Elasticsearch:Explain API - 如何计算分数

你想了解你的文档为何获得该分数吗?
文档
让我们通过一组示例文档来了解 Explain API。 就我而言,我将使用一小部分电影名言。
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "movie_quotes" } }
{ "title" : "The Incredibles", "quote": "Never look back, darling. It distracts from the now" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "movie_quotes" } }
{ "title" : "The Lion King", "quote": "Oh yes, the past can hurt. But, you can either run from it or learn from it" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "movie_quotes" } }
{ "title" : "Toy Story", "quote": "To infinity and beyond" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "movie_quotes" } }
{ "title" : "Ratatouille", "quote": "You must not let anyone define your limits because of where you come from" }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "movie_quotes" } }
{ "title" : "Lilo and Stitch", "quote": "Ohana means family, family means nobody gets left behind. Or forgotten" }BM25
在网址 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Okapi_BM25 你可以找到 Elasticsearch 中默认的评分算法。

- boost — 常数 2.2 = (k1 + 1),忽略,与排序无关
- freq — 该术语在字段中出现的次数
- N — 分片中的文档总数
- n — 包含该术语的文档数
- k1 — 常量 1.2,项饱和参数,可以更改
- b — 常数 0.75,长度归一化参数,可以更改
- dl — 字段的长度,特别是字段中的项数
- avgdl — 集群中每个文档的该字段的平均长度
示例 1:术语越少的字段越重要
GET movie_quotes/_search
{"explain": true,"query": {"match": {"quote": "the"}}
}上面命令返回的结果:
{"took": 1,"timed_out": false,"_shards": {"total": 1,"successful": 1,"skipped": 0,"failed": 0},"hits": {"total": {"value": 2,"relation": "eq"},"max_score": 0.94581884,"hits": [{"_shard": "[movie_quotes][0]","_node": "M9Dx5c1BTk6ehVVSCiJAvQ","_index": "movie_quotes","_id": "LMpi64YBn8MlrX4RQHf9","_score": 0.94581884,"_source": {"title": "The Incredibles","quote": "Never look back, darling. It distracts from the now"},"_explanation": {"value": 0.94581884,"description": "weight(quote:the in 0) [PerFieldSimilarity], result of:","details": [{"value": 0.94581884,"description": "score(freq=1.0), computed as boost * idf * tf from:","details": [{"value": 2.2,"description": "boost","details": []},{"value": 0.87546873,"description": "idf, computed as log(1 + (N - n + 0.5) / (n + 0.5)) from:","details": [{"value": 2,"description": "n, number of documents containing term","details": []},{"value": 5,"description": "N, total number of documents with field","details": []}]},{"value": 0.4910714,"description": "tf, computed as freq / (freq + k1 * (1 - b + b * dl / avgdl)) from:","details": [{"value": 1,"description": "freq, occurrences of term within document","details": []},{"value": 1.2,"description": "k1, term saturation parameter","details": []},{"value": 0.75,"description": "b, length normalization parameter","details": []},{"value": 9,"description": "dl, length of field","details": []},{"value": 11,"description": "avgdl, average length of field","details": []}]}]}]}},{"_shard": "[movie_quotes][0]","_node": "M9Dx5c1BTk6ehVVSCiJAvQ","_index": "movie_quotes","_id": "Lcpi64YBn8MlrX4RQHf9","_score": 0.71575475,"_source": {"title": "The Lion King","quote": "Oh yes, the past can hurt. But, you can either run from it or learn from it"},"_explanation": {"value": 0.71575475,"description": "weight(quote:the in 1) [PerFieldSimilarity], result of:","details": [{"value": 0.71575475,"description": "score(freq=1.0), computed as boost * idf * tf from:","details": [{"value": 2.2,"description": "boost","details": []},{"value": 0.87546873,"description": "idf, computed as log(1 + (N - n + 0.5) / (n + 0.5)) from:","details": [{"value": 2,"description": "n, number of documents containing term","details": []},{"value": 5,"description": "N, total number of documents with field","details": []}]},{"value": 0.3716216,"description": "tf, computed as freq / (freq + k1 * (1 - b + b * dl / avgdl)) from:","details": [{"value": 1,"description": "freq, occurrences of term within document","details": []},{"value": 1.2,"description": "k1, term saturation parameter","details": []},{"value": 0.75,"description": "b, length normalization parameter","details": []},{"value": 17,"description": "dl, length of field","details": []},{"value": 11,"description": "avgdl, average length of field","details": []}]}]}]}}]}
}详细说明
对于最先出现的文件 The incredibles,我们得到分数 0.94581884,计算如下:
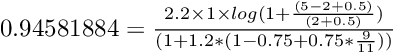
对于第二个文件,The Lion King,我们得到 0.71575475,计算如下:
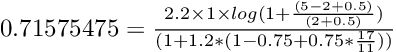
对于这个例子,方程式再次非常相似,但是文档有非常不同的分数,比更短的字段例子更是如此。 现在的区别在于频率和字段长度,第一个文档中的字段长度更短,术语频率更高,字段长度对一个点很重要,但频率更重要到一个点,见下一个例子 . 我们还看到第二个文档和前面例子中的第一个文档有相同的分数,这是因为情况相同,相同的频率和相同的字段长度,实际上是同一个文档。
示例 2:某个术语在该领域出现的频率越高越重要
GET movie_quotes/_search
{"explain": true,"query": {"match": {"quote": "you"}}
}详细说明
这次跳过完整输出,对于先出现的文档 Ratatouille,我们得到分数 1.1180129,计算如下:
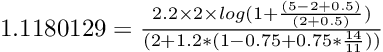
对于第二个文件 The Lion King,我们得到 0.71575475,计算如下:
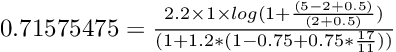
对于这个例子,方程式再次非常相似,但是文档有非常不同的分数,比更短的字段例子更是如此。 现在的区别在于频率和字段长度,第一个文档中的字段长度更短,术语频率更高,字段长度对一个点很重要,但频率更重要到一个点,见下一个例子 . 我们还看到第二个文档和前面例子中的第一个文档有相同的分数,这是因为情况相同,相同的频率和相同的字段长度,实际上是同一个文档。
示例 3:搞乱算法
如果术语频率如此重要,我是否可以通过一遍又一遍地重复相同的术语来确保我的文档始终位于顶部?
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "movie_quotes" } }
{ "title" : "Movie 1", "quote": "Movie movie movie movie." }
{ "index" : { "_index" : "movie_quotes" } }
{ "title" : "Movie 2", "quote": "Movie movie movie movie movie movie movie movie." }GET movie_quotes/_search
{"explain": true,"query": {"match": {"quote": "movie"}}
}描述
对于电影 2,我们得到 2.2614799,对于电影 1,我们得到 2.1889362。 这2个分数现在非常相似,原因是 freq 在分子和分母中,一开始,随着 term 的频率增加,分数提高得很快,但是当频率变高时,它变得越来越少相关,即使电影 2 文档的术语频率翻倍。
结论
这些是简单匹配查询的简短示例,我们还没有看到每种可能条件的相互作用,但即便如此,这也是一个很好的起点,可以真正掌握我们的文档获得的分数,并了解如何开始调优 我们的文件利用了这个算法。 有必要在这一点上提到并理解分数的确切值是无关紧要的,相对分数是唯一对排序有用的东西。 一些你自己尝试的进一步的例子。
- 包含该术语多次的真正长字段,不如仅包含该术语几次的短字段相关。
- 每个文档中出现的术语都会带回太多文档,例如 the、an 或 a,也称为停用词。 这个样本集太小,无法真正了解停用词如何真正影响返回的文档数量。
- 由于这是一个电影数据库,你可能会发现一组全新的特定于电影的停用词,例如 film、movie、flick、actor、camera 等。 使用更大的电影数据库,你会发现搜索其中一些术语会返回相关性错误的结果。
- 通过向请求添加更多参数来增加查询的复杂性,例如在多个字段中搜索多个术语,或在多个字段中查找相同的术语或在多个字段中查找不同的术语。
- 开始探索 Elasticsearch 查询 DSL 中的不同查询类型,尤其是布尔查询,它真正开始发挥 Elasticsearch 中相关性调整的强大功能。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!