【图像识别】基于k-means聚类实现手势识别matlab代码
1 简介
k-means算法是一种聚类算法,所谓聚类,即根据相似性原则,将具有较高相似度的数据对象划分至同一类簇,将具有较高相异度的数据对象划分至不同的类簇。聚类与分类最大的区别在于,聚类过程为无监督过程,即待处理数据对象没有任何先验知识,而分类过程为有监督过程,即存在有先验知识的训练数据集。k-means算法中的 k代表类簇的个数,means代表类簇内数据对象的均值(这种均值是一种对类簇中心的描述),因此 k-means 算法又称为 k-均值算法。k-means 算法是一种基于划分的聚类算法,以距离作为数据对象间相似性度量的标准,即数据对象间的距离越小,则它们的相似性越高,则它们越有可能在同一个类簇。数据对象间距离的计算有很多种,k-means 算法通常采用欧氏距离来计算数据对象间的距离。
2 部分代码
%------------------hand shape analysis
%
close all
format long %显示小数点后4位的数据
%读入hand的landmark数值fid=fopen('shapes.txt');
hand=fscanf(fid, '%g %g',[40,inf]); % X(1,1)X(2,1)...X(56,1);X(1,2)X(2,2)...X(56,2)
% choose 40 shapes as a row column
Shape=600*hand;%-----------------------------------------------------
% shape 矩阵每行112列,对应一个手的数据,
% 前56列对应X坐标 后56列对应Y坐标
% Odata中所有形状的质点已经平移到原点% meanxt=mean(xt);
% for j=1:40
% yt(j,:)=V*(xt(j,:)'-meanxt');
% end%----------Compute the centroid of aligned ----------------------
%
% for i=1:40
% for j=1:56
% X(i,j)=(i,j);
% Y(i,j)=preHand(i,j+56);
% end
% end
% xmeanl=mean(X);
% ymeanl=mean(Y);% plot(x1(:,1),x1(:,2),'-r');
% hold on;
% plot(x2(:,1),x2(:,2),'-g');
%
%-----------------Compute the shape after alignment
% for i=1:40
% for j=1:56
% X(i,j)=6000*preHand(i,j);
% Y(i,j)=6000*preHand(i,j+56);
% end
% end
% plot(X,Y,'r*');
%show the 40 unaligned annotations
% h=figure();
% subplot(1,2,1);
% plot(X,Y,'r*');
% hold on;
% plot(MX,MY);
% %show the first hand landmark imposed on the hand image
% subplot(1,2,2);
% jpg=imread('images\0000.jpg');
% imshow(jpg);
% hold on;
% plot(X(1,:),Y(1,:),'r*');% text(X,Y,'1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11');% subplot(1,2,2);
% plt=plot(X,Y,'r*');
% set(plt,YDir,'reverse');
% % grid on;
3 仿真结果
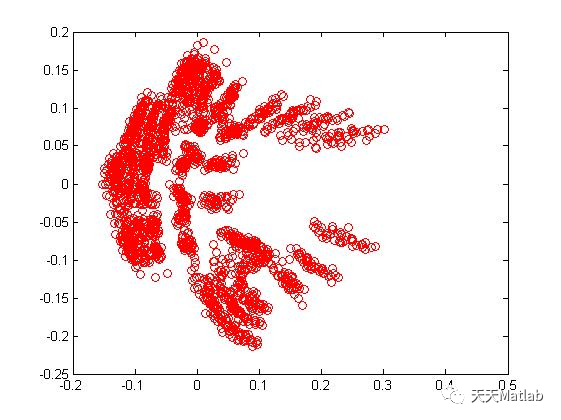
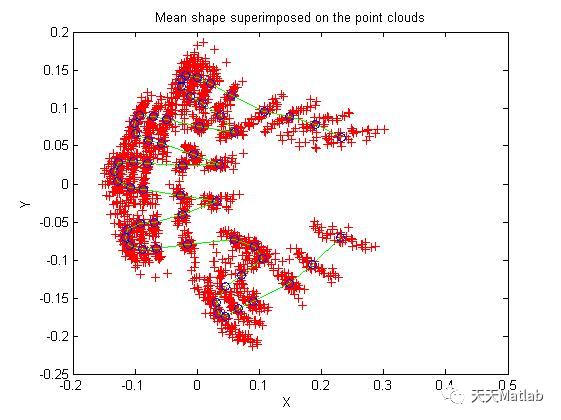
4 参考文献
[1]束仁义等. "基于k-means的手势识别系统设计." 廊坊师范学院学报(自然科学版) 019.001(2019):46-50.

本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!