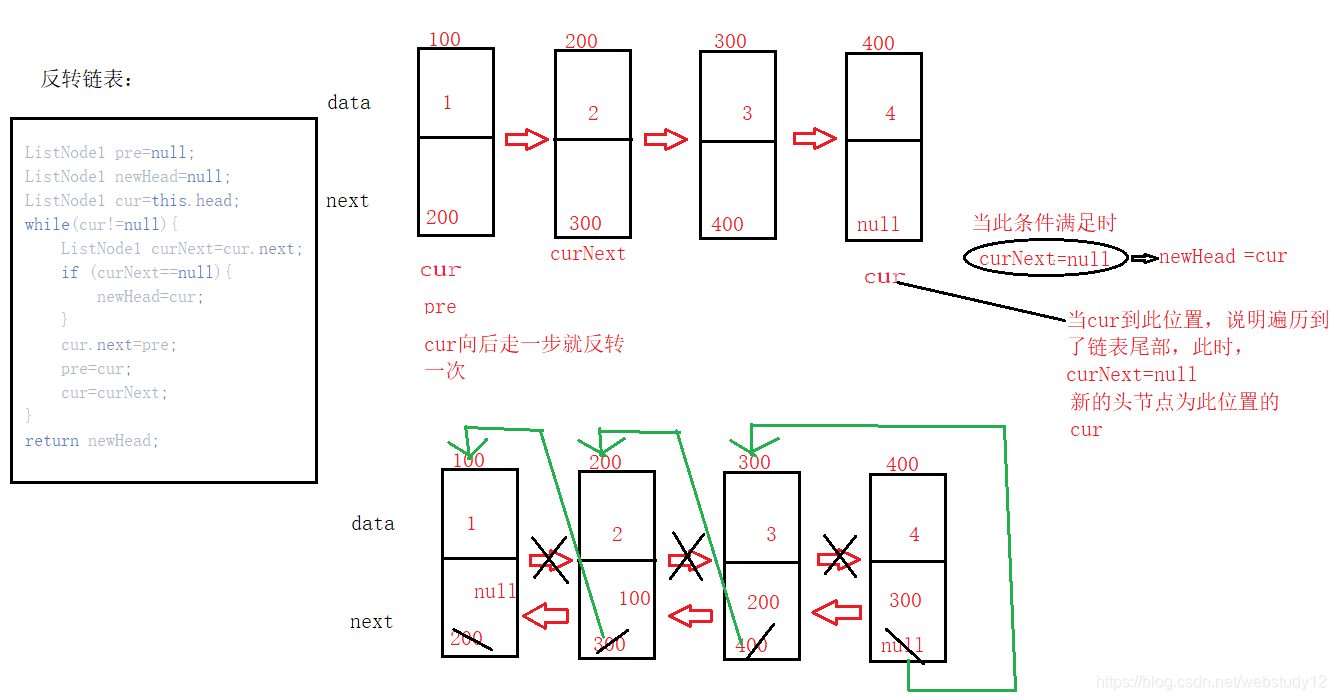
注意:上述代码中所有方法必须通过画图才能理解,不然很是抽象
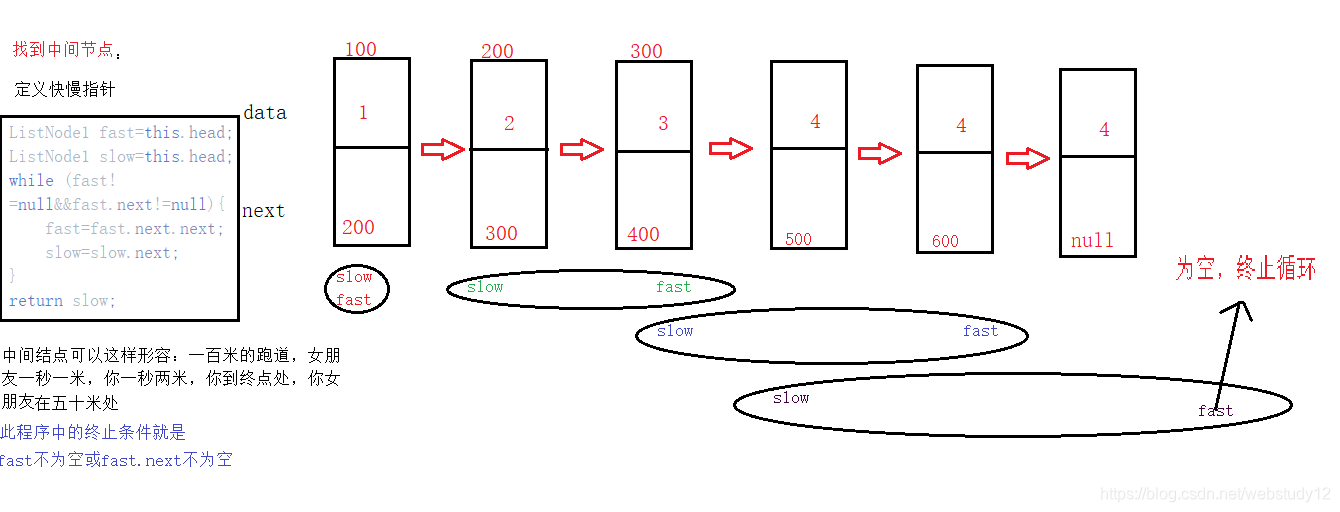
找中间结点:
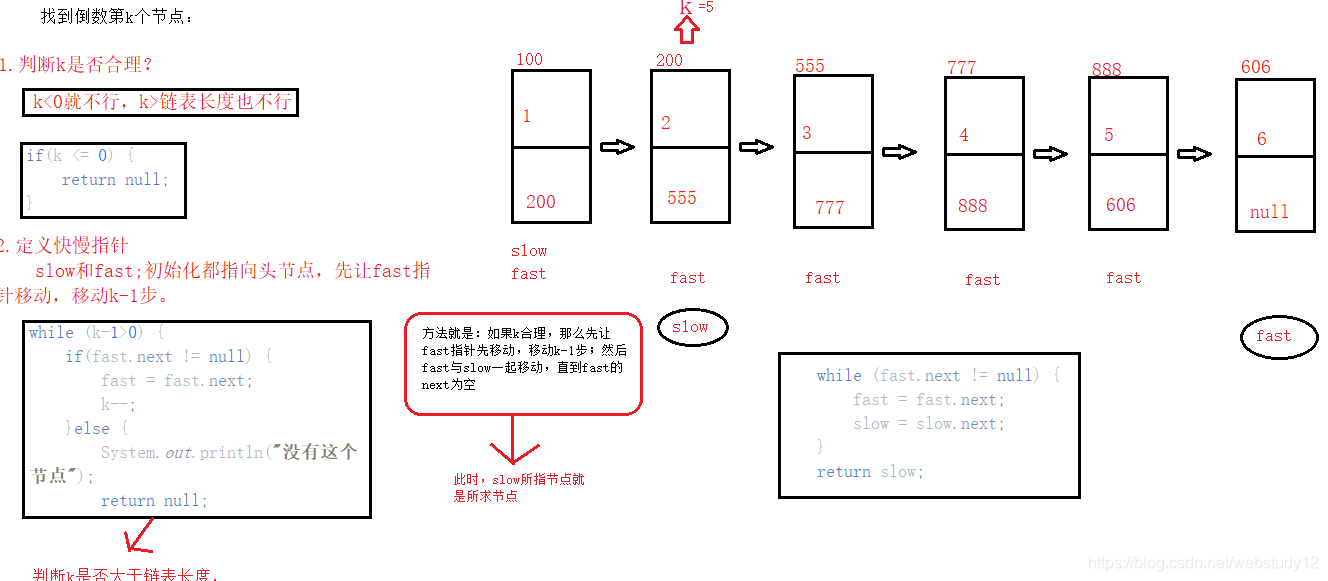
找到倒数第k个节点
未完待续…
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!