libiptc库的使用,实现iptables命令对nat表的部分操作(添加)
文章目录
- 前言
- 这条命令要实现起来最主要的难点在于对multiport模块的处理(如果没有这个模块会容易很多,之后的代码部分会提及)
- 一、libiptc库的应用
- 1.iptc_init
- 2.iptc_append_entry
- struct ipt_ip ip
- unsigned char elems[0]
- 首先我们看一下match的结构体的定义:
- 到这里,match的部分就暂时结束,然后是target结构体的定义:
- iptc_append_entry的总结
- 3.iptc_commit
- 二、iptc库实现-m 扩展模块的注意事项
- 1.直接填充match结构体会碰到的问题
- 2.问题的解决
- 总结
前言
最近在项目中需要使用iptc库对iptables防火墙中的nat表进行操作,完成对应的网络地址转换,基本上要实现的命令是:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p udp -m multiport -d proxyip --dport port1,port2,port3 -j DNAT --to-destination serverIp
这条命令要实现起来最主要的难点在于对multiport模块的处理(如果没有这个模块会容易很多,之后的代码部分会提及)
一、libiptc库的应用
这里我只会提到自己使用的一些函数接口,如果有其他接口的需求,可以自行百度iptc库,网上的介绍还是很多的
1.iptc_init
struct iptc_handle *h = NULL;
h = iptc_init("nat");
iptc_init唯一的参数就是表的名称,我们这里使用的是nat表,因此就填nat,返回值是一个操作nat表的句柄,之后的规则添加、删除、修改之类的操作都会用到
2.iptc_append_entry
int iptc_append_entry(const xt_chainlabel chain,const struct ipt_entry *e,struct xtc_handle *handle);
这相当于插入的函数,意义为向 handle对应的表中的chain链(这是个char[32]类型的数组,本质上是个字符串,对应上面iptables命令中的PREROUTING ,其余的还有INPUT、OUTPUT、POSTROUTING等,这些链所代表的意义,可以自行百度,算是iptables基础)中插入一条 e结构体代表的规则
不难看出,这个函数最核心的点就是对struct ipt_entry *e的填充,我们先来看一下这个结构体
/* This structure defines each of the firewall rules. Consists of 3parts which are 1) general IP header stuff 2) match specificstuff 3) the target to perform if the rule matches */
struct ipt_entry {struct ipt_ip ip;/* Mark with fields that we care about. */unsigned int nfcache;/* Size of ipt_entry + matches */u_int16_t target_offset;/* Size of ipt_entry + matches + target */u_int16_t next_offset;/* Back pointer */unsigned int comefrom;/* Packet and byte counters. */struct xt_counters counters;/* The matches (if any), then the target. */unsigned char elems[0];
};
不难看出,这个结构体最核心的部分是ip、elems两个成员:
struct ipt_ip ip
这个成员主要是源地址,目的地址,掩码等,对它的填充也很简单:
int fill_entry(struct ipt_entry *e, __u32 size, __u32 match_size, __u32 src_ip, uint32_t src_msk, __u32 dst_ip, uint32_t dst_msk, __u32 protocol) {if (e == NULL) {printf("fill_entry_error! %x \n", *(char *) e);return -1;}/*初始化entry的源地址,目的地址和掩码*/e->ip.src.s_addr = src_ip;e->ip.dst.s_addr = dst_ip;if (src_msk == -1) {e->ip.dmsk.s_addr = htonl(0xFFFFFFFF << (32 - dst_msk));} else {e->ip.smsk.s_addr = htonl(0xFFFFFFFF << (32 - src_msk));}if (protocol == P_TCP) {e->ip.proto = IPPROTO_TCP;} else if (protocol == P_UDP) {e->ip.proto = IPPROTO_UDP;}e->target_offset = IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct ipt_entry)) +match_size ;e->next_offset = size;return 0;
}
其中关于target_offset 、next_offset 我们接下来谈
unsigned char elems[0]
这是一个柔型数组,对C语言不是很熟悉的朋友可以直接搜索,这里就不具体讨论了
这个地址很重要,它是iptables模块添加的起始位置,match和target都从这个位置开始填充,我的理解其中match代表的是iptables规则的匹配条件,target代表的是符合条件之后要完成的动作(对符合这个规则的数据包怎么操作,是接受ACCEPT、丢弃DROP、还是修改)
首先我们看一下match的结构体的定义:
//这两个文件是内核netfilter的头文件
//ip_tables.h
#define ipt_entry_match xt_entry_match
//x_tables.h
struct xt_entry_match {union {struct {__u16 match_size;/* Used by userspace */char name[XT_FUNCTION_MAXNAMELEN-1];__u8 revision;} user;struct {__u16 match_size;/* Used inside the kernel */struct xt_match *match;} kernel;/* Total length */__u16 match_size;} u;unsigned char data[0];
};
这个结构体中联合体的理解应该不难,name数组存储扩展模块的名称,对应iptables命令中的-m multiport,如果在iptables源码中加一行打印,name的打印值就是multiport
重点依然是unsigned char data[0]这个柔性数组,这个地址指向的是模块对应要填充的结构体,我这里要使用的是multiport模块,因此需要使用multiport对应的结构体:
//xt_multiport.h
enum xt_multiport_flags {XT_MULTIPORT_SOURCE,XT_MULTIPORT_DESTINATION,XT_MULTIPORT_EITHER
};#define XT_MULTI_PORTS 15/* Must fit inside union xt_matchinfo: 16 bytes */
struct xt_multiport {__u8 flags; /* Type of comparison */__u8 count; /* Number of ports */__u16 ports[XT_MULTI_PORTS]; /* Ports */
};struct xt_multiport_v1 {__u8 flags; /* Type of comparison */__u8 count; /* Number of ports */__u16 ports[XT_MULTI_PORTS]; /* Ports */__u8 pflags[XT_MULTI_PORTS]; /* Port flags */__u8 invert; /* Invert flag */
};
其中,我的Linux中iptables的版本是1.4.21,源码中使用的是xt_multiport_v1结构体,我们重点关注ports成员,multiport模块主要是提供分段端口的设置功能,具体到iptables命令就是:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p udp -m multiport -d proxyip --dport port1,port2,port3 -j DNAT --to-destination serverIp
其中:–dport port1,port2,port3的三个端口就是对应的ports,如果没有multiport模块,那么–dport参数就只能有一个(随口一提,要想使用范围端口的设置,需要iprange模块)
到这里,match的部分就暂时结束,然后是target结构体的定义:
//ip_tables.h
#define ipt_entry_target xt_entry_target
//x_tables.h
struct xt_entry_target {union {struct {__u16 target_size;/* Used by userspace */char name[XT_FUNCTION_MAXNAMELEN-1];__u8 revision;} user;struct {__u16 target_size;/* Used inside the kernel */struct xt_target *target;} kernel;/* Total length */__u16 target_size;} u;unsigned char data[0];
};
可以看出target和match结构体在定义上其实很相似,我们可以主要关注data地址:
我这里使用的iptables命令中用到的target是 -j DNAT,也就是目的地址转换,需要填充的结构体为
//nf_nat.h
/* Single range specification. */
struct nf_nat_range
{/* Set to OR of flags above. */unsigned int flags;/* Inclusive: network order. */__be32 min_ip, max_ip;/* Inclusive: network order */union nf_conntrack_man_proto min, max;
};/* For backwards compat: don't use in modern code. */
struct nf_nat_multi_range_compat
{unsigned int rangesize; /* Must be 1. *//* hangs off end. */struct nf_nat_range range[1];
};#define nf_nat_multi_range nf_nat_multi_range_compat
具体的代码:
int fill_target(struct ipt_entry *e, struct ipt_entry_target *pt, struct nf_nat_multi_range_compat * p_target, const char *target, __u32 match_size,__u32 target_size, __u32 out_ip, __u16 out_port, __u32 protocol) {if (e == NULL || pt == NULL || p_target == NULL) {printf("fill_target_error! %x---%x---%x\n", *(char *) e, *(char *) pt, *(char *) p_target);return -1;}pt = (struct ipt_entry_target *) (e->elems + match_size);pt->u.target_size = target_size;strncpy(pt->u.user.name, target, sizeof(pt->u.user.name) - 1);p_target = (struct nf_nat_multi_range_compat *) pt->data;
//p_target->rangesize = 1;out_port = 0;if (out_port == 0) {p_target->range[0].flags = 1;} else {p_target->range[0].flags = 3;}p_target->range[0].min_ip = out_ip;p_target->range[0].max_ip = out_ip;if (protocol == P_TCP) {p_target->range[0].min.tcp.port = out_port;p_target->range[0].max.tcp.port = out_port;} else if (protocol == P_UDP) {p_target->range[0].min.udp.port = out_port;p_target->range[0].max.udp.port = out_port;} return 0;
}
iptc_append_entry的总结
至此,关于iptc_append_entry函数最重要的部分ipt_entry结构体的介绍就大体结束了,值得注意的是,match和target部分都可以是有多个的,因此ipt_entry结构体真正的结构应该是:
struct ipt_entry + (struct xt_entry_match + 对应模块的结构体如struct xt_multiport_v1)+(struct xt_entry_match + 对应模块的结构体) + ... +(struct xt_entry_target + 对应target的结构体如struct nf_nat_multi_range_compat)(struct xt_entry_target + 对应target的结构体) + ...
又因为使用了柔性数组,因此这一长串的空间地址都是连续的
3.iptc_commit
ret = iptc_commit(h);
if (ret <= 0) {printf("iptc_commit error:\n%s\n", iptc_strerror(ret));
}
iptc_free(h);
这个函数是将我们iptc_append_entry增加的规则真正的提交到linux内核的防火墙模块生效,参数h是iptc_init函数返回的,iptables真正的工作部分还是在内核防火墙模块,如果出错,可以调用iptc_strerror打印出错信息
二、iptc库实现-m 扩展模块的注意事项
在对struct ipt_entry的介绍中,在match部分我只是介绍了match结构体的成员,并没有贴出填充这个结构体的具体的代码。因为这一块我想放到这里,是-m扩展模块的重点
1.直接填充match结构体会碰到的问题
根据对match的熟悉,我首先在测试是尝试了直接填充对应的match结构:
int fill_match(struct ipt_entry *e, struct ipt_entry_match *pm, __u32 match_size, __u16 src_port, __u16 dst_port, __u32 protocol) {if (e == NULL || pm == NULL ) {printf("fill_match_error! %x --- %x\n", *(char *) e, *(char *) pm);return -1;}pm = (struct ipt_entry_match*) e->elems;
// pm->u.match_size = match_size;pm->u.user.match_size = match_size;strcpy(pm->u.user.name, "multiport");struct xt_multiport_v1 *pmultiport = (struct xt_multiport_v1 *)pm->data;int i;for(i = 0; i < 15; i++){pmultiport->pflags[i] = 0;}pmultiport->flags = XT_MULTIPORT_DESTINATION;pmultiport->count = 3;pmultiport->ports[0] = dst_port;pmultiport->ports[1] = dst_port + 1;pmultiport->ports[2] = dst_port + 2;pmultiport->pflags[0] = 1;pmultiport->pflags[1] = 1;pmultiport->pflags[2] = 1;return 0;
}
简单粗暴的直接填充,在iptc_append_entry中并没有任何问题,但是在iptc_commit时却返回了一个错误:
Incompatible with this kernel
与此内核不兼容,咋看一下好像是内核版本兼容性的问题,但是仔细一想,在使用iptables的系统命令时却没有任何问题,我ldd查看了一下两个程序的动态库依赖,是依赖的相同的动态库,这样一来就很奇怪,调用同样的接口,一个成功,一个失败,其中必定会有深层次的原因。
2.问题的解决
在不断的阅读iptables(1.4.21)的源码,并自己加打印信息编译运行之后,我注意到了xtables.c这个文件
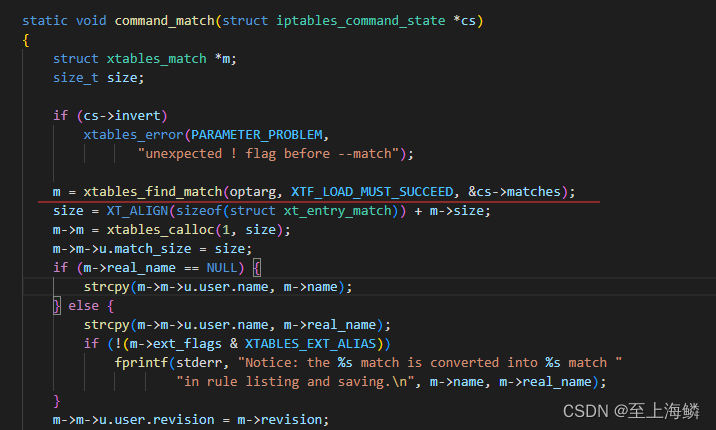
iptables第一步解析-m参数时,核心就调用了xtables_find_match,见名基本知意,optarg的值就是multiport,而这个函数中,尤其值得注意的就是:

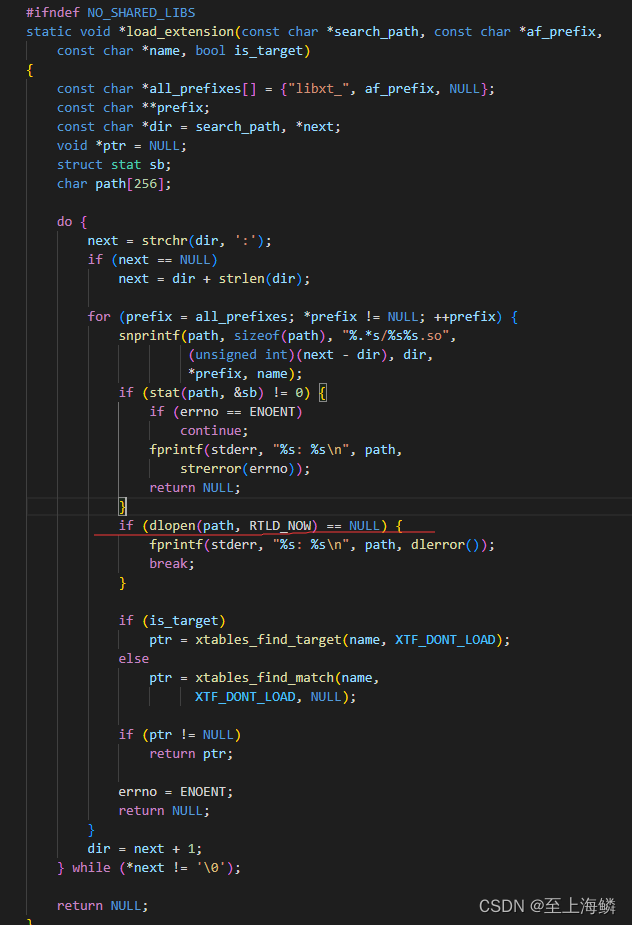
load_extension中,dlopen了一个动态库,因为是multiport,因此打开的动态库是libxt_multiport.so,而这个动态库中接口在iptables源码extensions文件夹,事实上,所有的扩展模块都在这个文件夹:
//......
static struct xtables_match multiport_mt_reg[] = {{.family = NFPROTO_IPV4,.name = "multiport",.revision = 0,.version = XTABLES_VERSION,.size = XT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct xt_multiport)),.userspacesize = XT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct xt_multiport)),.help = multiport_help,.x6_parse = multiport_parse,.x6_fcheck = multiport_check,.print = multiport_print,.save = multiport_save,.x6_options = multiport_opts,},{.family = NFPROTO_IPV6,.name = "multiport",.revision = 0,.version = XTABLES_VERSION,.size = XT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct xt_multiport)),.userspacesize = XT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct xt_multiport)),.help = multiport_help,.x6_parse = multiport_parse6,.x6_fcheck = multiport_check,.print = multiport_print6,.save = multiport_save6,.x6_options = multiport_opts,},{.family = NFPROTO_IPV4,.name = "multiport",.version = XTABLES_VERSION,.revision = 1,.size = XT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct xt_multiport_v1)),.userspacesize = XT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct xt_multiport_v1)),.help = multiport_help_v1,.x6_parse = multiport_parse_v1,.x6_fcheck = multiport_check,.print = multiport_print_v1,.save = multiport_save_v1,.x6_options = multiport_opts,},{.family = NFPROTO_IPV6,.name = "multiport",.version = XTABLES_VERSION,.revision = 1,.size = XT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct xt_multiport_v1)),.userspacesize = XT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct xt_multiport_v1)),.help = multiport_help_v1,.x6_parse = multiport_parse6_v1,.x6_fcheck = multiport_check,.print = multiport_print6_v1,.save = multiport_save6_v1,.x6_options = multiport_opts,},
};void
_init(void)
{xtables_register_matches(multiport_mt_reg, ARRAY_SIZE(multiport_mt_reg));
}
其中最重要的是x6_parse所指向的回调函数,即multiport_parse_v1:
static void __multiport_parse_v1(struct xt_option_call *cb, uint16_t pnum,uint8_t invflags)
{const char *proto;struct xt_multiport_v1 *multiinfo = cb->data;xtables_option_parse(cb);switch (cb->entry->id) {case O_SOURCE_PORTS:proto = check_proto(pnum, invflags);parse_multi_ports_v1(cb->arg, multiinfo, proto);multiinfo->flags = XT_MULTIPORT_SOURCE;break;case O_DEST_PORTS:proto = check_proto(pnum, invflags);parse_multi_ports_v1(cb->arg, multiinfo, proto);multiinfo->flags = XT_MULTIPORT_DESTINATION;break;case O_SD_PORTS:proto = check_proto(pnum, invflags);parse_multi_ports_v1(cb->arg, multiinfo, proto);multiinfo->flags = XT_MULTIPORT_EITHER;break;}if (cb->invert)multiinfo->invert = 1;
}static void multiport_parse_v1(struct xt_option_call *cb)
{const struct ipt_entry *entry = cb->xt_entry;return __multiport_parse_v1(cb,entry->ip.proto, entry->ip.invflags);
}
这个回调函数主要是作参数的解析,填充struct xt_multiport_v1结构体,对应到iptables命令中就是–dport port1,port2,port3,其中cb->arg就是port1,port2,port3三个分段端口
起初,我是有些不理解的,我自己的程序和iptables唯一的区别就是它使用了一个动态库(dlopen)去处理命令行的参数,填充相应的结构体,而我是直接填充struct ipt_entry结构体,但是我的程序却产生了错误。这其实是令人恼火的,Linux内核这一块我熟悉一些的都是网络部分,对防火墙netfilter部分了解不多,只能在网上不断浏览其他人的博客寻找方法,然后对照iptables源码,运气比较好,终于是让我找到了原因:
iptables match模块扩展 数据传递(用户空间 -> 内核空间)

/*** @arg: input from command line* @ext_name: name of extension currently being processed* @entry: current option being processed* @data: per-extension kernel data block* @xflags: options of the extension that have been used* @invert: whether option was used with !* @nvals: number of results in uXX_multi* @val: parsed result* @udata: per-extension private scratch area* (cf. xtables_{match,target}->udata_size)*/
struct xt_option_call {const char *arg, *ext_name;const struct xt_option_entry *entry;void *data;unsigned int xflags;bool invert;uint8_t nvals;union {uint8_t u8, u8_range[2], syslog_level, protocol;uint16_t u16, u16_range[2], port, port_range[2];uint32_t u32, u32_range[2];uint64_t u64, u64_range[2];double dbl;struct {union nf_inet_addr haddr, hmask;uint8_t hlen;};struct {uint8_t tos_value, tos_mask;};struct {uint32_t mark, mask;};uint8_t ethermac[6];} val;/* Wished for a world where the ones below were gone: */union {struct xt_entry_match **match;struct xt_entry_target **target;};void *xt_entry;void *udata;
};
简单来说x6_parse指向的回调函数的参数struct xt_option_call的data成员会将数据传递到内核,iptables每一个extensions文件夹中的libxt_.c文件都对应一个libxt_.so动态库,而每个libxt_.so动态库在内核都有一个xt_.ko模块和它对应,iptables能操作内核防火墙,这个对应关系是绝对不能少的:
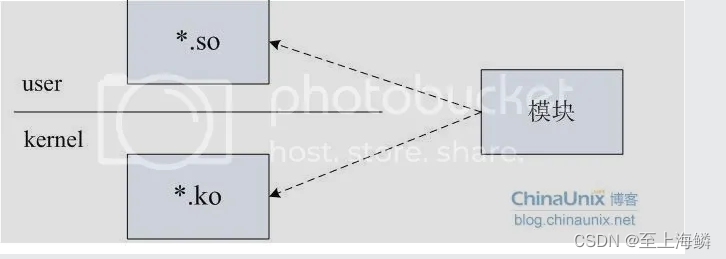
到了这里之后,要做的事情就很清晰了:
参照iptables源码,抽取出其调用libxt_multiport.so的逻辑来完成我们自己的参数填充,具体的代码如下:
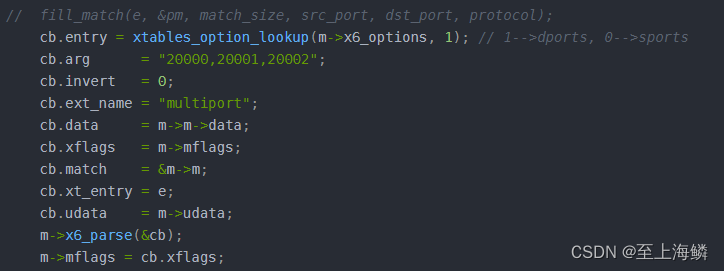
int iptc_entry_add(struct iptc_handle *handle, const char *chain, const char *target, __u32 protocol, __u32 src_ip, __u16 src_port, __u32 src_msk,__u32 dst_ip, __u16 dst_port, __u32 dst_msk, __u32 out_ip, __u16 out_port) {struct xt_option_call cb;struct xtables_match *m;struct xtables_rule_match *matches;m = xtables_find_match("multiport", XTF_LOAD_MUST_SUCCEED, &matches);if(m->init != NULL)m->init(m->m);if (handle == NULL || chain == NULL || target == NULL) {printf("iptc_entry_add error! %x---%x---%x\n", *(char *) handle, *(char *) chain, *(char *) target);return -1;}struct ipt_entry *e = NULL;struct ipt_entry_match pm;struct ipt_entry_target pt;struct nf_nat_multi_range_compat p_target;__u32 target_size, match_size, size;__u32 ret = 0;if(protocol == P_TCP){match_size = IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct ipt_entry_match)) + IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct ipt_tcp));}else if(protocol == P_MULTI){match_size = IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct ipt_entry_match)) + IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct xt_multiport_v1));}else{match_size = IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct ipt_entry_match)) + IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct ipt_udp));}target_size = IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct ipt_entry_target))+ IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct nf_nat_multi_range_compat));// target_size = sizeof(struct ipt_standard_target)+ sizeof(struct nf_nat_multi_range_compat);size = IPT_ALIGN(sizeof(struct ipt_entry)) + target_size + match_size;e = malloc(size);memset((void *) e, 0, size);m->m = e->elems;m->m->u.match_size = match_size;if (m->real_name == NULL) {strcpy(m->m->u.user.name, m->name);} else {strcpy(m->m->u.user.name, m->real_name);}m->m->u.user.revision = m->revision;fill_entry(e, size, match_size, src_ip, src_msk, dst_ip, dst_msk, protocol);// fill_match(e, &pm, match_size, src_port, dst_port, protocol);cb.entry = xtables_option_lookup(m->x6_options, 1); // 1-->dports, 0-->sportscb.arg = "20000,20001,20002";cb.invert = 0;cb.ext_name = "multiport";cb.data = m->m->data;cb.xflags = m->mflags;cb.match = &m->m;cb.xt_entry = e;cb.udata = m->udata;m->x6_parse(&cb);m->mflags = cb.xflags;fill_target(e, &pt, &p_target, target, match_size, target_size, out_ip, out_port, protocol);/* 在规则链中插入一项 */ret = iptc_append_entry(chain, e, handle);if(ret <= 0){printf("iptc_append_entry:\n%s\n\n", iptc_strerror(ret));}if (e) {free(e);}return ret;}
核心部分是对struct xt_option_call 结构体的填充:
编译运行,有一个地方需要修改,在iptables源码中,xtoptions.c文件中:
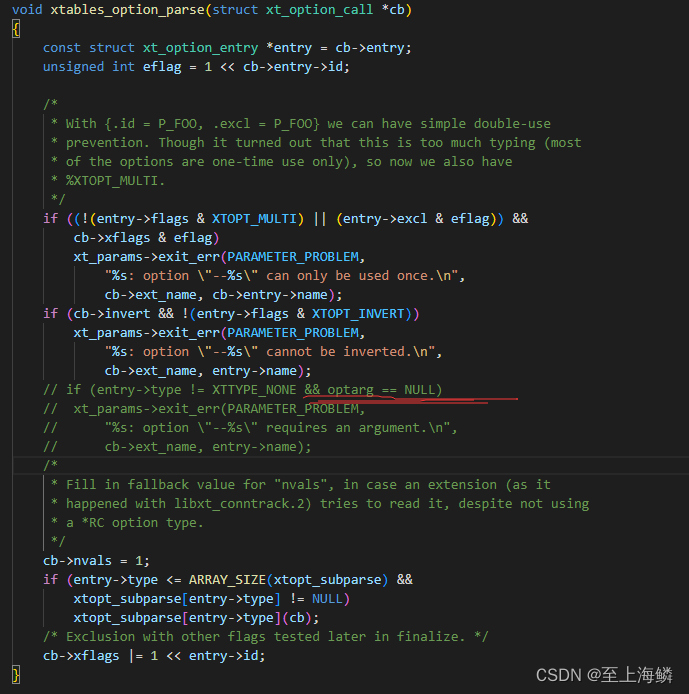
optarg参数是iptables用了getopt_long函数来解析linux命令行参数,但是如果我的程序没有使用这个函数,当程序运行到这里就会因为optarg==NULL而退出,因此我将这个判断注释掉了,重新编译了iptables源码,并替换libxtables.so动态库
之后再编译程序,运行正常,iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p udp -m multiport -d proxyip --dport port1,port2,port3 -j DNAT --to-destination serverIp这条命令即使不系统调用iptables,在我自己的程序中也能通过ipt_commit提交添加并生效,iptables -t nat -nvL查看也能正常显示。
总结
其实要根本的解决问题,还是应该弄明白iptables和内核交互的具体流程和代码,但是这需要更扎实的知识储备和时间,暂时作为一个长期规划处理吧
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!