Android框架源码解析之(一)Volley
前几天面试CVTE,HR面挂了。让内部一个学长帮我查看了一下面试官评价,发现二面面试官的评价如下:
- 广度OK,但缺乏深究能力,深度与实践不足
- 源码:只能说流程,细节代码不清楚,retrofit和volley都是。
感觉自己一方面:自己面试技巧有待提高吧(框架只说了流程,而没说源码,源码实在是不知道怎么说)
另一方面:源码虽然说系统的看过,但是细节不够深入。
所以,就开个专栏,分析框架源码吧
第一篇Volley解析,虽然Volley已经很少有人使用了,但是内部设计三级缓存机制值得我们学习。
先看一下volley的基本使用:
//1、创建RequestQueen
RequestQueue mQueue = Volley.newRequestQueue(context);//2、创建请求RequestStringRequest stringRequest = new StringRequest("http://www.baidu.com",new Response.Listener() {@Overridepublic void onResponse(String response) {Log.d("TAG", response);}}, new Response.ErrorListener() {@Overridepublic void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {Log.e("TAG", error.getMessage(), error);}});//3、将请求添加到RequestQueen中
mQueue.add(stringRequest); Volley的源码解析:
下载地址:https://github.com/google/volley
下载后直接导入Android studio中即可
1、从RequestQueen入手
RequestQueue mQueue = Volley.newRequestQueue(context);源码:
public class Volley {/** Default on-disk cache directory. */// /默认缓存文件夹,文件名为Volley,默认最大为5Mprivate static final String DEFAULT_CACHE_DIR = "volley";/*** Creates a default instance of the worker pool and calls {@link RequestQueue#start()} on it.** @param context A {@link Context} to use for creating the cache dir.* @param stack A {@link BaseHttpStack} to use for the network, or null for default.* @return A started {@link RequestQueue} instance.*/public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context, BaseHttpStack stack) {//BasicNetwork 网络请求类BasicNetwork network;//创建网络请求实现类// stack 默认网络请求实现类,如果Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 9 则stack =HttpURLConnecton,否则 stack =HttpClientif (stack == null) {if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 9) {network = new BasicNetwork(new HurlStack());} else {// Prior to Gingerbread, HttpUrlConnection was unreliable.// See: http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2011/09/androids-http-clients.html// At some point in the future we'll move our minSdkVersion past Froyo and can// delete this fallback (along with all Apache HTTP code).String userAgent = "volley/0";try {String packageName = context.getPackageName();PackageInfo info =context.getPackageManager().getPackageInfo(packageName, /* flags= */ 0);userAgent = packageName + "/" + info.versionCode;} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {}network =new BasicNetwork(new HttpClientStack(AndroidHttpClient.newInstance(userAgent)));}} else {network = new BasicNetwork(stack);}//调用下面的回调方法return newRequestQueue(context, network);}/*** Creates a default instance of the worker pool and calls {@link RequestQueue#start()} on it.** @param context A {@link Context} to use for creating the cache dir.* @param stack An {@link HttpStack} to use for the network, or null for default.* @return A started {@link RequestQueue} instance.* @deprecated Use {@link #newRequestQueue(Context, BaseHttpStack)} instead to avoid depending* on Apache HTTP. This method may be removed in a future release of Volley.*/@Deprecated@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context, HttpStack stack) {if (stack == null) {return newRequestQueue(context, (BaseHttpStack) null);}return newRequestQueue(context, new BasicNetwork(stack));}private static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context, Network network) {//创建磁盘缓存文件File cacheDir = new File(context.getCacheDir(), DEFAULT_CACHE_DIR);//创建请求队列RequestQueue queue = new RequestQueue(new DiskBasedCache(cacheDir), network);//开启请求队列queue.start();return queue;}/*** Creates a default instance of the worker pool and calls {@link RequestQueue#start()} on it.** @param context A {@link Context} to use for creating the cache dir.* @return A started {@link RequestQueue} instance.*/public static RequestQueue newRequestQueue(Context context) {return newRequestQueue(context, (BaseHttpStack) null);}
}
可以看到,Volley.newRequestQueue(context);中主要做了以下操作:
1、创建网络请求实现类
2、创建缓存
3、创建请求队列,并开启请求队列
2、接下来看RequestQueen的start()方法
/** Starts the dispatchers in this queue. */public void start() {stop(); // Make sure any currently running dispatchers are stopped.// Create the cache dispatcher and start it.//创建一个缓存调度线程,并开启mCacheDispatcher = new CacheDispatcher(mCacheQueue, mNetworkQueue, mCache, mDelivery);mCacheDispatcher.start();// Create network dispatchers (and corresponding threads) up to the pool size.//创建4个网络调度线程,并开启for (int i = 0; i < mDispatchers.length; i++) {NetworkDispatcher networkDispatcher =new NetworkDispatcher(mNetworkQueue, mNetwork, mCache, mDelivery);mDispatchers[i] = networkDispatcher;networkDispatcher.start();}}做了以下操作:
1、创建一个缓存调度线程和4个网络调度线程
2、开启这些线程
一会分析而这些线程
3、Request.add(stringRequest);
源码:
public Request add(Request request) {// Tag the request as belonging to this queue and add it to the set of current requests.request.setRequestQueue(this);synchronized (mCurrentRequests) {mCurrentRequests.add(request);}// Process requests in the order they are added.//按照添加顺序,设置请求顺序request.setSequence(getSequenceNumber());request.addMarker("add-to-queue");// If the request is uncacheable, skip the cache queue and go straight to the network.//判断request是否可以缓存,如果不可以缓存,直接加入网络请求队列if (!request.shouldCache()) {mNetworkQueue.add(request);return request;}//如果可以缓存,将请求加入缓存请求队列mCacheQueue.add(request);return request;} 判断request是否可以缓存,如果不能缓存,直接将请求添加到网络请求队列。若能,将请求添加到缓存请求队列。默认是可以缓存的。
如何判断request是否可以缓存:
看源码:
Request.java
/** Whether or not responses to this request should be cached. */// TODO(#190): Turn this off by default for anything other than GET requests.//默认是可以缓存的private boolean mShouldCache = true;/** Returns true if responses to this request should be cached. */public final boolean shouldCache() {return mShouldCache;}4、CacheDispatcher缓存调度线程
先看一下类的定义
public class CacheDispatcher extends Thread {说明CacheDispatcher是一个线程类,那直接看run方法
@Overridepublic void run() {if (DEBUG) VolleyLog.v("start new dispatcher");Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);// Make a blocking call to initialize the cache.//初始化缓存mCache.initialize();while (true) {try {
//重点在这processRequest();} catch (InterruptedException e) {// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.if (mQuit) {//如果quit,则中断线程Thread.currentThread().interrupt();return;}VolleyLog.e("Ignoring spurious interrupt of CacheDispatcher thread; "+ "use quit() to terminate it");}}}
初始化了缓存,调用了processRequest();
查看processRequest();源码
private void processRequest() throws InterruptedException {// Get a request from the cache triage queue, blocking until// at least one is available.final Request request = mCacheQueue.take();//调用下面回调processRequest(request);}@VisibleForTestingvoid processRequest(final Request request) throws InterruptedException {request.addMarker("cache-queue-take");// If the request has been canceled, don't bother dispatching it.//如果request请求取消,则停止分发if (request.isCanceled()) {request.finish("cache-discard-canceled");return;}// Attempt to retrieve this item from cache.Cache.Entry entry = mCache.get(request.getCacheKey());//尝试读取缓存,如果缓存为空,则将Request添加到网络请求队列if (entry == null) {request.addMarker("cache-miss");// Cache miss; send off to the network dispatcher.if (!mWaitingRequestManager.maybeAddToWaitingRequests(request)) {mNetworkQueue.put(request);}return;}// If it is completely expired, just send it to the network.//如果缓存过期,则将Request添加到网络请求队列/*判断缓存过期的条件 Cache.java/*public boolean isExpired() {return this.ttl < System.currentTimeMillis();面试被问到,无奈,过期时间是否小于当前时间}*/if (entry.isExpired()) {request.addMarker("cache-hit-expired");request.setCacheEntry(entry);if (!mWaitingRequestManager.maybeAddToWaitingRequests(request)) {mNetworkQueue.put(request);}return;}// We have a cache hit; parse its data for delivery back to the request.//存在缓存,且缓存没有过期,并命中,则将缓存结构解析,并回调给主线程request.addMarker("cache-hit");Response response =request.parseNetworkResponse(new NetworkResponse(entry.data, entry.responseHeaders));request.addMarker("cache-hit-parsed");if (!entry.refreshNeeded()) {// Completely unexpired cache hit. Just deliver the response.//回调给主线程,一会分析这个类mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);} else {// Soft-expired cache hit. We can deliver the cached response,// but we need to also send the request to the network for// refreshing.request.addMarker("cache-hit-refresh-needed");request.setCacheEntry(entry);// Mark the response as intermediate.response.intermediate = true;if (!mWaitingRequestManager.maybeAddToWaitingRequests(request)) {// Post the intermediate response back to the user and have// the delivery then forward the request along to the network.mDelivery.postResponse(request,response,new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {mNetworkQueue.put(request);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// Restore the interrupted statusThread.currentThread().interrupt();}}});} else {// request has been added to list of waiting requests// to receive the network response from the first request once it returns.mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);}}}总结:
首先从缓存队列中取出请求,判断请求是否取消,若果没有取消,则判断缓存是否有响应,若果有响应,并且没有过期,则解析缓存并回调给主线程。如果没有缓存或者缓存过期,则将请求添加到网络调度线程。接下来查看网络调度线程。
5、网络调度线程
public class NetworkDispatcher extends Thread {同样集成Thread,直接查看run方法;
@Overridepublic void run() {Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);while (true) {try {//重点在这processRequest();} catch (InterruptedException e) {// We may have been interrupted because it was time to quit.if (mQuit) {//如果quit,则中断线程Thread.currentThread().interrupt();return;}VolleyLog.e("Ignoring spurious interrupt of NetworkDispatcher thread; "+ "use quit() to terminate it");}}}可以看出调用了processRequest();方法
processRequest()源码:
private void processRequest() throws InterruptedException {// Take a request from the queue.//从队列中取出请求Request request = mQueue.take();processRequest(request);}@VisibleForTestingvoid processRequest(Request request) {long startTimeMs = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();try {request.addMarker("network-queue-take");// If the request was cancelled already, do not perform the// network request.//如果request被取消,中断网络请求if (request.isCanceled()) {request.finish("network-discard-cancelled");request.notifyListenerResponseNotUsable();return;}addTrafficStatsTag(request);// Perform the network request.//具体的网络请求在这里实现mNetwork.performRequest(request);NetworkResponse networkResponse = mNetwork.performRequest(request);request.addMarker("network-http-complete");// If the server returned 304 AND we delivered a response already,// we're done -- don't deliver a second identical response.//如果服务器返回304并且,request已经分发出去,则不进行第二次网络请求if (networkResponse.notModified && request.hasHadResponseDelivered()) {request.finish("not-modified");request.notifyListenerResponseNotUsable();return;}// Parse the response here on the worker thread.//解析请求Response response = request.parseNetworkResponse(networkResponse);request.addMarker("network-parse-complete");// Write to cache if applicable.// TODO: Only update cache metadata instead of entire record for 304s.//更新缓存if (request.shouldCache() && response.cacheEntry != null) {mCache.put(request.getCacheKey(), response.cacheEntry);request.addMarker("network-cache-written");}// Post the response back.request.markDelivered();//回调给主线程进行显示mDelivery.postResponse(request, response);request.notifyListenerResponseReceived(response);} catch (VolleyError volleyError) {volleyError.setNetworkTimeMs(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTimeMs);parseAndDeliverNetworkError(request, volleyError);request.notifyListenerResponseNotUsable();} catch (Exception e) {VolleyLog.e(e, "Unhandled exception %s", e.toString());VolleyError volleyError = new VolleyError(e);volleyError.setNetworkTimeMs(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - startTimeMs);mDelivery.postError(request, volleyError);request.notifyListenerResponseNotUsable();}}总结:
判断请求是否取消,若没被取消,则请求网络,得到响应,回调给主线程并将缓存存入缓存。
6、真正的网络请求实现类BasicNetwork实现方法为performRequest()
看源码:
@Overridepublic NetworkResponse performRequest(Request request) throws VolleyError {long requestStart = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();while (true) {HttpResponse httpResponse = null;byte[] responseContents = null;List responseHeaders = Collections.emptyList();try {// Gather headers.Map additionalRequestHeaders =getCacheHeaders(request.getCacheEntry());//真真真 的网络请求实现httpResponse = mBaseHttpStack.executeRequest(request, additionalRequestHeaders);int statusCode = httpResponse.getStatusCode();responseHeaders = httpResponse.getHeaders();// Handle cache validation.if (statusCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {Entry entry = request.getCacheEntry();if (entry == null) {return new NetworkResponse(HttpURLConnection.HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED,/* data= */ null,/* notModified= */ true,SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart,responseHeaders);}// Combine cached and response headers so the response will be complete.List combinedHeaders = combineHeaders(responseHeaders, entry);return new NetworkResponse(HttpURLConnection.HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED,entry.data,/* notModified= */ true,SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart,combinedHeaders);}// Some responses such as 204s do not have content. We must check.InputStream inputStream = httpResponse.getContent();if (inputStream != null) {responseContents =inputStreamToBytes(inputStream, httpResponse.getContentLength());} else {// Add 0 byte response as a way of honestly representing a// no-content request.responseContents = new byte[0];}// if the request is slow, log it.long requestLifetime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart;logSlowRequests(requestLifetime, request, responseContents, statusCode);if (statusCode < 200 || statusCode > 299) {throw new IOException();}return new NetworkResponse(statusCode,responseContents,/* notModified= */ false,SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart,responseHeaders);} catch (SocketTimeoutException e) {attemptRetryOnException("socket", request, new TimeoutError());} catch (MalformedURLException e) {throw new RuntimeException("Bad URL " + request.getUrl(), e);} catch (IOException e) {int statusCode;if (httpResponse != null) {statusCode = httpResponse.getStatusCode();} else {throw new NoConnectionError(e);}VolleyLog.e("Unexpected response code %d for %s", statusCode, request.getUrl());NetworkResponse networkResponse;if (responseContents != null) {networkResponse =new NetworkResponse(statusCode,responseContents,/* notModified= */ false,SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - requestStart,responseHeaders);if (statusCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED|| statusCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_FORBIDDEN) {attemptRetryOnException("auth", request, new AuthFailureError(networkResponse));} else if (statusCode >= 400 && statusCode <= 499) {// Don't retry other client errors.throw new ClientError(networkResponse);} else if (statusCode >= 500 && statusCode <= 599) {if (request.shouldRetryServerErrors()) {attemptRetryOnException("server", request, new ServerError(networkResponse));} else {throw new ServerError(networkResponse);}} else {// 3xx? No reason to retry.throw new ServerError(networkResponse);}} else {attemptRetryOnException("network", request, new NetworkError());}}}} 主要是通过mBaseHttpStack.executeRequest(request, additionalRequestHeaders);请求网络,
接下来根据不同相应的饿状态码,返回不同的Response。
HttpStack具体的实现类是HttpUrlConnection和HttpClient,因此Volley具体底层的实现操作还是HttpUrlConnection和HttpClient。
7、如何将response回调到主线程 ?ResponseDelivery的postResponse()方法
public interface ResponseDelivery {/** Parses a response from the network or cache and delivers it. */void postResponse(Request request, Response response);/*** Parses a response from the network or cache and delivers it. The provided Runnable will be* executed after delivery.*/void postResponse(Request request, Response response, Runnable runnable);/** Posts an error for the given request. */void postError(Request request, VolleyError error);
}ResponseDelivery 是一个接口,来看它的实现的类ExecutorDelivery
源码:
/** Delivers responses and errors. */
public class ExecutorDelivery implements ResponseDelivery {/** Used for posting responses, typically to the main thread. */private final Executor mResponsePoster;/*** Creates a new response delivery interface.** @param handler {@link Handler} to post responses on*///内部实例化了Handler,用于工作线程和UI线程的切换public ExecutorDelivery(final Handler handler) {// Make an Executor that just wraps the handler.mResponsePoster =new Executor() {@Overridepublic void execute(Runnable command) {handler.post(command);}};}/*** Creates a new response delivery interface, mockable version for testing.** @param executor For running delivery tasks*/public ExecutorDelivery(Executor executor) {mResponsePoster = executor;}@Overridepublic void postResponse(Request request, Response response) {postResponse(request, response, null);}//利用handler进行转发 handler.post(Runable)@Overridepublic void postResponse(Request request, Response response, Runnable runnable) {request.markDelivered();request.addMarker("post-response");mResponsePoster.execute(new ResponseDeliveryRunnable(request, response, runnable));}//利用handler进行转发 handler.post(Runable)@Overridepublic void postError(Request request, VolleyError error) {request.addMarker("post-error");Response response = Response.error(error);mResponsePoster.execute(new ResponseDeliveryRunnable(request, response, null));}/** A Runnable used for delivering network responses to a listener on the main thread. */@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")private static class ResponseDeliveryRunnable implements Runnable {private final Request mRequest;private final Response mResponse;private final Runnable mRunnable;public ResponseDeliveryRunnable(Request request, Response response, Runnable runnable) {mRequest = request;mResponse = response;mRunnable = runnable;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")@Overridepublic void run() {// NOTE: If cancel() is called off the thread that we're currently running in (by// default, the main thread), we cannot guarantee that deliverResponse()/deliverError()// won't be called, since it may be canceled after we check isCanceled() but before we// deliver the response. Apps concerned about this guarantee must either call cancel()// from the same thread or implement their own guarantee about not invoking their// listener after cancel() has been called.// If this request has canceled, finish it and don't deliver.if (mRequest.isCanceled()) {mRequest.finish("canceled-at-delivery");return;}// Deliver a normal response or error, depending.if (mResponse.isSuccess()) {//调用Request进行转发mRequest.deliverResponse(mResponse.result);} else {//调用Request进行转发mRequest.deliverError(mResponse.error);}// If this is an intermediate response, add a marker, otherwise we're done// and the request can be finished.if (mResponse.intermediate) {mRequest.addMarker("intermediate-response");} else {mRequest.finish("done");}// If we have been provided a post-delivery runnable, run it.if (mRunnable != null) {mRunnable.run();}}}
}调用Request.deliverResponse(mResponse.result)进行转发
Request是一个抽象类,看看他的子类StringRequest 的实现方法
8、StringRequest源码
@Overrideprotected void deliverResponse(String response) {Response.Listener listener;synchronized (mLock) {listener = mListener;}if (listener != null) {//重点在这listener.onResponse(response);
//}} 在deliverResponse方法中调用了listener.onResponse(response);,最终将Response回调给了Response.Listener的onResponse()方法。
看看我们刚开始的网络请求操作
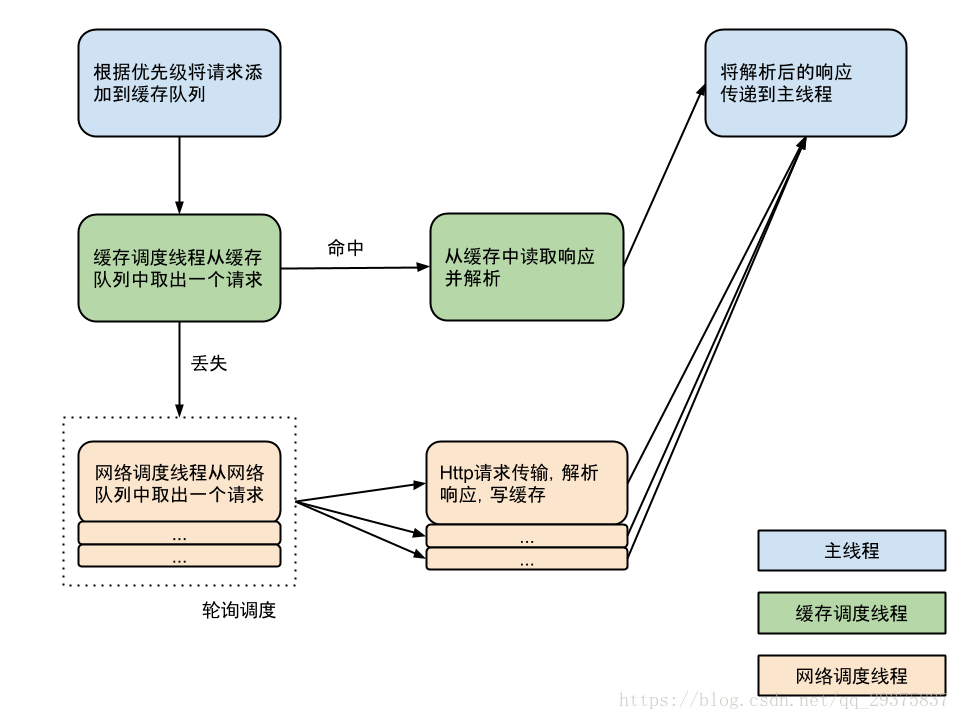
StringRequest stringRequest = new StringRequest("http://www.baidu.com",//最终会将事件回调到这块new Response.Listener() {@Overridepublic void onResponse(String response) {Log.d("TAG", response);}}, new Response.ErrorListener() {@Overridepublic void onErrorResponse(VolleyError error) {Log.e("TAG", error.getMessage(), error);}}); 最后来张图总结一下吧
总结:
Volley分为三类线程,分别是主线程,缓存调度线程和网络调度线程,其中网络调度线程默认开启四个。首先请求会加入缓存队列,缓存调度线程从缓存队列中取出请求。如果找到该请求的缓存响应就直接读取缓存响应并回调给主线程。如果没有缓存效应,或者缓存已过期,则将请求加入到网络队列,然后网络调度线程会轮询取出网络队列中的请求,取出后发送HTTP请求,解析响应回调给主线程,并将相应存入主线程。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场,不承担相关法律责任。如若转载,请注明出处。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请点击【内容举报】进行投诉反馈!