顺 序 表
#顺序表
## 1概念及结构
1.顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组
上完成数据的增删查改。
### 顺序表一般可以分为:
1. 静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。
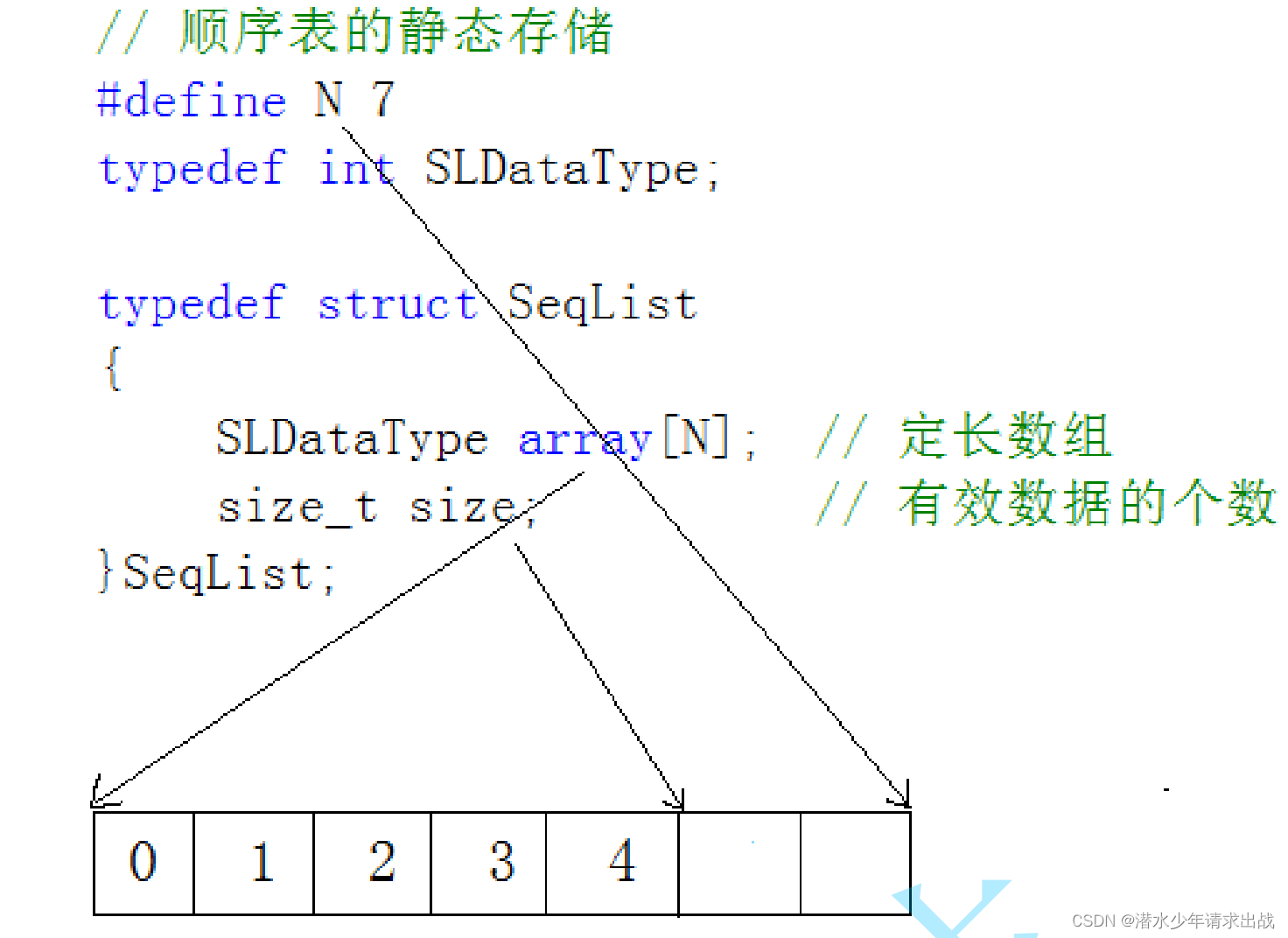
2. 接口实现
静态顺序表只适用于确定知道需要存多少数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组导致N定大了,空间开多了浪
费,开少了不够用。所以现实中基本都是使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态的分配空间大小,所以下面我们实
现动态顺序表。
typedef int SLDataType;
// 顺序表的动态存储
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* array; // 指向动态开辟的数组
size_t size ; // 有效数据个数
size_t capicity ; // 容量空间的大小
}SeqList;
// 基本增删查改接口
// 顺序表初始化
void SeqListInit(SeqList* psl, size_t capacity);
// 检查空间,如果满了,进行增容
void CheckCapacity(SeqList* psl);
// 顺序表尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x);
// 顺序表尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* psl);
// 顺序表头插
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x);
// 顺序表头删
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* psl);
// 顺序表查找
int SeqListFind(SeqList* psl, SLDataType x);
// 顺序表在pos位置插入x
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* psl, size_t pos, SLDataType x);
// 顺序表删除pos位置的值
void SeqListErase(SeqList* psl, size_t pos);
// 顺序表销毁
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* psl);
// 顺序表打印
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* psl);
看到这里小伙伴就懵了 ,我们先作道题
链接: oj题:移除元素.
//思路:将数组中要删除的元素用后面的元素覆盖掉
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val)
{int i=0, j=0;for(i=0; i<numsSize; i++){// 将数组中不等于val的值依次挪动到数组的开始位置if(nums[i]!=val){nums[j]=nums[i];++j;}}return j;
}
看到这里大家就发现头删就是下一个数往前覆盖没错;而头删恰好相反,它是往后移动。
3.代码操作
1.(头文件里放)
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include2.(.c里面放)
#include"SeqList.h"void SLInit(SL* ps)
{assert(ps != NULL);ps->a = NULL;ps->size = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{assert(ps != NULL);// 检查容量空间,满了扩容if (ps->size == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;SLDateType* tmp = (SLDateType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDateType));if (tmp == NULL){printf("realloc fail\n");//exit(-1);return;}ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}
}int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps != NULL);if (ps->size == ps->capacity){SLCheckCapacity(ps);}//查找int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){if (ps->a[i] == x){return i;}}return -1;
}void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps != NULL);assert((pos >= 0) && (ps->size >= pos));//检查是否增容。SLCheckCapacity(ps);int end = ps->size - 1;while (end >= pos){ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];--end;}ps->a[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps != NULL);assert((pos >= 0) && (ps->size >= pos));int start = pos;while (start < ps->size - 1){ps->a[start] = ps->a[start + 1];++start;}ps->size--;
}void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps != NULL);SLInsert(ps, 0, x);
}void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps != NULL);SLInsert(ps, ps->size - 1, x);
}void SLPopFront(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps != NULL);SLErase(ps, 0, x);
}
void SLPopBack(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps != NULL);SLErase(ps, ps->size - 1, x);
}SLModify(SL* ps, int pos, SLDateType x)
{assert(ps != NULL);//查找int c = SLFind(ps, x);ps->a[c] = x;
}void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{assert(ps != NULL);int i = 0;for (i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);}
}void SLDestory(SL* ps)
{assert(ps != NULL);if (ps->a){free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;}
}
当然还在需要一个.c文件测试,里面有main函数。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!