python中几种队列Queue用法区别
python中使用到的队列模块大致有三个:
1、from queue import Queue
此模块适用于线程间通信,但不能用于进程间通信。
示例代码1: 【注意:此时代码存在错误!!!】
import time
import threading
from queue import Queuedef task_func():global queuewhile queue.qsize() > 0:x = queue.get()print(f"num: {x}")time.sleep(0.1)def producer_data():global queuefor i in range(100):queue.put(i)time.sleep(0.1)if __name__ == '__main__':queue = Queue()producer_thread = threading.Thread(target=producer_data)producer_thread.start()thread_list = []for i in range(5):thread = threading.Thread(target=task_func)thread.start()thread_list.append(thread)for thread in thread_list:thread.join()print("主程序执行结束!")
注意:上述写法:
while queue.qsize() > 0:x = queue.get()当生产者速度没有消费者速度快时,上述消费者代码会提前结束,导致生产者的速度不能消费。
while True:x = queue.get()这种写法也存在问题,此时消费者队列会一直监听生产者队列是否有数据,导致线程一直处于阻塞状态,程序会一直阻塞不会停止,严重浪费系统资源。如果使用apscheduler等定时任务的库的话,会导致定时任务无法启动。
其实queue队列中的put()或者get()方法中都提供了timeout参数,利用这个参数可以有效解决上述消除不能消费和线程一直阻塞问题。
示例代码2:
import time
import threading
from queue import Queuedef task_func():global queuewhile True:x = queue.get(timeout=10)print(f"num: {x}")def producer_data():global queuefor i in range(100):queue.put(i)time.sleep(0.1)if __name__ == '__main__':queue = Queue()producer_thread = threading.Thread(target=producer_data)producer_thread.start()thread_list = []for i in range(5):thread = threading.Thread(target=task_func)thread.start()thread_list.append(thread)for thread in thread_list:thread.join()print("主程序执行结束!")
运行结果:

根据不同的情境,可以根据实际情况设置timeout的值。如果使用定时任务,使用timeout是可以的,不会使程序抛异常停止的。
2、from multiprocessing import Queue
此模块用于对进程,但是不能用于进程池
示例代码:
import time
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue
import queuedef producer(queue):queue.put("a")time.sleep(2)def consumer(queue):time.sleep(2)data = queue.get()print(data)if __name__ == "__main__":# queue = queue.Queue()queue = Queue()my_producer = Process(target=producer, args=(queue, ))my_consumer = Process(target=consumer, args=(queue, ))my_producer.start()my_consumer.start()my_producer.join()my_consumer.join()
# 使用queue模块的Queue()会报错
# 使用multiprocessing中的Queue(),正确输出a运行结果:
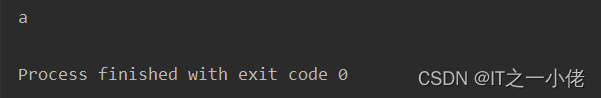
3、from multiprocessing import Manager
示例代码:
import time
from multiprocessing import Process, Queue, Pool, Managerdef producer(queue):queue.put("a")time.sleep(2)def consumer(queue):time.sleep(2)data = queue.get()print(data)if __name__ == "__main__":# queue = Queue()queue = Manager().Queue()pool = Pool()# pool中的进程间通信需要使用Managerpool.apply_async(producer, args=(queue, ))pool.apply_async(consumer, args=(queue, ))pool.close()pool.join()
运行结果:
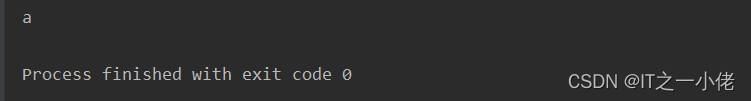
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!