文章目录
- 一 享元模式
- 二 桥接模式
- 三 外观模式
- 四 观察者模式
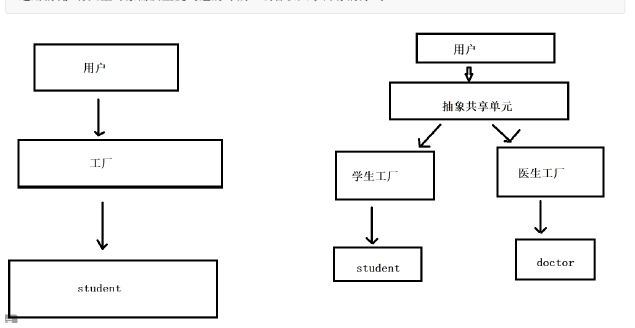
一 享元模式
主要通过与其它类对象共享数据来减少内存的使用
适用情况:有大量对象需要重复创建的时候,或者以共享内存的方式
#include
#include
二 桥接模式
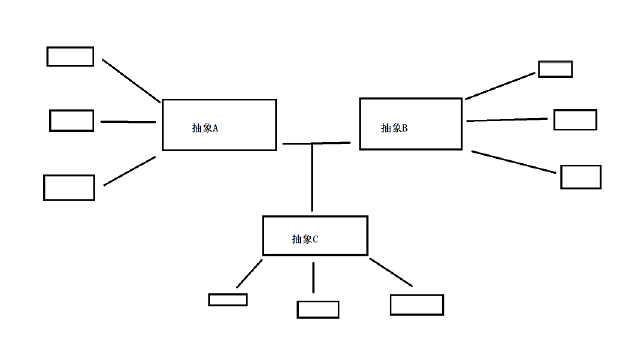
将抽象和实现分离,使他们可以独立变化。
基于类的最小设计原则
#include
#include
三 外观模式
提供一个简单一致的界面,为了系统中统一的一套接口
#include
#include
四 观察者模式
当对象存在一对多的关系的时候,使用观察者模式,当一个对象被修改的时候,则会自动通知
依赖他的所有对象。
#include
#include
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!


