Spring框架—IOC容器—属性赋值的几种方式
目录
- 一、常用的赋值方式
- 1.1 set注入
- 1.1.1 ApplicationContext.xml配置文件
- 1.1.2 测试类:
- 1.1.2 控制台输出:
- 1.2 构造注入
- 1.2.1 修改Student类
- 1.2.2 配置ApplicationContext.xml文件
- 1.2.2 测试类
- 1.2.3 控制台输出
- 1.2.3 使用重载构造方法赋值
- 1.2.3.1 解决办法
- 二、 其他赋值方式
- 2.1 P名称空间赋值
- 2.2 导入名称空间
- 2.2 测试类
- 2.3 控制台输出
一、常用的赋值方式
在Spring中,有两种常用的赋值方式:set注入和构造注入。
1.1 set注入
通过对应的setXxxx()方法为属性赋值。
1.1.1 ApplicationContext.xml配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><bean id="s1" class="com.wyl.spring.Student" ><property name="sid" value="10001">property><property name="sname" value="张三">property>bean>
beans>
标签:通过set方式为属性赋值。
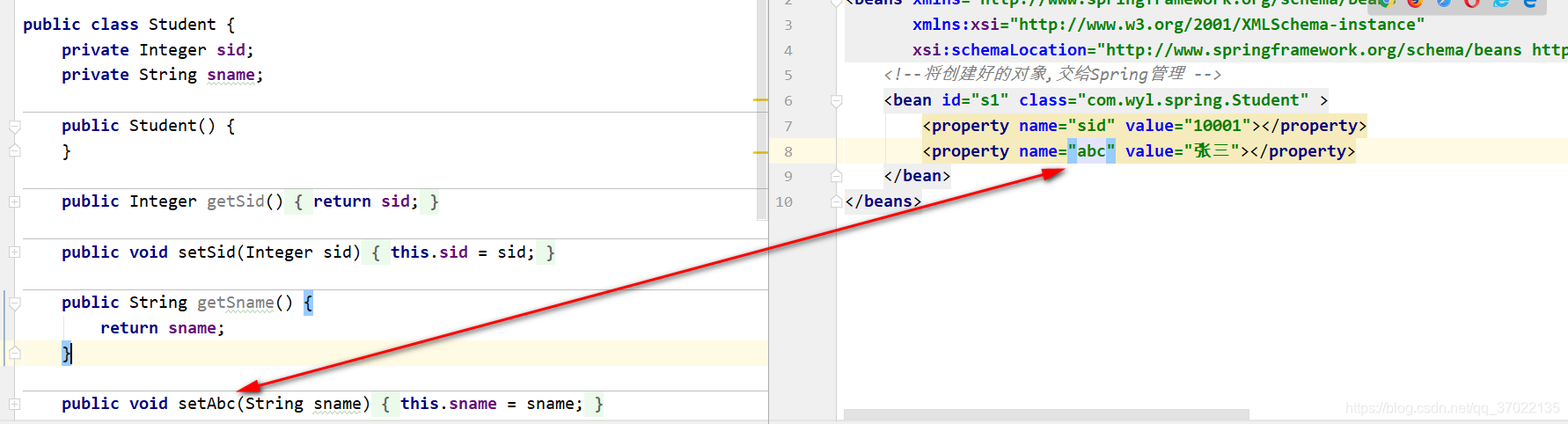
name属性:对应的并不是属性名字,对应的是setXxxx()方法。
sid对应的是一个叫做setSid()的方法。
sname对应的是一个叫做setSname()的方法。
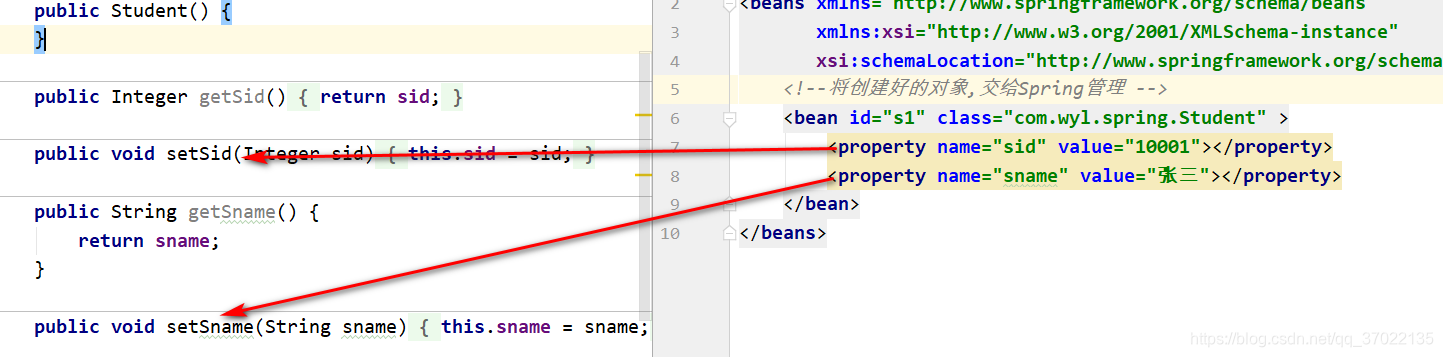
如果将对应类中的属性名不变,只改变set方法名,则在Spring配置文件中也需要指定name属性名为set方法后的首字母小写的全部字母,否则Spring将无法为属性赋值。
value属性:为属性赋的值。
1.1.2 测试类:
package com.wyl.spring;import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;public class SpringBeanTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1.创建IOC容器,并指定配置文件位置ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");// 2.从IOC容器中获取管理的对象Student bean = ac.getBean("s1",Student.class);// 3.输出验证System.out.println(bean);}
}1.1.2 控制台输出:
Student{sid=10001, sname='张三'}
1.2 构造注入
通过对应的构造方法为属性赋值。
1.2.1 修改Student类
package com.wyl.spring;public class Student {private Integer sid;private String sname;// 新增一个属性private Double score;public Student() {}public Integer getSid() {return sid;}public void setSid(Integer sid) {this.sid = sid;}public String getSname() {return sname;}public void setSname(String sname) {this.sname = sname;}public Double getScore() {return score;}public void setScore(Double score) {this.score = score;}// 新增两个参数的有参构造public Student(Integer sid, String sname) {this.sid = sid;this.sname = sname;}// 新增三个参数的有参构造public Student(Integer sid, String sname, Double score) {this.sid = sid;this.sname = sname;this.score = score;}// 重载三个参数的有参构造public Student(Double score, String sname, Integer sid){this.sid = sid;this.sname = sname;this.score = score;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"sid=" + sid +", sname='" + sname + '\'' +'}';}
}1.2.2 配置ApplicationContext.xml文件
<bean id="s2" class="com.wyl.spring.Student" ><constructor-arg value="10002">constructor-arg><constructor-arg value="李四">constructor-arg>bean>
标签: 通过构造方法为属性赋值。
value属性:需要赋的值。
Spring会自动的匹配到两个参数的构造方法,然后为其属性赋值。
1.2.2 测试类
package com.wyl.spring;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class SpringBeanTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1.创建IOC容器,并指定配置文件位置ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");// 2.从IOC容器中获取管理的s2对象Student bean = ac.getBean("s2",Student.class);// 3.输出验证System.out.println(bean);}
}
1.2.3 控制台输出
Student{sid=10002, sname='李四'}
1.2.3 使用重载构造方法赋值
在使用构造方法赋值时,Spring会自动的匹配到对应参数个数的构造方法,然后为其属性赋值,但是如果出现了重载方法,Spring会匹配其中一个构造方法来赋值,有些时候就会造成,赋值并不是想要的结果。
<bean id="s2" class="com.wyl.spring.Student" ><constructor-arg value="10002">constructor-arg><constructor-arg value="96">constructor-arg><constructor-arg value="李四">constructor-arg>bean>
使用之前的测试类运行,结果:
Student{sid=96, sname='李四', score=10002.0}
Spring匹配的是这个构造方法
// 重载三个参数的有参构造public Student(Double score, Integer sid,String sname){this.sid = sid;this.sname = sname;this.score = score;}
结果出现了偏差,并不是想要的样子。
1.2.3.1 解决办法
- 使用索引,指定为某个位置的属性赋值
<bean id="s2" class="com.wyl.spring.Student" ><constructor-arg index="1" value="10002">constructor-arg><constructor-arg index="0" value="96">constructor-arg><constructor-arg index="2" value="李四">constructor-arg>bean>
使用之前的测试类运行,结果:
Student{sid=10002, sname='李四', score=96.0}
- 使用参数类型区分构造方法参数
<bean id="s2" class="com.wyl.spring.Student" ><constructor-arg type="java.lang.Integer" value="10002">constructor-arg><constructor-arg type="java.lang.Double" value="96">constructor-arg><constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="李四">constructor-arg>bean>
使用之前的测试类运行,结果:
Student{sid=10002, sname='李四', score=96.0}
- 使用类型、索引组合方式
这种方式更加精确的匹配构造方法。
<bean id="s2" class="com.wyl.spring.Student" ><constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.Integer" value="10002">constructor-arg><constructor-arg index="1" type="java.lang.Double" value="96">constructor-arg><constructor-arg index="2" type="java.lang.String" value="李四">constructor-arg>bean>
使用之前的测试类运行,结果:
Student{sid=10002, sname='李四', score=96.0}
Spring匹配的是这个构造方法
// 新增三个参数的有参构造public Student(Integer sid, Double score,String sname) {this.sid = sid;this.sname = sname;this.score = score;}
二、 其他赋值方式
2.1 P名称空间赋值
P名称空间是为了简化Spring XML配置文件的复杂程度。它与set注入方式基本相同,也是简化了标签的配置方式。
2.2 导入名称空间
需要在Spring的配置文件导入P标签的命名空间
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"><bean id="s3" class="com.wyl.spring.Student"p:sid="1003" p:sname="123" p:score="96">bean>
beans>
P是前缀
sid是后缀,对应的就是set注入的name属性。
2.2 测试类
package com.wyl.spring;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class SpringBeanTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1.创建IOC容器,并指定配置文件位置ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");// 2.从IOC容器中获取管理的对象Student bean = ac.getBean("s3",Student.class);// 3.输出验证System.out.println(bean);}
}
2.3 控制台输出
Student{sid=1003, sname='123', score=96.0}本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!