leetcode1-100
文章目录
- 重做
- 1.两数之和(hash)
- find的时间复杂度
- 2. 两数相加(链表)
- 3. 无重复字符的最长子串(滑动窗口双指针)
- 4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
- 5. 最长回文子串(dp)
- 6.Z 字形变换
- 7.整数反转
- stoi、stod、stoll
- 8. 字符串转换整数 (atoi)
- 9.回文数
- 10. 正则表达式匹配(dp)
- 11. 盛最多水的容器
- 12. 整数转罗马数字
- 13.罗马数字转换
- map:
- 14.最长公共前缀
- 15. 三数之和(双指针,巧妙去重)
- 16. 最接近的三数之和
- 17. 电话号码的字母组合(dfs,bfs)
- 18. 四数之和
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
- 20.有效的括号(堆栈的运用)
- 21.合并链表
- 22. 括号生成
- 全排列函数next_permutation
- 23. 合并K个排序链表
- 3。归并排序
- 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 25. K 个一组翻转链表
- 26. 删除排序数组中的重复项
- 27. 移除元素
- 30. 串联所有单词的子串
- 31. 下一个排列
- 32. 最长有效括号
- 33. 搜索旋转排序数组
- 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
- 35. 搜索插入位置(二分法***************)
- lower_bound
- 二分法使用的模板
- 36. 有效的数独
- 38. 外观数列
- 39. 组合总和
- dfs深度优先搜索***
- (**二叉树常用算法:回溯、队列、递归、剪枝**)
- 40. 组合总和 II
- 41. 缺失的第一个正数
- 42. 接雨水
- 43. 字符串相乘
- 44. 通配符匹配
- 45. 跳跃游戏 II
- 贪心算法
- 46. 全排列(bfs)
- 回溯问题+决策树
- 47. 全排列 II
- 48. 旋转图像
- 49. 字母异位词分组
- 50. Pow(x, n)
- 51. N皇后(回溯dfs)
- 53. 最大子序和(贪心)
- 54. 螺旋矩阵
- 55. 跳跃游戏
- 56. 合并区间(贪心)
- 57. 插入区间
- 58. 最后一个单词的长度
- 59. 螺旋矩阵 II
- 60. 第k个排列
- 61. 旋转链表
- 62. 不同路径(dp)
- 63. 不同路径 II
- 64. 最小路径和(dp)
- 66. 加一
- 69. x 的平方根(二分法)
- 70. 爬楼梯(dp)
- 72. 编辑距离
- 73. 矩阵置零
- 75. 颜色分类(三数快排)
- 快速排序
- 74. 搜索二维矩阵
- 76. 最小覆盖子串
- 哈希表遍历
- 77. 组合
- 78. 子集
- 79. 单词搜索(dfs)
- dfs中的顺序
- 80. 删除排序数组中的重复项 II
- 81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II
- 82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
- 83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
- 84. 柱状图中最大的矩形(单调栈)
- 85. 最大矩形(单调栈)
- 86. 分隔链表
- 88. 合并两个有序数组
- lower_bound必须是在有序数组中使用
- 89. 格雷编码
- 90. 子集 II
- dfs之前排序
- 91. 解码方法
- 符串拼接问题
- 字符串转数字
- 字符转数字
- 92. 反转链表 II
- 93. 复原IP地址
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- 递归
- 非递归
- 95. 不同的二叉搜索树 II(不会)
- 96. 不同的二叉搜索树
- 97. 交错字符串
- 98. 验证二叉搜索树(dfs)
- 99. 恢复二叉搜索树
- 中序遍历的利用
重做
1,2,3,
不严格的三刷,这遍的侧重点:
1.每道题找其最优解,面试很看重
2.对难以记忆的记录下来
3.对每种解法评估其事件复杂度
1.两数之和(hash)
find的时间复杂度
如果直接再原数组进行find。对i遍历的事件复杂度是n,每一个find又是n,所以这种的时间复杂度是n放(另外:map和set红黑树的时间复杂度是logn,哈希表直接取值是1)
class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {//这里不能排序,因为就失去了原来的顺序了for(int i = 0;i<nums.size();i++){auto iter = find(nums.begin()+i+1,nums.end(),target-nums[i]);if(iter==nums.end())continue;else {int j = iter-nums.begin();return {i,j};}}return {0,0};}
};
一开始想对数组进行排序,这样可以极大程度的进行剪枝,但是排序之后丢失了原有的下标,如果返回的是元素不是下标的话这样就是可行的,但是下标不能用这种方法
哈希表的方法:
class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {unordered_map<int,vector<int>> mp;for(int i = 0;i<nums.size();i++)mp[nums[i]].push_back(i);for(int i = 0 ;i<nums.size();i++){if( mp.find(target-nums[i])!=mp.end() ){if(i!=mp[target-nums[i]][0])return {i,mp[target-nums[i]][0]};else if(mp[target-nums[i]].size()==2)return {i,mp[target-nums[i]][1]};}}return {0,0};}
};
class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {unordered_map<int,int> m;for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)m[nums[i]] = i; //向map中添加元素for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++){if(m.find(target-nums[i]) != m.end() && m[target-nums[i]] != i) //如果m中存在对应的键值,并且不为i,后面这个条件很重要,因为会有重复的元素return {i , m[target-nums[i]]};}return {};}
};作者:zrita
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/solution/c-san-chong-fang-fa-jian-dan-yi-dong-ji-bai-100-z-/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
2. 两数相加(链表)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {auto head = new ListNode(0);auto temp = head;int b = 0;while(l1 && l2){int x = b + l1->val + l2->val;b = (x>=10)?1:0;auto t = new ListNode(x%10);temp->next = t;temp = t; l1 = l1->next; l2 = l2->next;}while(l1){int x = b + l1->val;b = (x>=10)?1:0;auto t = new ListNode(x%10);temp->next = t;temp = t; l1 = l1->next; }while(l2){int x = b + l2->val;b = (x>=10)?1:0;auto t = new ListNode(x%10);temp->next = t;temp = t; l2 = l2->next; }if(b){auto t = new ListNode(1);temp->next = t;t->next = NULL;return head->next;}else{temp->next = NULL;return head->next;}}
};
3. 无重复字符的最长子串(滑动窗口双指针)
对于字符串的题,最容易出现的就是超时,而这是更好的办法往往是哈希表法
class Solution
{
public:int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s){//s[start,end) 前面包含 后面不包含int start(0), end(0), length(0), result(0);int sSize = int(s.size());unordered_map<char, int> hash;while (end < sSize){char tmpChar = s[end];//仅当s[start,end) 中存在s[end]时更新startif (hash.find(tmpChar) != hash.end() && hash[tmpChar] >= start){start = hash[tmpChar] + 1;length = end - start;}hash[tmpChar] = end;end++;length++;result = max(result, length);}return result;}
};作者:pinku-2
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/solution/wu-zhong-fu-zi-fu-de-zui-chang-zi-chuan-cshi-xian-/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
推荐滑动窗口
class Solution {
public:int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {int res = 0;//不能使用map或者setvector<char> vt;for(int i =0 ;i<s.size();i++){if(find(vt.begin(),vt.end(),s[i])==vt.end()){vt.push_back(s[i]);res = max(res, (int)vt.size());}else{auto iter = find(vt.begin(),vt.end(),s[i]);vt.assign(iter+1,vt.end());vt.push_back(s[i]);}}return res;}
};
4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数
class Solution {
public:int findKthElm(vector<int>& nums1,vector<int>& nums2,int k){assert(1<=k&&k<=nums1.size()+nums2.size());int le=max(0,int(k-nums2.size())),ri=min(k,int(nums1.size()));while(le<ri){int m=le+(ri-le)/2;if(nums2[k-m-1]>nums1[m]) le=m+1;else ri=m;}//循环结束时的位置le即为所求位置,第k小即为max(nums1[le-1]),nums2[k-le-1]),但是由于le可以为0、k,所以//le-1或者k-le-1可能不存在所以下面单独判断下int nums1LeftMax=le==0?INT_MIN:nums1[le-1];int nums2LeftMax=le==k?INT_MIN:nums2[k-le-1];return max(nums1LeftMax,nums2LeftMax);}double findMedianSortedArrays(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {int n=nums1.size()+nums2.size();if(n&1){//两个数组长度和为奇数return findKthElm(nums1,nums2,(n>>1)+1);}else{//为偶数return (findKthElm(nums1,nums2,n>>1)+findKthElm(nums1,nums2,(n>>1)+1))/2.0;}}
};作者:nojoker
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/median-of-two-sorted-arrays/solution/jiang-qi-zhuan-wei-zhao-liang-ge-you-xu-shu-zu-de-/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
5. 最长回文子串(dp)
错误的做法
“aacdefcaa”
下面的方法找出的是这个字符串中最长的存在与它回文子串的子串,但其实它的回文子串不一定还是自己,这种情况下长度就比自身的长了
class Solution {
public:string longestPalindrome(string s) {string s1 = s;int len = s.size();reverse(s1.begin(),s1.end());vector<vector<int>> dp(len+1,vector<int>(len+1,0));int res = 0;int pos = 0;for(int i = 1;i<=len;i++){for(int j =1;j<=len;j++){if(s[i-1]==s1[j-1]){dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;if(dp[i][j]>res){res = dp[i][j];pos = i;}}}}return s.substr(pos-res,res);}
};
推荐动态规划法
class Solution {
public:string longestPalindrome(string &s) {int n=s.length(), begin=0, end=0;vector<vector<bool> > dp(n,vector<bool> (n,false));for(int j=0; j<n; ++j){for(int i=0; i<=j; ++i){if((j-i<=1 || dp[i+1][j-1]) && s[i]==s[j])dp[i][j]=true;if(dp[i][j] && j-i>end-begin)begin=i, end=j;}}return s.substr(begin,end-begin+1);}
};作者:joy-teng
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/solution/dong-tai-gui-hua-zhong-xin-kuo-zhan-ma-la-che-suan/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
6.Z 字形变换
class Solution {
public:string convert(string s, int numRows) {if(numRows==1)return s;string res;int len = s.size();vector<vector<int>> dp(numRows);int b = 0, j=0;for(int i = 0;i<len;i++){if(b==0){if(j<numRows-1){dp[j].push_back(s[i]);j++;}else if(j==numRows-1){dp[j].push_back(s[i]);j--;b=1;}}else{if(j>0){dp[j].push_back(s[i]);j--;}else if(j==0){dp[j].push_back(s[i]);j++;b=0;}}}for(int i =0;i<numRows;i++){for(auto j:dp[i]){res+=j;}}return res;}
};
7.整数反转
class Solution {
public:int reverse(int x) {int p = 10;int n;long result = 0;if(x == INT_MIN){return 0;}if (x >= 0){while(x > 0){n = x % p;x = x / p;result = result*10 + n;}if(result > INT_MAX){return 0;}return result;}else{int y = -x;while(y > 0){n = y % p;y = y / p;result = result*10 + n;}if(result > INT_MAX){return 0;}return -result;}}
};
stoi、stod、stoll
string转int、double、long long都有函数
如果使用atoi也可以转,但是要配合c_str()使用
class Solution {
public:int reverse(int x) {if(x< -2147483647 || x>= 2147483647)return 0;string s = to_string(x);int b = 0;if(s[0]=='-'){s = s.substr(1,s.size()-1); b=1;}::reverse(s.begin(),s.end());while(s.size()>0 && s[0]=='0'){s = s.substr(1,s.size()-1);}if(s.empty())return 0;long long MIN = -pow(2,31);long long MAX = pow(2,31)-1;if(b==1){s = '-'+s; if(stoll(s)<INT_MIN || stoll(s)>INT_MAX)return 0;return stoll(s);}else{if(stoll(s)<INT_MIN || stoll(s)>INT_MAX)return 0;return stoll(s); }}
};
8. 字符串转换整数 (atoi)
要考虑的情况太多了
class Solution {
public:int b = 0;int sign = 0;int myAtoi(string str) {if(str.empty())return 0;string s = str;if(s[0]>='0'&&s[0]<='9'){if(sign==2)return 0;long long res = 0,i =0;while(i<s.size()&&s[i]=='0')i++;if(b==0){while(s[i]>='0'&& s[i]<='9'){res = res*10 + int(s[i++]-'0');if(res>INT_MAX)return INT_MAX;}return res;}else{while(s[i]>='0'&& s[i]<='9'){res = res*10 + int(s[i++]-'0');if(-res<INT_MIN)return INT_MIN;} return -res; }}else if (s[0]=='+'){s = s.substr(1,s.size()-1);if(!s.empty()&&s[0] ==' ')return 0;sign++;return myAtoi(s);}else if(s[0]=='-'){s = s.substr(1,s.size()-1);if(!s.empty()&&s[0] ==' ')return 0;b=1;sign++;return myAtoi(s);}else if(s[0]==' '){int i =0;while(i<s.size()&&s[i]==' ')i++;s =s.substr(i,s.size()-i);return myAtoi(s);}return 0;}
};
9.回文数
这里使用了整数反转的思路,直接比对反转后是否相等就知道是否是回文数;
另外,为了防止超范围,result可以使用类型long;
另外,数字和字符串转换不如算法方式好;
class Solution {
public:bool isPalindrome(int x) {if(x < 0){return false;}else{long result = 0;int y = x;int n = 0;while(x > 0){n = x % 10;x = x / 10;result = result*10 + n;}if (result == y){return true;}else{return false;}}}
};
10. 正则表达式匹配(dp)
class Solution {
public:bool isMatch(string s, string p) {int lens = s.size();int lenp = p.size();vector<vector<int>> dp(lens+1,vector<int>(lenp+1,false));dp[0][0]=true;for(int i =1;i<=lenp;i++){ if(p[i-1]=='*')dp[0][i]=dp[0][i-2];}for(int i = 1;i<=lens;i++){for(int j =1;j<=lenp;j++){if(s[i-1]==p[j-1]||p[j-1]=='.'){dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1];}else if(p[j-1]=='*'){dp[i][j]=dp[i][j-2] || (dp[i-1][j] && (p[j-2]=='.'||s[i-1]==p[j-2]));}}}return dp[lens][lenp];}
};
11. 盛最多水的容器
class Solution {
public:int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {int i=0, j=height.size()-1;int res = 0;while(i<j){int area = min(height[i],height[j])*(j-i);res = max(res,area);if(height[i]<=height[j])i++;else j--;}return res;}
};
12. 整数转罗马数字
class Solution {
public:string intToRoman(int num) {vector<pair<int,string>> vt;vt.push_back(make_pair(1000,"M"));vt.push_back(make_pair(900,"CM"));vt.push_back(make_pair(500,"D"));vt.push_back(make_pair(400,"CD"));vt.push_back(make_pair(100,"C"));vt.push_back(make_pair(90,"XC"));vt.push_back(make_pair(50,"L"));vt.push_back(make_pair(40,"XL"));vt.push_back(make_pair(10,"X"));vt.push_back(make_pair(9,"IX"));vt.push_back(make_pair(5,"V"));vt.push_back(make_pair(4,"IV"));vt.push_back(make_pair(1,"I"));string res;int count = 0;for(auto v:vt){if(v.first<=num){int x= num/v.first;for(int i=0;i<x;i++)res = res + v.second;num = num % v.first;}}return res;}
};
13.罗马数字转换
class Solution {
public:int romanToInt(string s) {int res = 0;int i=0,len = s.size();unordered_map<char,int> mp = {{'I',1},{'V',5},{'X',10},{'L',50},{'C',100},{'D',500},{'M',1000}};while(i<len){if(i+1<len && mp[s[i]]<mp[s[i+1]]){res += mp[s[i+1]]-mp[s[i]];i+=2; }else{res += mp[s[i]];i++;}}return res;}
};
map:
优点:
有序性,这是map结构最大的优点,其元素的有序性在很多应用中都会简化很多的操作
红黑树,内部实现一个红黑书使得map的很多操作在lgn的时间复杂度下就可以实现,因此效率非常的高
缺点: 空间占用率高,因为map内部实现了红黑树,虽然提高了运行效率,但是因为每一个节点都需要额外保存父节点、孩子节点和红/黑性质,使得每一个节点都占用大量的空间
适用处:对于那些有顺序要求的问题,用map会更高效一些
unordered_map:
优点: 因为内部实现了哈希表,因此其查找速度非常的快
缺点: 哈希表的建立比较耗费时间
适用处:对于查找问题,unordered_map会更加高效一些,因此遇到查找问题,常会考虑一下用unordered_map
14.最长公共前缀
class Solution {
public:string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {if(strs.empty())return "";string res = strs[0];for(int i =1;i<strs.size();i++){int j =0;for(j =0; j<res.size(); j++){if(res[j]!=strs[i][j])break;}res = res.substr(0,j);if(res.empty())return "";}return res;}
};
15. 三数之和(双指针,巧妙去重)
之前有道盛水量的问题用双指针能最快的解决,但是这道题直接两边双指针不能智能收缩,但是进行遍历的话有会是n方的复杂度,比如下面这个,两边遍历收缩,中间使用二分法,这样就是nnlogn的复杂度,依然不行。这道题有一种能够智能收缩的方法,就是把一个当作固定的,这样就能后面范围收缩了
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {set<vector<int>> res;sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());//-4,-1,-1,0,1,2//-2,-1,0,1,2int len = nums.size();for(int i = 0;i<len-2;i++){for(int j = len-1;j>i+1;j--){//if(nums[i]+nums[j-1]+nums[j]<0){i++;continue;}//if(nums[i]+nums[i+1]+nums[j]>0){j--;continue;}set<int> st(nums.begin()+i+1,nums.begin()+j);vector<int> vt(st.begin(),st.end());int left = 0, right = vt.size();while(left<right){int mid = left + (right-left)/2;int temp = nums[i]+vt[mid]+nums[j]; if(temp==0){res.insert({nums[i],vt[mid],nums[j]}); break;}else if(temp<0) {left = mid+1;}else right = mid;}}}vector<vector<int>> r(res.begin(),res.end());return r;}
};
这里的去重太重要了,这里去重就不需要set和vector之间的转换了,就差这点时间复杂度
if(i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1])continue;//去重
while (l<r && nums[l] == nums[l+1]) l++; // 去重while (l<r && nums[r] == nums[r-1]) r--; // 去重作者:rt-huang
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/solution/shuang-zhi-zhen-fa-hashfa-c-by-rt-huang/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
#include > vt(res.begin(),res.end()); return res;}
};
自己写的,勉强不超时,考虑可能是去重那里费了比较多功夫
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {int len = nums.size();int k=0, i=1,j = len-1;sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());vector<vector<int>> res;while(k<=len-3){if(nums[k]+nums[k+1]+nums[k+2]>0)break;if(nums[k]+nums[k+1]+nums[k+2]==0){ vector<int> temp={nums[k],nums[k+1],nums[k+2]};res.push_back(temp);break;};//if(nums[k]+nums[i]+nums[j]>0){k++;i=k+1;j=len-1;continue;}if(nums[k]+nums[j-1]+nums[j]<0){k++;i=k+1;j=len-1;continue;}while(i<j){if(nums[i]+nums[j]==-nums[k]){vector<int> temp={nums[k],nums[i],nums[j]};res.push_back(temp);i++;j--;}else if(nums[i]+nums[j]>-nums[k]){j--;}else{i++;}}k++;i=k+1;j=len-1;}set<vector<int>> r(res.begin(),res.end());res.assign(r.begin(),r.end());return res;}
};
16. 最接近的三数之和
class Solution {
public:int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int res = 5e6;int len= nums.size();sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());for(int i = 0;i<len-2;i++){int t1 = nums[i]+nums[i+1]+nums[i+2]; if(t1>target){if(abs(t1-target)<abs(res-target)){res = t1;}break;}int t2 = nums[i]+nums[len-1]+nums[len-2];if(t2<target){if(abs(t2-target)<abs(res-target)){res=t2;}continue;}if(i>1 && nums[i]==nums[i-1])continue;int j =i+1,k=len-1;while(j<k){int temp = nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[k];if(temp==target){return target;}if(abs(temp-target)<abs(res-target)){res = temp;}if(temp<target)j++;else k--;}}return res;}
};
17. 电话号码的字母组合(dfs,bfs)
dfs:注意第一层不要循环,对里层进行循环
class Solution {
public:vector<string> res;string path;void dfs(unordered_map<int,string> mp, string dig,int p,int q){if(path.size()==dig.size()){res.push_back(path);return;}for(int j = q;j<mp[dig[p]-'0'].size();j++){path.push_back(mp[dig[p]-'0'][j]);dfs(mp,dig,p+1,q);path.pop_back();}}vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {if(digits.empty())return {};unordered_map<int,string> mp = {{2,"abc"},{3,"def"},{4,"ghi"},{5,"jkl"},{6,"mno"},{7,"pqrs"},{8,"tuv"},{9,"wxyz"}};dfs(mp,digits,0,0);return res;}
};
bfs更好理解,注意一点queue不能直接转换成vector
class Solution {
public:vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {if(digits.empty())return {};unordered_map<int,string> mp = {{2,"abc"},{3,"def"},{4,"ghi"},{5,"jkl"},{6,"mno"},{7,"pqrs"},{8,"tuv"},{9,"wxyz"}};int temp =digits[0]-'0';queue<string> qt;string s;for(auto i:mp[temp])qt.push(s+i);int len = digits.size() ,i =1;while(i<len){int l = qt.size();for(int j = 0;j<l;j++){auto t = qt.front();qt.pop();for(auto s:mp[digits[i]-'0']){qt.push(t+s);}}i++;}vector<string> res;while(!qt.empty()){res.push_back(qt.front());qt.pop();}return res;}
};
18. 四数之和
要特别注意里面排除i相同和j相同的语句,出现一个相同就直接排除,不同非等到i和j同时满足;另外当出现了等于target的时候,p和q不仅要去重而且还要同时进行缩小,因为仅仅一个变化,另外一个因为去重不可能再匹配上了,就算匹配上也是重复的结果,所以这时要同时进行缩进。
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());int len = nums.size();vector<vector<int>> res;//-3,-2,-1,0,0,1,2,3for(int i = 0;i<len-3;i++){if(i>=1&&nums[i]==nums[i-1])continue;int t1 = nums[i]+nums[i+1]+nums[i+2]+nums[i+3];if(t1>target)break;int t2 = nums[i]+nums[len-3]+nums[len-2]+nums[len-1];if(t2<target)continue;for(int j = i+1;j<len-2;j++){int t3 = nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[j+1]+nums[j+2];if(t3>target)break;int t4 = nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[len-2]+nums[len-1];if(t4<target)continue;if(j>i+1&&nums[j-1]==nums[j])continue;int p = j+1,q=len-1;while(p<q){int temp = nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[p]+nums[q];if(temp==target){res.push_back({nums[i],nums[j],nums[p],nums[q]});while(p<q&&nums[p]==nums[p+1])p++;while(p<q&&nums[q]==nums[q-1])q--;p++;q--;}else if(temp>target)q--;else p++;}}}return res;}
};
19. 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
添加这个头节点十分的重要!
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
c/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {auto head1 = new ListNode(0);head1->next = head;auto slow = head1;auto fast = head1;while(n--){fast = fast->next;}while(fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;}slow->next = slow->next->next;head=head1->next;delete head1;return head;}
};
20.有效的括号(堆栈的运用)
class Solution {
public:bool isValid(string s) {stack<char> st;for(auto c:s){if(c=='(' || c=='[' || c == '{')st.push(c);else if(c==')'){if(st.empty() || st.top()!= '(')return false;else {st.pop();}}else if(c==']'){if(st.empty() || st.top()!='[')return false;else {st.pop();}}else if(c=='}'){if(st.empty() || st.top()!='{')return false;else {st.pop();}}}if(!st.empty())return false;return true;}
};
21.合并链表
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {auto head = new ListNode(0);auto temp = head;while(l1 && l2){if(l1->val<=l2->val){auto t = new ListNode(l1->val);temp->next = t;temp = t;l1=l1->next; }else{auto t = new ListNode(l2->val);temp->next = t;temp = t;l2=l2->next; }}temp->next = (l1)?(l1):(l2);return head->next;}
};
22. 括号生成
class Solution {
public://DFSvoid generateParenthesis_(int left,int right,vector<string>& rs,string str){if (left == 0 && right == 0) {rs.push_back(str);return;}if (left > 0) generateParenthesis_(left - 1, right, rs, str + "(");if (left < right) generateParenthesis_(left, right - 1, rs, str + ")");}vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {vector<string> rs;generateParenthesis_(n,n,rs,"");return rs;}//BFSvector<string> generateParenthesis2(int n) {vector<string> rs;queue<pair<string, pair<int, int>>>q; // pair<当前的括号, pair<左括号剩余, 右括号剩余>>q.push({"",{n,n}});while (!q.empty()) {auto top = q.front();q.pop();string str = top.first;int left = top.second.first;int right = top.second.second;if (left == 0 && right == 0) {rs.push_back(str);}if (left > 0) {q.push({str + '(',{left-1,right}});}if (right > 0 && right > left) {q.push({str + ')',{left,right-1}});}}return rs;}
};作者:chuang-bian-gu-shi
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/generate-parentheses/solution/c-dfs-by-chuang-bian-gu-shi/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
bfs
class Solution {
public:vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {queue<pair<string,pair<int,int>>> qt;//auto t = make_pair("(",make_pair(1,0));//qt.push(t);qt.push({ "(", {1,0} });while(qt.front().first.size()<2*n){int len = qt.size();for(int i = 0;i<len;i++){auto temp = qt.front(); qt.pop();int left = temp.second.first;int right = temp.second.second;if(left>right && left<n){auto t1 = temp;t1.first += '(';t1.second.first +=1;qt.push(t1);auto t2 = temp;t2.first += ')';t2.second.second +=1;qt.push(t2); }else if(left>right && left==n){auto t3 = temp;t3.first += ')';t3.second.second +=1;qt.push(t3);}else if (left == right){auto t1 = temp;t1.first += '(';t1.second.first +=1;qt.push(t1);auto t2 = temp;t2.first += ')';t2.second.second +=1;qt.push(t2); }}}vector<string> res;while(!qt.empty()){res.push_back(qt.front().first);qt.pop();}return res;}
};
dfs
class Solution {
public:vector<string> res;string path;void dfs(int n, int left, int right){if(left>n || right>n || right>left)return;if(left==n&&right==n){res.push_back(path);return;}path += ')';dfs(n,left,right+1);path.pop_back();path += '(';dfs(n,left+1,right);path.pop_back();}vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {dfs(n,0,0);return res;}
};
找到所有括号的组合方式看起来比较复杂。
所以我们可以尝试换个思路:如果“(”对应数字1,“)”对应数字-1呢?
通过观察我们可以发现这样一个规律:
凡是有效的括号组合,转化成数字,任意前n项和都不小于0!
比如:“()()()”
前1位:1>=0;前2位:1+(-1)=0>=0;前3位:1+(-1)+1=1>=0;
…以此类推,前n位数字和均大于等于0.
又比如:“((()))”
前3位:1+1+1=3>=0;前4位:1+1+1+(-1)=2>=0;前5位:1+1+1+(-1)+(-1)=1>=0;
…依然满足规律。
至此,我们就能想到这样一个思路:
1.目标为n时,可以转化为n个-1和n个1
2.求这串数字的所有排列
3.满足以上规律的就是有效的括号组合
4.最后一步再将数字组合转化成括号组合
整个过程需要一些小的工具:
1.求全排列的函数:next_permutation
2.数字转化成括号:容器map
class Solution {
public:vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n){vector<string> result;if(n == 0){return result;}vector<vector<int>> mid;vector<int> temp;for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){temp.push_back(-1); //先放所有的-1}for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){temp.push_back(1); //再放所有的+1(这样的原因是因为全排列需要从小到大的顺序)}while(next_permutation(temp.begin(),temp.end())) //求全排列{int target = 0;int judg = 1;for(auto i:temp){target+=i;if(target < 0){judg = 0;break; //是否满足前n项之和不小于0}}if(judg == 1){mid.push_back(temp);}//如果不用剪枝,则可以将数组放入mid}map<int,string> invert;invert.insert(map<int,string>::value_type(1,"(")); //1对应左括号invert.insert(map<int,string>::value_type(-1,")")); //-1对应右括号for(auto i:mid){string s;for(auto j:i){s += invert[j]; //数字组合转化成字符串}result.push_back(s);}return result;}
};作者:da-lian-mao-ai-chi-yu
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/generate-parentheses/solution/gua-hao-tai-fu-za-shu-zi-zhuan-hua-ta-by-da-lian-m/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
全排列函数next_permutation
用这个函数一下子就省去了找所有可能的排列,在排列之后再转成括号就行了,由于只有一种括号,就用1和-1来代替并使用剪枝算法
while(next_permutation(temp.begin(),temp.end())) {}
next_permutation(num,num+n)函数是对数组num中的前n个元素进行全排列,同时并改变num数组的值。
另外,需要强调的是,next_permutation()在使用前需要对欲排列数组按升序排序,否则只能找出该序列之后的全排列数。
23. 合并K个排序链表
1.vector
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {vector<int> v;for(auto head:lists){while(head){v.push_back(head->val);head=head->next;}}sort(v.begin(),v.end());ListNode* head = new ListNode(0);ListNode* res = head;//int i = v.size();for(int i = 0 ; i<v.size(); i++){ListNode* temp =new ListNode(v[i]);res->next = temp;res = temp; }return head->next;}
};
2.使用优先队列
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {priority_queue<pair<int,ListNode*>,vector<pair<int,ListNode*>>,greater<pair<int,ListNode*>>> pt;for(int i = 0; i< lists.size() ;i++){while(lists[i]){pt.push(make_pair(lists[i]->val,lists[i]));lists[i] = lists[i]->next;}}auto head1 = new ListNode(0);auto temp = head1;while(!pt.empty()){temp->next = pt.top().second;temp = pt.top().second;pt.pop();}temp->next = NULL;return head1->next;}
};
3。归并排序
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode *a, ListNode *b) {if ((!a) || (!b)) return a ? a : b;ListNode head, *tail = &head, *aPtr = a, *bPtr = b;while (aPtr && bPtr) {if (aPtr->val < bPtr->val) {tail->next = aPtr; aPtr = aPtr->next;} else {tail->next = bPtr; bPtr = bPtr->next;}tail = tail->next;}tail->next = (aPtr ? aPtr : bPtr);return head.next;}ListNode* merge(vector <ListNode*> &lists, int l, int r) {if (l == r) return lists[l];if (l > r) return nullptr;int mid = (l + r) >> 1;return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, l, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, r));}ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {return merge(lists, 0, lists.size() - 1);}
};作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/solution/he-bing-kge-pai-xu-lian-biao-by-leetcode-solutio-2/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {auto head1 = new ListNode(0);head1->next = head;auto temp = head1;while(temp && temp->next && temp->next->next){auto pre = temp->next;auto cur = temp->next->next;pre->next = cur->next;cur->next = pre;temp->next = cur;temp = pre;}return head1->next;}
};
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {auto dummy=new ListNode(-1);dummy->next=head;for(auto p=dummy;p->next&&p->next->next;){auto a=p->next,b=a->next;p->next=b;a->next=b->next;b->next=a;p=a;}return dummy->next;}
};作者:TeFuirnever
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/solution/shou-hui-man-hua-tu-jie-leetcodezhi-liang-liang-ji/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {if(!head)return head;auto head1 = new ListNode(0);head1->next = head;auto last = head1;auto pre = head;auto cur = head->next;while(cur){auto temp = cur->next;last->next = cur;cur->next = pre;pre->next = temp;last = pre;pre = temp;if(!temp)break;else cur = temp->next;}auto res = head1->next;delete head1;return res;}
};
25. K 个一组翻转链表
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<ListNode*> reverselist(ListNode* head, ListNode* furture)
{auto head1 = new ListNode(0);head1->next = head;auto last = head;auto pre = head1;auto cur = head;auto sign = cur;while(cur!=furture){auto temp = cur->next;cur->next = pre;pre = cur;sign = cur;cur = temp;}head->next = furture;delete head1;vector<ListNode*> res = {sign,head};return res;
}ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {auto head1 = new ListNode(0);head1->next = head;auto p = head1;while(p){int count = k;auto temp = p->next;auto q = temp;while(temp && count){count--;temp = temp->next;}if(count==0){auto x = reverselist(q,temp);p->next = x[0];p = x[1];}else break;}auto res = head1->next;delete head1;return res;}
};
class Solution {
public:// 翻转一个子链表,并且返回新的头与尾pair<ListNode*, ListNode*> myReverse(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) {ListNode* prev = tail->next;ListNode* p = head;while (prev != tail) {ListNode* nex = p->next;p->next = prev;prev = p;p = nex;}return {tail, head};}ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {ListNode* hair = new ListNode(0);hair->next = head;ListNode* pre = hair;while (head) {ListNode* tail = pre;// 查看剩余部分长度是否大于等于 kfor (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {tail = tail->next;if (!tail) {return hair->next;}}ListNode* nex = tail->next;// 这里是 C++17 的写法,也可以写成// pair result = myReverse(head, tail); // head = result.first;// tail = result.second;tie(head, tail) = myReverse(head, tail);// 把子链表重新接回原链表pre->next = head;tail->next = nex;pre = tail;head = tail->next;}return hair->next;}
};作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/solution/k-ge-yi-zu-fan-zhuan-lian-biao-by-leetcode-solutio/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {if (head == NULL) return NULL;ListNode *a = head;ListNode *b = head;for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {if (b == NULL) return head;b = b->next;}ListNode *newNode = reverseOperator(a,b);a->next = reverseKGroup(b,k);return newNode;}ListNode* reverseOperator(ListNode* n,ListNode *b) {ListNode *pre, *cur, *nxt;pre = NULL; cur = n; nxt = n;while (cur != b) {nxt = cur->next;cur->next = pre;pre = cur;cur = nxt;}return pre;}
};作者:yu-fan-u
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/solution/c-di-gui-jian-dan-yi-dong-by-yu-fan-u/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
26. 删除排序数组中的重复项
class Solution {
public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {if(nums.empty())return 0;int i=0,j =0;while(i<nums.size()){while(i<nums.size() && nums[i]==nums[j]){i++;}if (i == nums.size())break;nums[++j]=nums[i++];}return j+1;}
};
class Solution {
public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {int i =1;int j = 0;int len = nums.size();if(len==0)return 0;for(i=1; i<len;i++){if(nums[i]==nums[j])continue;else{nums[++j] = nums[i];}}return j+1;}
};
27. 移除元素
循环这里必须加等号
class Solution {
public:int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {int i = 0 ; int j = nums.size()-1;while(i<=j){while(i<=j && nums[i]!=val) i++;while(i<=j && nums[j]==val)j--;if(i<=j) swap(nums[i],nums[j]);} return i;}
};
30. 串联所有单词的子串
超时了
class Solution {
public:vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {if(s.empty() || words.empty())return {};vector<int> res;int lenw = words.size();sort(words.begin(),words.end());string s1;for(auto w:words)s1 =s1+w;if(s1.size()>s.size())return {};for(int i =0 ; i<= s.size()-s1.size() ;i++){if(s.substr(i,s1.size())==s1)res.push_back(i);}while(next_permutation(words.begin(),words.end())){for(int i =0 ; i<= s.size()-s1.size() ;i++){s1 = "";for(auto w:words)s1 =s1+w;if(s.substr(i,s1.size())==s1)res.push_back(i);} }return res;}
};
利用字符都是等长的这点可以使用哈希表做,不然会比较麻烦
class Solution {
public:vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {if(s.empty() || words.empty())return {};unordered_map<string,int> mp;int sublen =words[0].size();int count = sublen*words.size();if(count>s.size())return {};for(auto i:words){mp[i]++;}vector<int> res;for(int i =0;i<=s.size()-count;i++){unordered_map<string,int> mp1;auto temp = s.substr(i,count);int j = 0;while(j<s.size()){if(mp.find(temp.substr(j,sublen))==mp.end())break;else {mp1[temp.substr(j,sublen)]++; j+=sublen;}}if(mp1==mp)res.push_back(i);}return res;}
};
31. 下一个排列
class Solution {
public:void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end());}
};作者:chronosphere
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/next-permutation/solution/c-4ms-5xing-by-chronosphere/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
#```cpp
从后向前查找第一个相邻升序的元素对 (i,j),满足 A[i] < A[j]。此时 [j,end) 必然是降序
在 [j,end) 从后向前查找第一个满足 A[i] < A[k] 的 k。A[i]、A[k] 分别就是上文所说的「小数」、「大数」
将 A[i] 与 A[k] 交换
可以断定这时 [j,end) 必然是降序,逆置 [j,end),使其升序
如果在步骤 1 找不到符合的相邻元素对,说明当前 [begin,end) 为一个降序顺序,则直接跳到步骤 4作者:imageslr
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/next-permutation/solution/xia-yi-ge-pai-lie-suan-fa-xiang-jie-si-lu-tui-dao-/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public:void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {bool b = false;for(int i = nums.size()-2;i>=0;i--){if(nums[i]<nums[i+1]){int m = 5e6,sign = 0;for(int j = nums.size()-1;j>=i+1;j--){ if(nums[j]>nums[i] && abs(nums[j]-nums[i])<m){sign = j;m = nums[j]-nums[i];}}if(sign){swap(nums[sign],nums[i]);reverse(nums.begin()+i+1,nums.end());b = !b;break;}}}if(b)return;else {reverse(nums.begin(),nums.end());return;}}
};
32. 最长有效括号
class Solution {
public:int longestValidParentheses(string s) {if(s.size() < 2)return 0;int ans = 0;stack<int> st;st.push(-1);for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){if(s[i] == '(')st.push(i);else{st.pop();if(st.empty())st.push(i); //重新开始记录elseans = max(ans, i - st.top());}}return ans;}
};作者:Sunny_SMILE
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-valid-parentheses/solution/32-zui-chang-you-xiao-gua-hao-3chong-jie-fa-by-sun/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
33. 搜索旋转排序数组
class Solution {
public:int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int right = nums.size();int left = 0;while(left<right){int mid = left + (right-left)/2;if(nums[mid]==target){return mid;}else if (nums[mid]>target){if(target>=nums[0] || nums[mid]<nums[0]){right = mid;}else{left=mid+1;}}else{if(nums[mid]>=nums[0] ||target<nums[0]){left=mid+1;}else{right=mid;}}}return -1;}
};
class Solution {
public:int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int lo = 0, hi = nums.size() - 1;while (lo < hi) {int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;if ((nums[0] > target) ^ (nums[0] > nums[mid]) ^ (target > nums[mid]))lo = mid + 1;elsehi = mid;}return lo == hi && nums[lo] == target ? lo : -1;}
};作者:LukeLee
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/solution/ji-jian-solution-by-lukelee/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
class Solution {
public:vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int left = 0, right = nums.size();while(left<right){int mid = left + (right-left)/2;if(nums[mid]==target){int t1 =mid-1, t2 = mid+1;while(t1>=0 && nums[t1]==target)t1--;while(t2<(int)nums.size() && nums[t2]==target)t2++;return {t1+1,t2-1};}else if(nums[mid]<target){left = mid +1;}else{right = mid;}}return {-1,-1};}
};
35. 搜索插入位置(二分法***************)
class Solution {
public:int searchInsert(vector<int>& nums, int target) {return lower_bound(nums.begin(),nums.end(),target)-nums.begin();}
};
lower_bound
返回第一个大于等于target的数,和二分法模板中最后的结果left的作用时一样的,upper_bound为返回第一个大于target的数
二分法使用的模板
用来求刚刚大于等于target的第一个值
class Solution {
public:int searchInsert(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int len = nums.size();int left=0,right = len;while(left<right){int mid = (left+right)/2;if(nums[mid]==target)return mid;else if(nums[mid]<target){left = mid+1;}else{right = mid;}}return left;}
};
36. 有效的数独
注意块表示法,i/3*3和i不是一样的结果
下面这个方法灵活运用了三个哈希表(二维数组实现)的,单次遍历,用目的区域(行、列、快)来表示行,用1-9来9个数字出现次数作为列,列为10因为直接对应,0不算,给9加一行
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {unordered_map<int,int> mp;for(int i =1;i<=9;i++) mp[i]=0;vector< unordered_map<int,int> > v1(9,mp);vector< unordered_map<int,int> > v2(9,mp);vector< unordered_map<int,int> > v3(9,mp);for(int i = 0 ;i<9;i++){for(int j = 0;j<9;j++){if(board[i][j]=='.')continue;int temp = board[i][j]-'0';if(v1[i][temp]==0)v1[i][temp]++;else return false;if(v2[j][temp]==0)v2[j][temp]++;else return false;if(v3[(i/3)*3+j/3][temp]==0)v3[(i/3)*3+j/3][temp]++;else return false; }}return true;//00-0 03-1 06-2 30-3 36-4 39-5 60-6 63-7 66-8 }
38. 外观数列
class Solution {
public:string countAndSay(int n) {string s = "1";while(n-1){int i = 0;string res;while(i<s.size()){ auto val = s[i];int start = i;while(i<s.size() && s[i]==val)i++;int len = i-start;res= res + to_string(len) + val; }s = res;n--;}return s;}
};
39. 组合总和
要特别注意将i放入下次dfs的写法,目的就是为了下次不再查找之前的元素,值得学习
class Solution {
private:vector<vector<int>> res;vector<int> path;int sum = 0;
public:void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& res,vector<int>& candidates,vector<int>& path, int sum,int target ,int j){if(sum == target){res.push_back(path);return;}if(sum>target)return;for(int i = j; i<(int)candidates.size() ;i++){path.push_back(candidates[i]);sum +=candidates[i];dfs(res, candidates, path, sum, target,i);path.pop_back();sum -=candidates[i];}}vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {sort(candidates.begin(),candidates.end());dfs(res,candidates,path,0,target,0);return res;}
};
dfs深度优先搜索***
回溯算法:当给定终点时,可以进行回退
再加上递归和剪枝算法
(二叉树常用算法:回溯、队列、递归、剪枝)
负递归算法:
// author:rmokerone
#include 正递归加剪枝算法:
要特别注意几点:
1.是用了剪枝是为了提速
2.除此之外,在深度优先搜索的时候可以设置从当前元素开始,因为之前的元素在之前的节点已经用过了,所以加了一个start变量用来记录在can容器中的位置
3.像sum这种的不用每次都计算,直接加个参数就行了,注意全局变量的定义位置,因为递归函数要用,所以定义在全局的地方,还可以在外面定义但是在函数中进行计算,比如siz这个变量,更严格点可以定义在private中
class Solution {
public:vector<int> tmp;vector<vector<int>> ans;int siz;void dfs(int now, int sum, int tar, vector<int>& num){if(sum > tar) return;if(sum == tar){ans.push_back(tmp);return;}for(int i = now; i < siz; i ++){tmp.push_back(num[i]); //一层一层往下走dfs(i, sum + num[i], tar, num); //当大于或者等于时都会返回tmp.pop_back();//回到上一个分叉节点,从整个树的最左边一条开始试}}vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {siz = candidates.size();dfs(0, 0, target, candidates);return ans;}
};作者:iswJXkYVv3
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/solution/c-di-gui-shen-sou-by-iswjxkyvv3/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
40. 组合总和 II
体会和上一题的区别
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> res;vector<int> path;int sum = 0;void dfs(vector<int>& candidates, int target, vector<int>& path, int sum,int p){if(sum>target)return;if(sum==target){res.push_back(path);return;}for(int i =p ;i< candidates.size() ;i++){sum = sum + candidates[i];path.push_back(candidates[i]);dfs(candidates,target,path,sum,i+1);sum = sum - candidates[i];path.pop_back();}}vector<vector<int>> combinationSum2(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {sort(candidates.begin(),candidates.end());dfs(candidates,target,path,0,0);set<vector<int>> st(res.begin(),res.end());vector<vector<int>> r(st.begin(),st.end());return r; }
};
41. 缺失的第一个正数
class Solution {
public:int firstMissingPositive(vector<int> nums) {int n = nums.size();bool b= false;for(auto i:nums){if(i==1){b = true;break;}}if(!b)return 1;for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){if(nums[i]<1 ||nums[i]>n)nums[i]=1;}for(int i =0;i<n;i++){if(nums[i]>0 && nums[nums[i]-1]>0)nums[nums[i]-1]=-nums[nums[i]-1];if (nums[i] < 0 && nums[-nums[i]-1]>0)nums[-nums[i]-1] = -nums[-nums[i]-1];}for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if (nums[i] > 0) {return i+1; }}return n+1;}
};
class Solution {
public:int firstMissingPositive(vector<int>& nums) {//return 0;int n = nums.size();bool flag = true;for(int i=0; i<n; i++){if(nums[i] == 1) flag = false;}if(flag) return 1;for(int i=0; i<n; i++){if(nums[i] <= 0 || nums[i] > n){nums[i] = 1;}}for(int i=0; i<n; i++){int pos = nums[i] > 0 ? nums[i] : (-nums[i]);nums[pos-1] = nums[pos-1] > 0 ? (-nums[pos-1]) : nums[pos-1];}//find the fist positive indexint ret = n+1;for(int i=0; i<n; i++){if(nums[i] > 0) return i+1;}return ret;}
};作者:edward_wang
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/first-missing-positive/solution/chang-shu-kong-jian-fu-za-du-jie-jue-lei-ha-xi-wen/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
42. 接雨水
class Solution {
public:int trap(vector<int>& height) {int res = 0;auto m = max_element(height.begin(),height.end())-height.begin();int i = 0,j=0;while(i<m && height[i]==0)i++;while(i<m){j = i+1;int sum = 0;while(j<=m && height[j]<height[i]){sum += height[j++];}res += min(height[i],height[j])*(j-i-1)-sum;i=j;}i = height.size()-1;while(i>m){j = i-1;int sum = 0;while(j>=m && height[j]<height[i]){sum += height[j--];}res += min(height[i],height[j])*(i-j-1)-sum;i=j; }return res;}
};
class Solution {
public:int trap(vector<int>& height) {int dp = 0;int res = 0;int m = 0;auto iter = max_element(height.begin(),height.end());m=iter-height.begin();for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){if(dp==0)dp = height[i];else if(height[i]<dp){res += dp-height[i];}else if(height[i]>dp){dp = height[i];}}dp = 0;for(int i = height.size()-1; i>m;i--){if(dp==0)dp = height[i];else if(height[i]<dp){res += dp-height[i];}else if(height[i]>dp){dp = height[i];}}return res;}
};
这是一个建立在一维数组上的问题,理论上这类的所有问题都可以用双指针来解决,这道题的难点在于找到最大值之后的后半部分怎么处理,怎么去找到剩下的部分,这时候需要求最大值,使用max_element函数,但是注意返回的是一个迭代器,用法如下
#include 当开始使用这个函数的时候想把里面所有的索引换成迭代器指针,但是发现在执行起来十分有困难,就是因为迭代器之间不传递,比如i和j都是v的迭代器,i++被允许,但是j=i+1就不被允许,所以能不使用迭代器就不使用,当要使用那些返回迭代器的方法时,可以用他减去v.begin()自然就返回的是下标位置
堆栈的方法,不是很好理解
直观想法
我们可以不用像方法 2 那样存储最大高度,而是用栈来跟踪可能储水的最长的条形块。使用栈就可以在一次遍历内完成计算。
我们在遍历数组时维护一个栈。如果当前的条形块小于或等于栈顶的条形块,我们将条形块的索引入栈,意思是当前的条形块被栈中的前一个条形块界定。如果我们发现一个条形块长于栈顶,我们可以确定栈顶的条形块被当前条形块和栈的前一个条形块界定,因此我们可以弹出栈顶元素并且累加答案到
\text{ans}ans 。算法
使用栈来存储条形块的索引下标。 遍历数组: 当栈非空且
\text{height}[current]>\text{height}[st.top()]height[current]>height[st.top()]
意味着栈中元素可以被弹出。弹出栈顶元素 \text{top}top。 计算当前元素和栈顶元素的距离,准备进行填充操作
\text{distance} = \text{current} - \text{st.top}() -
1distance=current−st.top()−1 找出界定高度 \text{bounded_height} =
\min(\text{height[current]}, \text{height[st.top()]}) -
\text{height[top]}bounded_height=min(height[current],height[st.top()])−height[top]
往答案中累加积水量\text{ans} \mathrel{+}= \text{distance} \times
\text{bounded_height}ans+=distance×bounded_height 将当前索引下标入栈 将
\text{current}current 移动到下个位置
作者:LeetCode
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solution/jie-yu-shui-by-leetcode/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
int trap(vector<int>& height)
{int ans = 0, current = 0;stack<int> st;while (current < height.size()) {while (!st.empty() && height[current] > height[st.top()]) {int top = st.top();st.pop();if (st.empty())break;int distance = current - st.top() - 1;int bounded_height = min(height[current], height[st.top()]) - height[top];ans += distance * bounded_height;}st.push(current++);}return ans;
}作者:LeetCode
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solution/jie-yu-shui-by-leetcode/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
43. 字符串相乘
没有思路,原来是利用乘法的计算方式来的
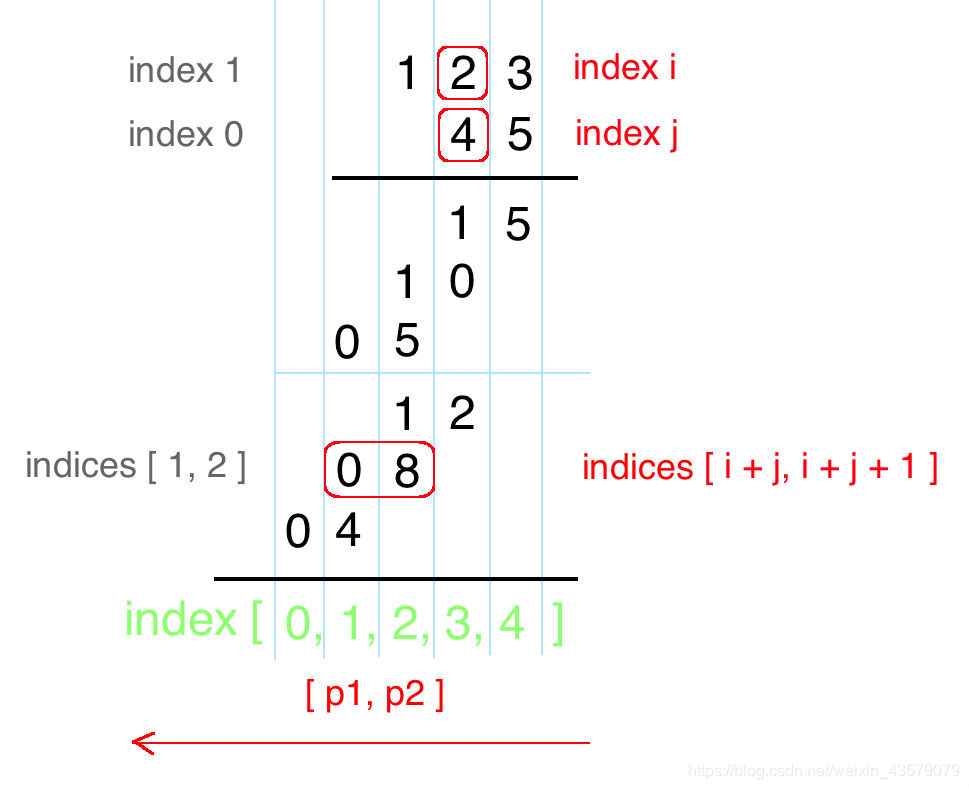
class Solution {
public:string multiply(string num1, string num2) {int n1=num1.size();int n2=num2.size();string res(n1+n2,'0');for(int i=n2-1;i>=0;i--){for(int j=n1-1;j>=0;j--){int temp=(res[i+j+1]-'0')+(num1[j]-'0')*(num2[i]-'0');res[i+j+1]=temp%10+'0';//当前位res[i+j]+=temp/10; //前一位加上进位,res[i+j]已经初始化为'0',加上int类型自动转化为char,所以此处不加'0'}}//去除首位'0'for(int i=0;i<n1+n2;i++){if(res[i]!='0')return res.substr(i);}return "0";}
};作者:carryzz
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/multiply-strings/solution/c-shu-shi-cheng-fa-dai-ma-jian-ji-you-ya-yi-dong-b/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
44. 通配符匹配
class Solution {
public:bool isMatch(string s, string p) {int lens = s.size();int lenp = p.size();vector<vector<bool>> vt(lens+1, vector<bool>(lenp+1,false));vt[0][0]=true;for(int i=1 ;i<=lenp ;i++){vt[0][i]=vt[0][i-1]&&p[i-1]=='*';}//*可以匹配任何0字符for(int i = 1 ;i<=lens ;i++){for(int j = 1 ;j<=lenp ;j++){if(s[i-1]==p[j-1] || p[j-1]=='?'){vt[i][j]=vt[i-1][j-1];}else if(p[j-1]=='*'){vt[i][j]=vt[i-1][j]||vt[i][j-1];}}}return vt[lens][lenp];}
};
45. 跳跃游戏 II
class Solution {
public:int jump(vector<int>& nums) {int res = 0;int i = 0, len = nums.size();while(i<len){int m = 0,point = 0;if(i==len-1)return res;if(i+nums[i]>=len-1)return res+1;for(int j = i ; j<= min(i+nums[i],len-1);j++){if(j+nums[j]>m){m=j+nums[j];point = j;}}i = point ;res++;}return res;}
};
贪心算法
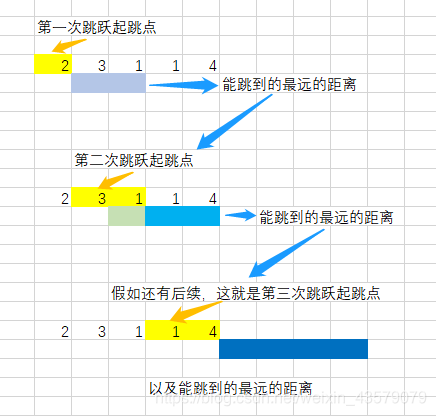
看了解答,发现这种思路整体是对的,就是追求每一次能走的最大,然而之前的错误在于,并不是比较start+nums[start]和max[start,start+len(start)]之间的最大值,应该比较的是和区间里每一个值和其值的和即i+len(i),这才是走的最远的方法,按照这种方法不断更新,就可以找到最后了
即使意思相近但是别人的表达也十分简介
int jump(vector<int> &nums)
{int ans = 0;int start = 0;int end = 1;while (end < nums.size()){int maxPos = 0;for (int i = start; i < end; i++){// 能跳到最远的距离maxPos = max(maxPos, i + nums[i]); //在遍历的过程中不断更新这个最大值}start = end; // 下一次起跳点范围开始的格子end = maxPos + 1; // 下一次起跳点范围结束的格子,加一是因为上面的遍历时左闭右开的ans++; // 跳跃次数}return ans;
}作者:ikaruga
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game-ii/solution/45-by-ikaruga/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
46. 全排列(bfs)
关于全排列next_permumation有几点需要说明
1.之气那要排序
2.只要开始全排列,第一个结果是已经改变之后的数组,而不是原来的
3。参数是首末迭代器
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {vector<vector<int> > res;sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());res.push_back(nums);while(next_permutation(nums.begin(),nums.end())){res.push_back(nums);}return res;}
};
这是使用队列层序遍历的方法写的
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {vector<vector<int> > res;if (nums.size()==0 || nums.size()==1){res.push_back(nums);return res;}sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());queue<vector<int>> q;for(auto i:nums){vector<int> temp;temp.push_back(i);q.push(temp);}//int i=nums.size()-1;while(q.front().size()!=nums.size()){ for (auto i:nums){vector<int> temp = q.front();if(find(temp.begin(),temp.end(),i)==temp.end()){temp.push_back(i);q.push(temp);}}q.pop();}while(!q.empty()){res.push_back(q.front());q.pop();}return res;}
};
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> res;vector<int> path;void dfs(vector<int>& nums){if(path.size()==nums.size()){res.push_back(path);return;}for(int i = 0 ; i <nums.size();i++){if(find(path.begin(),path.end(),nums[i])==path.end()){path.push_back(nums[i]);dfs(nums);path.pop_back();}}}vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {dfs(nums);return res;}
};
回溯问题+决策树
算法模板
递归{递归出口;for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++){add(i);进入递归;remove(i);}
}作者:windliang
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees-ii/solution/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-by-2-7/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
void backtrack(路径,选择列表)
{if(终止条件){传出路径结果return;}for i in 选择列表{进入该选择back(路径,选择列表)退出该选择}
}
这是根据该思想写的代码,代码结构简单,清晰,但是优化的不好
class Solution {
private:vector<vector<int> > res;int len;vector<int> path;
public:void backtrack(vector<int> &path, vector<int>& nums){set<int> s(path.begin(),path.end());if(path.size()==len){if (s.size()==len){res.push_back(path);return; }else{return;}} for(auto i : nums){path.push_back(i);backtrack(path,nums);path.pop_back();}}vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {len = nums.size();if (nums.size()==0 || nums.size()==1){res.push_back(nums);return res;}sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());backtrack(path,nums);return res;}
};
47. 全排列 II
与重复相比不一样的地方:用一个set接收,而且数组一开开始必须排序
class Solution {
public:set<vector<int> > res;vector<int> path;void dfs(vector<int> nums, int len, vector<bool>& judge){if(path.size()==len){res.insert(path);return;}for(int i = 0; i<len ;i++){if(!judge[i]){judge[i]=true;path.push_back(nums[i]);dfs(nums,len,judge);path.pop_back();judge[i]=false;}}}vector<vector<int>> permuteUnique(vector<int>& nums) {int len = nums.size();sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());vector<bool> judge(len,false);dfs(nums,len,judge);vector<vector<int>> r(res.begin(),res.end());return r;}
};
48. 旋转图像
将图片沿正对角线和竖轴翻转一下就可以了
class Solution {
public:void rotate(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {int n = matrix.size();int m = matrix[0].size();// 对于正对角线对称翻转for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = i; j < m; j++) {swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);}}// 竖轴镜像操作for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {reverse(matrix[i].begin(), matrix[i].end());}}
};作者:happy_yuxuan
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-image/solution/leetcode48-fan-zhuan-gui-lu-by-happy_yuxuan/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
49. 字母异位词分组
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {vector<vector<string>> res;vector<pair<multiset<char>,vector<string>>> st;for(auto str:strs){multiset<char> temp(str.begin(),str.end());bool b = false;for(int i = 0 ;i<(int)st.size() ;i++){if(st[i].first==temp){st[i].second.push_back(str);b = true;break;}}if(!b){st.push_back(pair<multiset<char>,vector<string>>(temp,{str}));}}for(auto i:st){vector<string> temp;for(auto j:i.second){temp.push_back(j);}res.push_back(temp);}return res;}
};
更好的办法:哈希表和数组联系,只要引入一个hash表,索引是排序后的单词,值为结果vector的下标,循环一遍就好了
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {vector<vector<string>> res; int sub=0; //结果vector的下标值string tmp; //临时stringunordered_map<string,int> work; //判断排序后单词是否存在,即字母组成是否一致for(auto str:strs){tmp=str;sort(tmp.begin(),tmp.end());if(work.count(tmp)){res[work[tmp]].push_back(str);}else{vector<string> vec(1,str);res.push_back(vec);work[tmp]=sub++;}}return res;}
};作者:rjs
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/group-anagrams/solution/c-yin-ru-hashbiao-shi-jian-32ms-ji-bai-9948-nei-cu/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
50. Pow(x, n)
class Solution {
public:double dfs(double x, long long n){if(n==1)return x;if(n%2==0){double temp = dfs(x,n/2);//这里可以减少计算次数,提前计算好return temp*temp;}else{return x*dfs(x,n-1); }}double myPow(double x, int n) {if(n==0)return 1;if(x==0)return 0;bool k = (n>0)?true:false;n = abs(n);double res = dfs(x,n);return k?res:(1/res);}
};
51. N皇后(回溯dfs)
不知道哪里有问题
思路非常清晰,典型的n皇后的问题,稍微麻烦的问题是判断是否额能够满足条件,而且注意不用在最后才检查条件。应该在中间进行判断,只要能够满足条件才继续下去,这样到最后也就满足条件了,放一个满足一个,最后就一定满足,这里一行一行建立的会稍微简单一点
class Solution {vector<vector<string>> res;//存结果vector<string> tmp;//存棋盘
public:vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {string line(n,'.');//既然一行一行试,那就一行一行存solveNQueens(line, 0, n);//从第0行开始return res;}private://试某一行void solveNQueens(string& line, int row, int n){if(tmp.size() == n)//棋盘绘制够n行存进结果,不用继续试了{res.push_back(tmp);return;}for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)//一格一格,每格都要试{if(checkAll(row, i, n)) //符合条件了{line[i] = 'Q'; //就把当前试的这一格放皇后tmp.push_back(line); //然后把这一行绘制进棋盘line[i] = '.'; //棋盘的下一行应该是没有皇后的solveNQueens(line, row + 1, n);//去试下一行tmp.pop_back(); //接下来要去试下一格,刚才绘制进去的那一行删掉}}}//暴力检查条件bool checkAll(int row, int col, int n){for(int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; --i,--j)//左上方{if(tmp[i][j] == 'Q')return false;}for(int i = row - 1; i >= 0; --i)//正上方{if(tmp[i][col] == 'Q')return false;}for(int i = row -1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; --i, ++j)//右上方{if(tmp[i][j] == 'Q')return false;}return true;}
};作者:zynflicker
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-queens/solution/4ms89mhui-su-fa-jian-dan-yi-dong-by-zynflicker/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
53. 最大子序和(贪心)
很典型的使用贪心算法的例题
class Solution
{
public:int maxSubArray(vector<int> &nums){//类似寻找最大最小值的题目,初始值一定要定义成理论上的最小最大值int result = INT_MIN;int numsSize = int(nums.size());int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++){sum += nums[i];result = max(result, sum);//如果sum < 0,重新开始找子序串if (sum < 0){sum = 0;}}return result;}
};作者:pinku-2
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/solution/zui-da-zi-xu-he-cshi-xian-si-chong-jie-fa-bao-li-f/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
54. 螺旋矩阵
class Solution {
public:vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {if(matrix.empty())return {};int m = matrix.size(),n=matrix[0].size();vector<vector<bool>> board(m,vector<bool>(n,false));board[0][0]=true;vector<int> res={matrix[0][0]};string s = "right";int i = 0,j=0;while(res.size()<m*n){if(s=="right"){if(j<n-1 && board[i][j+1]==false){res.push_back(matrix[i][++j]);board[i][j]=true;}else{s="down";}}else if(s=="down"){if(i<m-1 && board[i+1][j]==false){res.push_back(matrix[++i][j]);board[i][j]=true;}else{s="left";}} else if(s=="left"){if(j>0 && board[i][j-1]==false){res.push_back(matrix[i][--j]);board[i][j]=true;}else{s="up";}}else if(s=="up"){if(i>0 && board[i-1][j]==false){res.push_back(matrix[--i][j]);board[i][j]=true;}else{s="right";}}}return res;}
};
55. 跳跃游戏
每次跟新一次位置,当最远达到的地方是0,说明false,代码用vs会出现莫名其妙的问题,但是做法应该是对的
另外由于可能出现的请情况太多了,在边界的设置上出错的地方太多了
class Solution {
public:bool canJump(vector<int>& nums) {int left = 0;int len = nums.size();while(1){if(left>=len-1 || left+nums[left]>=len-1)return true;int max = 0;int temp = 0;for(int i = left ; i<=len-1 &&i<=left+nums[left] ;i++){if(i+nums[i]>max){max = i+nums[i];temp=i;}}if(max<len-1&& nums[max]==0)return false;left = temp;}return false;}
};
同样意思但更简洁的代码
解题思路:
1.如果某一个作为 起跳点 的格子可以跳跃的距离是 3,那么表示后面 3 个格子都可以作为 起跳点。
2.可以对每一个能作为 起跳点 的格子都尝试跳一次,把 能跳到最远的距离 不断更新。
3.如果可以一直跳到最后,就成功了。
作者:ikaruga
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game/solution/55-by-ikaruga/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
bool canJump(vector<int>& nums)
{int k = 0;for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if (i > k) return false;//k表示到i的时候,之前所有位置能到达的最大距离,每一个都走一下,但是不用考虑怎么走的,当走到一个位置不能再更新了,就会小于下一个ik = max(k, i + nums[i]);}return true;
}作者:ikaruga
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game/solution/55-by-ikaruga/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
56. 合并区间(贪心)
同样的格式,但是改成max了,而且维护的不是一个树,而是先放到二维向量中的末尾
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {vector<vector<int>> res;if(intervals.empty())return res;sort(intervals.begin(),intervals.end());res.push_back(intervals[0]);for(int i = 1 ;i< (int)intervals.size() ;i++){if(intervals[i][0]<= res.back()[1]){res.back()[1] = max(res.back()[1],intervals[i][1]);}else{res.push_back(intervals[i]);}}return res;}
};
使用长度为1的滑动窗口在滑动,但是没想到题目还是会出现后面区间包含前面的情况,这样就要重新设计了
看到答案说sort函数排序可以默认按照第一个第二个这样排序,可以排序之后在做,排序之后后面的值肯定是大于等于前面的,但是还要考虑后面包含前面的情况
考点:排序+数组
思路:先对二维数组表示的所有区间的左端点进行升序排序,然后从第二个区间(下标为1)开始遍历判断是否可以做合并操作:只要前一个区间的右端点大于等于当前区间的左端点,那说明这两个区间可以合并,合并后的区间左端点是前一个区间的左端点,只需要更新右端点为两个区间右端点的最大值即可。
否则,说明两个区间没有重叠,直接更新表示不重复区间的pos值
作者:xing2fan
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-intervals/solution/qu-jian-he-bing-de-pai-xu-fa-by-xing2fan/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {if (!intervals.size()) return {};//先把区间集合按照左端点从小到大进行排序sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), less<vector<int>>());int pos = 0;//pos的值是每个不重叠的区间//直接在原区间上做就可以//从第二个区间开始去比较for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); ++i) {//两个区间若能合并,则第一个区间的右端点一定大于等于第二个区间的左端点//比如[1,3] [2,6]if (intervals[pos][1] >= intervals[i][0]) {//第一个区间的尾部需要更新为:两个区间的最大值即[1,6]intervals[pos][1] = max(intervals[pos][1], intervals[i][1]);} else//没有重叠时 {//[1,6] [2,8]====>区间1就是目前的这个区间intervals[++pos] = intervals[i];}}intervals.resize(pos + 1);//把最后的不用的弹出return intervals;}};作者:xing2fan
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-intervals/solution/qu-jian-he-bing-de-pai-xu-fa-by-xing2fan/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {if (intervals.empty()) {return intervals;}sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end());vector<vector<int>> result{ intervals.front() };for (auto&& interval : intervals) {if (interval.front() > result.back().back()) {result.emplace_back(move(interval));} else {result.back().back() = max(interval.back(), result.back().back());}}return result;}
};作者:klaxxi
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-intervals/solution/c-pai-xu-tan-xin-by-klaxxi/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
57. 插入区间
和上题一样,先插入再做
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> insert(vector<vector<int>>& intervals, vector<int>& newInterval) {vector<vector<int>> res;if(newInterval.empty())return intervals;intervals.push_back(newInterval);sort(intervals.begin(),intervals.end());res.push_back(intervals[0]);for(int i =1; i< (int)intervals.size() ;i++){if(intervals[i][0]<= res.back()[1]){res.back()[1] = max(res.back()[1], intervals[i][1]);}else{res.push_back(intervals[i]);}}return res;}
};
58. 最后一个单词的长度
class Solution {
public:int lengthOfLastWord(string s) {int len = s.size();if(len==0)return 0;int count = 0;int i = len-1;while(i>=0 && s[i]==' '){i--;}while(i>=0 && s[i]!=' '){i--;count++;}return count;}
};
59. 螺旋矩阵 II
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> generateMatrix(int n) {vector<vector<int>> res(n,vector<int>(n,0));vector<vector<bool>> judge(n,vector<bool>(n,false));int i = 0,j=0,count=1;res[0][0]=count; judge[0][0]=true;string s = "right";while(count<n*n){if( s=="right" ){if(j<n-1 && judge[i][j+1]==false){res[i][++j]=++count;judge[i][j]=true;}else {s="down";}}else if(s=="down"){if(i<n-1 && judge[i+1][j]==false){res[++i][j]=++count;judge[i][j]=true;}else{s="left";}} else if(s=="left"){if(j>0 && judge[i][j-1]==false){res[i][--j]=++count;judge[i][j]=true;}else{s="up";}}else if(s=="up"){if(i>0 && judge[i-1][j]==false){res[--i][j]=++count;judge[i][j]=true;}else{s="right";}}}return res;}
};
60. 第k个排列
class Solution {
public:string getPermutation(int n, int k) {string s = "123456789";string s1 = s.substr(0,n);while(k-1 && next_permutation(s1.begin(),s1.end()))k--;return s1;}
};
class Solution {
public:string next(string s,int n){for(int i =n-1;i>=0;i--){if(s[i]<s[i+1]){int m = INT_MAX,point = 0;for(int j = i+1;j<=n;j++){if(s[j]>s[i] && s[j]-s[i]<m){m = s[j]-s[i];point = j;}}swap(s[i],s[point]);reverse(s.begin()+i+1,s.end());return s;}}return {};}string getPermutation(int n, int k) {string s;for(int i =1;i<=n;i++)s += to_string(i);while(k>1){k--;s = next(s,n);}return s;}
};
61. 旋转链表
先变成一个环,再进行截断
class Solution {
public:ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {if(!head || !head->next)return head;int count = 1;auto temp = head;while(temp->next){temp = temp->next;count++;}auto tail = head;k = k%count;while((count-k)>1){k++;tail=tail->next;}temp->next = head;auto res = tail->next;tail->next = NULL;return res;}
};
62. 不同路径(dp)
class Solution {
public:int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {vector<vector<int>> board(m,vector<int>(n,1));for(int i =1 ;i<m;i++){for(int j =1;j<n;j++){board[i][j]=board[i-1][j]+board[i][j-1];}}return board[m-1][n-1];}
};
超时的dfs,而且剪枝的地方不多
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> board;int res = 0;vector<pair<int,int>> path;void dfs(int m,int n){int i = path.back().first;int j = path.back().second;if(i>= m || j>= n)return;if(i==m-1 && j== n-1){res++;return;}i++;auto temp1 = make_pair(i,j);path.push_back(temp1);dfs(m,n);path.pop_back();i--;j++;auto temp2 = make_pair(i,j);path.push_back(temp2);dfs(m,n);path.pop_back();j--; }int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {board = vector<vector<int>>(m,vector<int>(n,0));path.push_back(make_pair(0,0));dfs(m,n);return res;}
};
63. 不同路径 II
class Solution {
public:int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector<vector<int>>& obstacleGrid) {if(obstacleGrid.empty())return 0;int len1 = obstacleGrid.size();int len2 = obstacleGrid[0].size();vector<vector<int>> dp(len1,vector<int>(len2,1));bool k = true;for(int i = 0; i<len1 ;i++){if(k==false || obstacleGrid[i][0]==1){dp[i][0]=0;k=false;}}k = true;for(int i = 0;i<len2;i++){if(k==false || obstacleGrid[0][i]==1){dp[0][i]=0;k=false;}}for(int i = 1 ;i<len1 ;i++){for(int j =1 ;j<len2 ;j++){if(obstacleGrid[i][j]==1)dp[i][j]=0;else{dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];}}}return dp[len1-1][len2-1];}
};
64. 最小路径和(dp)
很典型的动态规划题目,和上题一样
class Solution {
public:int minPathSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {if(grid.empty())return 0;int m = grid.size();int n = grid[0].size();vector<vector<int>> board(m,vector<int>(n,0));board[0][0]=grid[0][0];for(int i = 1 ; i< n ;i++){board[0][i] = grid[0][i]+board[0][i-1];}for(int i = 1 ; i< m ; i++){board[i][0] = grid[i][0]+board[i-1][0];}for(int i = 1 ; i < m ;i++){for(int j = 1 ; j< n; j++){board[i][j] = grid[i][j] + min( board[i-1][j],board[i][j-1]);}}return board[m-1][n-1];}
};
66. 加一
class Solution {
public:vector<int> plusOne(vector<int>& digits) {int len = digits.size();int b = 0;for(int i = len-1 ; i>=0;i--){int temp = b + digits[i];if(i==len-1)temp++;if(temp>=10){b = 1;}else{b = 0;}digits[i]=temp%10;} if(b)digits.insert(digits.begin(),1);return digits;}
};
class Solution {
public:string addBinary(string a, string b) {int lena = a.size();int lenb = b.size();int bb = 0;string res;int i =lena-1,j=lenb-1 ;while( i>=0&&j>=0){int temp = (a[i--]-'0')+(b[j--]-'0');res = to_string((temp+bb)%2) + res;if(temp+bb==2 || temp+bb==3){bb=1;}else bb=0;}while(i>=0){int temp = a[i--]-'0';res = to_string((temp+bb)%2) + res;if(temp+bb==2)bb=1;else bb=0;}while(j>=0){int temp = b[j--]-'0';res = to_string((temp+bb)%2) + res;if(temp+bb==2)bb=1;else bb=0;} if(bb)res = "1"+res;return res;}
};
69. x 的平方根(二分法)
e
class Solution {
public:int mySqrt(int x) {if(x==1)return 1;int left = 1,right = x/2+1;while(left<right){int mid = left + (right-left)/2;if((double)x/mid == mid)return mid;else if((double)x/mid > mid)left = mid + 1;else right = mid;}return left-1;}
};
70. 爬楼梯(dp)
动态规划
class Solution {
public:int climbStairs(int n) {if(n==0)return 0;if(n==1)return 1;if(n==2) return 2;vector<int> dp(n+1,0);dp[0]=0;dp[1]=1;dp[2]=2;for(int i = 3 ; i<n+1; i++){dp[i] = dp[i-1]+ dp[i-2];}return dp[n];}
};
class Solution {
public:string simplifyPath(string path) {vector<string> vt;int point = 0;int i = 0,j=0;int len = path.size();while (i < len){while (i < len && path[i] == '/')i++;j = i;while (i < len && path[i] != '/')i++;if (i > j) {string temp = path.substr(j, i - j);if (temp == ".."){if (!vt.empty()){vt.pop_back();point--;}}else if (temp == "."){if (point < vt.size() - 1){point++;}}else{vt.push_back(temp);point++;}}}string res = "/";for(auto i:vt){res = res + i + '/';}if(res!="/")res.pop_back();return res;}
};
72. 编辑距离
class Solution {
public:int minDistance(string word1, string word2) {int len1 = word1.size();int len2 = word2.size();vector<vector<int>> dp(len1+1, vector<int>(len2+1,0));for(int i = 0 ;i<=len1; i++){dp[i][0] = i;}for(int j = 0 ; j<=len2 ;j++){dp[0][j] = j;}for(int i=1 ;i<=len1 ;i++){for(int j=1; j<=len2 ;j++){if(word1[i-1]==word2[j-1]){dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] ;}else{dp[i][j] = min(dp[i-1][j-1],min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]))+1;}}}return dp[len1][len2];}
};
73. 矩阵置零
class Solution {
public:void setZeroes(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {if(matrix.size()==0)return;vector<int> row;vector<int> col;int len1 = matrix.size();int len2 = matrix[0].size();for(int i= 0 ;i<len1 ; i++){for(int j = 0 ; j <len2 ;j++){if(matrix[i][j]==0) {row.push_back(i);col.push_back(j);}}}for(auto i :row){for(int j = 0 ; j<len2 ;j++){matrix[i][j]=0;}}for(auto j:col){for(int i = 0 ; i<len1 ; i++){matrix[i][j] = 0;}}return;}
};
75. 颜色分类(三数快排)
只有三个数的时候排序可以如此简单
class Solution {
public:void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {int left = 0 , right = nums.size()-1;for(int i = left ;i<=right ;i++){if(nums[i]==0)swap(nums[left++],nums[i]);if(nums[i]==2)swap(nums[right--],nums[i--]);}return;}
};
快速排序
巩固一下快速排序,要特注意的是先循环j再循环i
class Solution {
public:void quicksort(int left,int right, vector<int>& nums){if(left>=right)return;int i = left;int j = right;while(i<j){while(i<j && nums[j]>=nums[left])j--;while(i<j && nums[i]<=nums[left])i++;if(i<j){swap(nums[i],nums[j]);}}swap(nums[left],nums[i]);quicksort(left,i-1,nums);quicksort(i+1,right,nums);}void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {int len = nums.size();if(len==0 || len==1)return;quicksort(0,len-1,nums);return;}
};
74. 搜索二维矩阵
采用了两个二分法模板做的,注意衔接的时候,要考虑小于第一个个值的情况
class Solution {
public:bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {if(matrix.empty())return false;if(matrix[0].empty())return false;int len = matrix.size();int left = 0,right = len;while(left<right){int mid = (left+right)/2;if(matrix[mid][0]==target)return true;else if(matrix[mid][0]<target){left = mid+1;}else{right = mid;}}int temp = left-1;if(temp<0)return false;len = matrix[0].size();left = 0;right=len;while(left<right){int mid = (left+right)/2;if(matrix[temp][mid]==target) return true;else if(matrix[temp][mid]<target){left=mid+1;}else{right=mid;}}return false;}
};
76. 最小覆盖子串
维护哈希表并滑动窗口,超时了
哈希表遍历
class Solution {
public:bool judge(unordered_map<char, int> mp, unordered_map<char, int> mt){for (auto m:mt){if (mp[m.first] < mt[m.first])return false;}return true;}string minWindow(string s, string t) {unordered_map<char,int> mt;for(auto t1:t)mt[t1]++;int lens = s.size();int lent = t.size();if(lens<lent)return "";int start = 0, len = INT_MAX;int i =0 ,j =0;unordered_map<char,int> mp;//Awhile(i<lens){if (mt.find(s[i]) != mt.end()){ mp[s[i]]++; }while (judge(mp,mt)){if (mt.find(s[j]) == mt.end())j++;else{if (i - j + 1 < len) { len = i - j + 1; start = j; }mp[s[j]]--;if (mp[s[j]] == 0)mp.erase(s[j]);j++;}}i++;}return len==INT_MAX?"":s.substr(start,len);}
};
77. 组合
由于这个pos代表的是初始位置,当进行过一次遍历后,这个值也要加1才行
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> res;vector<int> path;void dfs(int p,int n,int k){if(path.size()==k){res.push_back(path);return;}for(int i = p ;i<=n;i++){path.push_back(i);dfs(i+1,n,k);path.pop_back();}}vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {dfs(1,n,k);return res;}
};
其他解答,道理是一样的
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {vector<vector<int>> list;vector<int> result;dfs(list,result,n,k,0,-1); return list;}void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& list, vector<int>& result, int n, int k, int pos,int pre){if(pos == k){list.push_back(result);return;}if((pos + (n-pre)) <= k)return;//剪枝,添加之后用时节省了2/3//在当前对不合理的取值进行判断,结束下一层的递归操作。//如果当前剩余可操作数字的个数即(n-pre)< k-pos+1(即组合中有待赋值的位置个数),(+1是因为当前pos还没有进行操作),则可以判断该条路径不可能得到正确的解,不再向下探寻。for(int i=pre+1; i<n ; i++){result.push_back(i+1);pre = i;dfs(list,result,n,k,pos+1,pre);result.pop_back();//回溯}return;}
};作者:rouzi
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combinations/solution/dfsjian-zhi-by-rouzi/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
78. 子集
注意return的位置
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> res;vector<int> path;void dfs(vector<int>& nums,int p){res.push_back(path);if(p==nums.size())return;for(int i= p;i<nums.size();i++){path.push_back(nums[i]);dfs(nums,i+1);path.pop_back();}}vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {dfs(nums,0);return res;}
};
79. 单词搜索(dfs)
dfs中的顺序
这道题要么注释的在前,要么就想下面这样换个条件放后面。如果按照正常理解的话应该是注释这句,但是注意它的位置,因为判断false这一句会直接导致无法到达这句。上面那道题也是,要注意顺序,如果先return了就无法放到res中了。所以dfs的return既不一定在最前,而且true和false之间也是有讲究的,一般来说true应该放在false的前面
class Solution {
public:bool dfs(int i ,int j, int m, int n, vector<vector<char>>& board, string word,int p ){//if(p==word.size())return true;if(i<0 || i==m || j<0 || j==n || board[i][j]!=word[p])return false;if(p==word.size()-1 && board[i][j]==word[p])return true;auto temp = board[i][j];board[i][j]='0';bool b = dfs(i+1,j,m,n,board,word,p+1) || dfs(i,j+1,m,n,board,word,p+1) || dfs(i-1,j,m,n,board,word,p+1) || dfs(i,j-1,m,n,board,word,p+1);board[i][j]=temp;return b;}bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {int m = board.size(),n = board[0].size();for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){for(int j = 0;j<n;j++){if(dfs(i,j,m,n,board,word,0))return true;}}return false;}
};
80. 删除排序数组中的重复项 II
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {int i = 0 , j = 0 , len = nums.size();while(i<len-1){auto temp = nums[i];if(nums[i]==temp && nums[i+1]==temp){while(i<len && nums[i]==temp)i++;nums[j++]=temp;nums[j++]=temp;}else {nums[j++]=nums[i++];}}if(i==len-1)nums[j++]=nums[i];return j;}
class Solution {
public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {int len = nums.size();int i = 0, j = 0;while(i<len){int temp = i;while(i<len && nums[i]==nums[temp])i++;if(i-temp==1){nums[j++]=nums[temp];}else if(i-temp>=2){nums[j++]=nums[temp];nums[j++]=nums[temp];}}return j;}
};
81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II
先去重
class Solution {
public:bool search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {if(nums.empty())return false;int j = 0;for(int i =1 ;i<(int)nums.size() ;i++){if(nums[i]!=nums[j])nums[++j]=nums[i];}vector<int> num;num.assign(nums.begin(),nums.begin()+j+1);if((int)num.size()>1 && num[j]==num[0]){num.pop_back();}int right = num.size();int left = 0;while(left<right){int mid = left + (right-left)/2;if(num[mid]==target){return true;}else if (num[mid]>target){if(target>=num[0] || num[mid]<num[0]){right = mid;}else{left=mid+1;}}else{if(num[mid]>=num[0] ||target<num[0]){left=mid+1;}else{right=mid;}}}return false; }
};
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
要注意将末尾指针指空,不然会指向其他的地方
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {if(!head )return head;auto head1 = new ListNode(0);head1->next = head;auto slow = head1;auto fast = head;while(fast){if(fast->next && fast->next->val==fast->val){auto temp = fast->val;while(fast && fast->val==temp ){fast = fast->next;}} else {slow->next =fast;slow = fast;fast = fast->next;}}slow->next =NULL;return head1->next;}
};
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {if(!head || !head->next)return head;auto head1 = new ListNode(INT_MAX);head1->next = head;auto slow = head1;auto fast = head;while(fast && fast->next){if(fast->val==fast->next->val){while(fast->next && fast->val == fast->next->val){fast = fast->next;}fast = fast->next;}else{slow->next = fast;slow = fast;fast = fast->next;}}slow->next = fast;return head1->next;}
};
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {if(!head || !head->next)return head;auto slow = head;auto fast = head->next;while(fast){if(fast->val==slow->val){fast = fast->next;}else{slow->next = fast;slow = fast;}}slow->next = NULL;return head;}
};
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形(单调栈)
//维护一个单调非递减的栈。
//核心思想还是选取中心元素尽量向两侧延申。
//当heights[i]小于栈顶元素时,以栈顶元素为高的矩形已不能继续向右延申(达到右边界)。
//矩形左边界就是栈内元素的前一个元素。
class Solution {
public:int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> heights) {//单调栈存放idstack<int> st;st.push(0);heights.insert(heights.begin(),0);heights.push_back(0);int res = 0;for(int i =1;i<heights.size();i++){while (!st.empty() &&heights[st.top()] > heights[i]){auto temp = st.top(); st.pop();res = max(res,heights[temp]*(i-st.top()-1));} st.push(i);}return res;}
};
85. 最大矩形(单调栈)
class Solution {
public:int func(vector<int> nums){int res = 0;nums.insert(nums.begin(),0);nums.push_back(0);stack<int> st;st.push(0);for(int i = 1; i<nums.size();i++){while(!st.empty() && nums[st.top()]>nums[i]){auto temp = st.top(); st.pop();res = max(res,(nums[temp])*(i-st.top()-1));}st.push(i);}return res;}int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {if(matrix.empty())return 0;int m = matrix.size();int n = matrix[0].size();vector<int> dp(n,0);int res = 0;for(int i = 0;i<m;i++){for(int j = 0;j<n;j++){dp[j] = matrix[i][j]=='1'?dp[j]+1:0;}res = max(res, func(dp));}return res;}
};
86. 分隔链表
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {auto head1 = new ListNode(0);auto temp1 = head1;auto head2 = new ListNode(0);auto temp2 = head2;int count=0;while(head){if(head->val<x){temp1->next = head;temp1 = head;}else{temp2->next = head;temp2=head;}head=head->next;}temp1->next = head2->next;temp2->next = NULL;return head1->next;}
};
88. 合并两个有序数组
lower_bound必须是在有序数组中使用
class Solution {
public:void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {for(int i = 0;i<n;i++){auto temp = lower_bound(nums1.begin(),nums1.begin()+m+i,nums2[i]);nums1.insert(temp,nums2[i]);}while(n--)nums1.pop_back();return ;}
};
class Solution {
public:void merge(vector<int>& arr1, int m, vector<int>& arr2, int n) {//int len1 = arr1.size();//int len2 = arr2.size();if(m==0){arr1.assign(arr2.begin(),arr2.end());return;}if(n==0) return;int i = m - 1;int j = n - 1;int k = m + n - 1;while (i>= 0 && j>= 0){while (i>= 0 && j>=0 && arr1[i] >= arr2[j]){arr1[k--] = arr1[i--];}while (i >= 0 && j >= 0 && arr1[i] <= arr2[j]){arr1[k--] = arr2[j--];}}while (i>=0 ){arr1[k--] = arr1[i--];}while (j>=0){arr1[k--] = arr2[j--];}return ; }
};
89. 格雷编码
n = 0, [0]
n = 1, [0,1] //新的元素1,为0+2^0
n = 2, [0,1,3,2] // 新的元素[3,2]为[0,1]->[1,0]后分别加上2^1
n = 3, [0,1,3,2,6,7,5,4] // 新的元素[6,7,5,4]为[0,1,3,2]->[2,3,1,0]后分别加上2^2->[6,7,5,4]
作者:chengm15
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/gray-code/solution/zhi-xing-yong-shi-nei-cun-xiao-hao-ji-bai-liao-1-5/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public:vector<int> grayCode(int n) {if(n==0)return {0};vector<int> res = {0,1};while(n-1){n--;int p = pow(2,n);auto res1 = res;reverse(res1.begin(),res1.end());for(int i =0;i<res1.size();i++)res.push_back(res1[i]+p);}return res;}
};
90. 子集 II
dfs之前排序
做这种有重复元素的dfs之前要对数组进行排序,这样去重时可以保证内部同时去重了
class Solution {
public:set<vector<int>> st;vector<int> path;void dfs(vector<int>& nums, int p,int len){st.insert(path);if(p==len)return;for(int i = p;i<len;i++){path.push_back(nums[i]);dfs(nums,i+1,len);path.pop_back();}}vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int>& nums) {int len = nums.size();sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());dfs(nums,0,len);vector<vector<int>> res(st.begin(),st.end());return res;}
};
91. 解码方法
动态规划,暂时不考虑0的情况
符串拼接问题
本来是想使s[i-1]+s[i]拼接成一个string字符串,但是发现直接相加拼接是不可以的,甚至写成注释那样在一行都是不可以的,因为程序会先执行等号右边的内容,只有写成两个小式子才可以。对于这种拼接(连续的)最好直接使用substr,实在要拼接也要先定义string然后分布写才行
int numDecodings(string s) {int len= s.size();vector<int> dp(len,1);for(int i = 1;i<len;i++){string s1;//s1 += s[i-1]+s[i];s1 += s[i - 1]; s1 += s[i];int temp = stoi(s1);if( temp<=26 )dp[i]=dp[i-1]+1;else dp[i]=dp[i-1];}return dp[len-1];}
#include 字符串转数字
atoi(str.c_str());
stoi(str);
字符转数字
int(char-'0')
92. 反转链表 II
涉及到的参量实在太多了,必须要画图进行分析才行
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {auto head1 = new ListNode(0);head1->next = head;auto temp = head1;while(m-1){m--; temp = temp -> next;}auto start = temp;auto pre1 = start->next,pre = pre1;auto cur = pre->next;temp = head;while(n-1){n--;temp = temp->next;}auto end = temp;auto nexts = end->next;while(cur != nexts){auto temp = cur->next;cur->next = pre;pre = cur;cur = temp;}start->next = end;pre1->next = nexts;return head1->next;}
};
93. 复原IP地址
dfs里的循环方法设置的比较巧妙,设置一个p然后在这三位进行寻找,使用这种回溯的始终是比较快的,但是要注意的是越界问题,所以设置i的循环时要加min这是一种比较重要的防止越界的方法。另外注意path和p都有可能先到达极限,所以对这两个变量都要设置终止递归条件
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<string>> res;vector<string> path;void dfs(string s, int p){if(path.size()==4 ){if(p==s.size()){res.push_back(path);}return;}if (p >= s.size())return;for(int i=p;i<=min((int)s.size()-1,p+2);i++){auto temp = s.substr(p,i-p+1);if(temp[0]=='0' && temp.size()>1)break;if(stoi(temp)<=255){path.push_back(temp);dfs(s,i+1);path.pop_back();}}}vector<string> restoreIpAddresses(string s) {dfs(s,0);vector<string> ss;for(auto r:res){string s1;for(auto rr:r){s1 += rr + '.';}s1.pop_back();ss.push_back(s1);}return ss;}
};
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
递归
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
vector<int> res;
public:void dfs(TreeNode* root){if(!root) return;dfs(root->left);res.push_back(root->val);dfs(root->right);}vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {if(!root) return res;dfs(root);return res;}
};
非递归
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> st;vector<int> res;auto cur = root;while(cur || !st.empty()){while(cur){st.push(cur);cur = cur->left;}auto temp = st.top(); st.pop();res.push_back(temp->val);if(temp->right)cur = temp->right;}return res;}
};
95. 不同的二叉搜索树 II(不会)
看不懂为什么这么做
解法一完全没有用到查找二叉树的性质,暴力尝试了所有可能从而造成了重复。我们可以利用一下查找二叉树的性质。左子树的所有值小于根节点,右子树的所有值大于根节点。
所以如果求 1…n 的所有可能。
我们只需要把 1 作为根节点,[ ] 空作为左子树,[ 2 … n ] 的所有可能作为右子树。
2 作为根节点,[ 1 ] 作为左子树,[ 3…n ] 的所有可能作为右子树。
3 作为根节点,[ 1 2 ] 的所有可能作为左子树,[ 4 … n ] 的所有可能作为右子树,然后左子树和右子树两两组合。
4 作为根节点,[ 1 2 3 ] 的所有可能作为左子树,[ 5 … n ] 的所有可能作为右子树,然后左子树和右子树两两组合。
…
n 作为根节点,[ 1… n ] 的所有可能作为左子树,[ ] 作为右子树。
至于,[ 2 … n ] 的所有可能以及 [ 4 … n ] 以及其他情况的所有可能,可以利用上边的方法,把每个数字作为根节点,然后把所有可能的左子树和右子树组合起来即可。
如果只有一个数字,那么所有可能就是一种情况,把该数字作为一棵树。而如果是 [ ],那就返回 null。
作者:windliang
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees-ii/solution/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-by-2-7/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
public List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n) {List<TreeNode> ans = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();if (n == 0) {return ans;}return getAns(1, n);}private List<TreeNode> getAns(int start, int end) { List<TreeNode> ans = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();//此时没有数字,将 null 加入结果中if (start > end) {ans.add(null);return ans;}//只有一个数字,当前数字作为一棵树加入结果中if (start == end) {TreeNode tree = new TreeNode(start);ans.add(tree);return ans;}//尝试每个数字作为根节点for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {//得到所有可能的左子树List<TreeNode> leftTrees = getAns(start, i - 1);//得到所有可能的右子树List<TreeNode> rightTrees = getAns(i + 1, end);//左子树右子树两两组合for (TreeNode leftTree : leftTrees) {for (TreeNode rightTree : rightTrees) {TreeNode root = new TreeNode(i);root.left = leftTree;root.right = rightTree;//加入到最终结果中ans.add(root);}}}return ans;
}作者:windliang
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees-ii/solution/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-by-2-7/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public:vector<TreeNode*> generateTrees(int n) {if(n == 0) return {};return helper(1, n);}vector<TreeNode*> helper(int start, int end) {if(start > end) return {nullptr};vector<TreeNode*> res;for(int i=start; i<=end; i++) {auto left = helper(start, i-1), right = helper(i+1, end);for(auto a:left) {for(auto b:right) {TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(i);node->left = a;node->right = b;res.push_back(node);}}}return res;}
};作者:lioney
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees-ii/solution/lioney-cjian-dan-di-gui-by-lioney-16/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
96. 不同的二叉搜索树
都不需要使用节点就可以求,和上题的思路一样
class Solution {
public:int dfs(int p,int q){if(p>q)return 1;int res = 0;for(int i =p; i<=q ;i++){res += dfs(p,i-1)*dfs(i+1,q);}return res;}int numTrees(int n) {if(n==0)return 0;return dfs(1,n);}
};
97. 交错字符串
能正确判断,但是超时了,因为递归的效率比较低;
对于字符串的题,使用递归都比较耗时
class Solution {
public:bool dfs(string s1, string s2, string s3, int a1, int a2 ,int a3){if( a1==s1.size() && a2==s2.size() && a3==s3.size() )return true;if(s3[a3]!=s1[a1] && s3[a3]!=s2[a2] )return false;else if(s3[a3]==s1[a1] && s3[a3]!=s2[a2] )return dfs(s1,s2,s3,a1+1,a2,a3+1);else if(s3[a3]!=s1[a1] && s3[a3]==s2[a2] )return dfs(s1,s2,s3,a1,a2+1,a3+1);else if(s3[a3]==s1[a1] && s3[a3]==s2[a2] )return dfs(s1,s2,s3,a1+1,a2,a3+1)||dfs(s1,s2,s3,a1,a2+1,a3+1);return false;}bool isInterleave(string s1, string s2, string s3) {if(s3.size()!=s1.size()+s2.size())return false;return dfs(s1,s2,s3,0,0,0);}
};
public class Solution {public boolean isInterleave(String s1, String s2, String s3) {if (s3.length() != s1.length() + s2.length()) {return false;}boolean dp[][] = new boolean[s1.length() + 1][s2.length() + 1];for (int i = 0; i <= s1.length(); i++) {for (int j = 0; j <= s2.length(); j++) {if (i == 0 && j == 0) {dp[i][j] = true;} else if (i == 0) {dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] && s2.charAt(j - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1);} else if (j == 0) {dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] && s1.charAt(i - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1);} else {dp[i][j] = (dp[i - 1][j] && s1.charAt(i - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1)) || (dp[i][j - 1] && s2.charAt(j - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1));}}}return dp[s1.length()][s2.length()];}
}作者:LeetCode
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/interleaving-string/solution/jiao-cuo-zi-fu-chuan-by-leetcode/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
class Solution {
public:bool isInterleave(string s1, string s2, string s3) {int N1 = s1.size();int N2 = s2.size();int N3 = s3.size();if (N1 + N2 != N3) return false;vector<vector<bool> > dp(N1 + 1, vector<bool>(N2 + 1, false));dp[0][0] = true;for (int i = 0; i <= N1; ++i) {for (int j = 0; j <= N2; ++j) {if (i > 0 && s1[i - 1] == s3[i + j - 1]) {dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] || dp[i - 1][j];}if (j > 0 && s2[j - 1] == s3[i + j - 1]) {dp[i][j] = dp[i][j] || dp[i][j - 1];}}}return dp[N1][N2];}
};作者:da-li-wang
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/interleaving-string/solution/c-dong-tai-gui-hua-by-da-li-wang-32/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
98. 验证二叉搜索树(dfs)
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:vector<int> res;void dfs(TreeNode* root){if(!root)return;dfs(root->left);res.push_back(root->val);dfs(root->right);}bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {dfs(root);for(int i = 1;i<res.size();i++){if(res[i]<=res[i-1])return false;}return true;}
};
之前的思路是判断两百边的数组,但是获得数组就需要进行遍历,十分麻烦,下面的解法目的不是求节点是否在左右节点数组的中间,而是每个节点和一个区间进行比较,这个区间一开始是无限大,每经过一个节点就将区间范围缩小,往左节点走时父节点作为有边界,往右边界走时父节点作为左边界,这样可以不断的将父节点的区间范围传递下去,十分巧妙
思路:引入上下边界
对于树的每个节点 val ,设其上下边界 low , high。(用 long 防止 INT_MAX 溢出 )
判断根结点时,须满足 low < val < high ,否则返回 false
判断左节点时,仅 上界 变化 ( 新上界为 high 与 val 较小值。又因 val 必小于 high,故新上界为 val )
判断右节点时,仅 下界 变化 ( 同理,新下界为 val )
bool fun(struct TreeNode* root, long low, long high) {if (root == NULL) return true;long num = root->val;if (num <= low || num >= high) return false;return fun(root->left, low, num) && fun(root->right, num, high);
}
bool isValidBST(struct TreeNode* root){return fun(root, LONG_MIN, LONG_MAX);
}作者:penn-10
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/solution/cyu-yan-yan-zheng-er-cha-sou-suo-shu-by-penn-10/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
99. 恢复二叉搜索树
中序遍历的利用
这道题用到了一个特别重要的知识:中序遍历一定是顺序的,如果发生了节点交换,通过中序遍历就可以找出是哪些节点被该改变了
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:vector<int> res;int point1= 0,point2 = 0;void dfs2(TreeNode* root){if(!root)return;if(root->val==point1){root->val=point2;}else if(root->val==point2){root->val=point1;}dfs2(root->left);dfs2(root->right);}void dfs1(TreeNode* root){if(!root)return;dfs1(root->left);res.push_back(root->val);dfs1(root->right);}void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {dfs1(root);for(int i = 0;i<res.size()-1;i++){if(res[i]>res[i+1]){point1 = res[i];break;}}for(int i = res.size()-1;i>0;i--){if(res[i]<res[i-1]){point2 = res[i];break;}}dfs2(root);return;}
};
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:vector<int> res;void dfs1(TreeNode* root){if(!root)return;dfs1(root->left);res.push_back(root->val);dfs1(root->right);}void dfs2(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& res1){if(!root)return;dfs2(root->left,res1);if(root->val==res1.front())res1.erase(res1.begin());else {root->val=res1.front();res1.erase(res1.begin());}dfs2(root->right,res1);}void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {dfs1(root);auto res1 = res;sort(res1.begin(),res1.end());dfs2(root,res1);return;}
};
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!